![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
standard amino acids
|
20 amino acids that DNA codes for
|
|
|
side chain
|
R group of amino acid; classifies amino acid
|
|
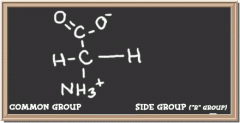
|
glycine
|
|
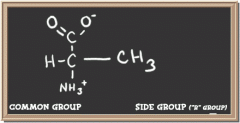
|
alanine
|
|
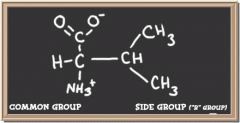
|
valine
|
|
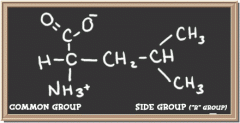
|
leucine
|
|
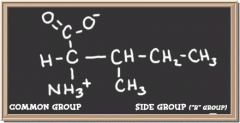
|
isoleucine
|
|
|
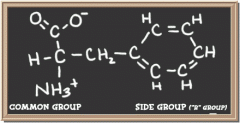
phenylalanine
|
|
|
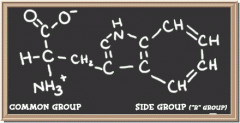
tryptophan
|
|
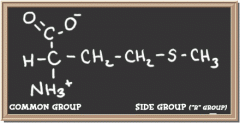
|
methionine
|
|
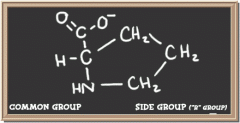
|
proline
|
|
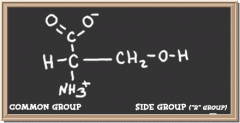
|
serine
|
|
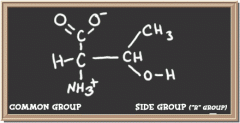
|
threonine
|
|
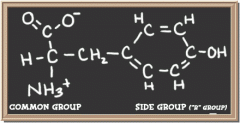
|
tyrosine
|
|
|
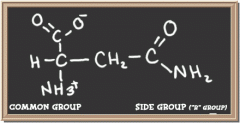
asparagine
|
|
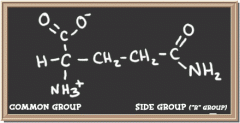
|
glutamine
|
|
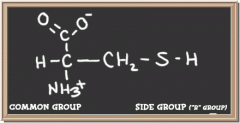
|
cysteine
|
|
|
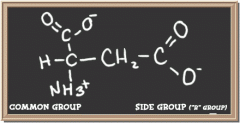
aspartate
|
|
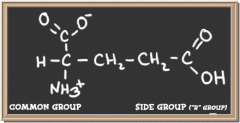
|
glutamate
|
|
|
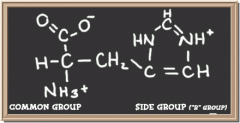
histidine
|
|
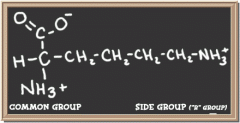
|
lysine
|
|
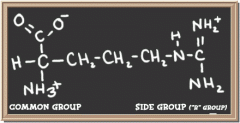
|
arginine
|
|
|
nonpolar
|
What do the following amino acids have in common:
glycine alanine valine leucine isoleucine phenylalanine tryptophan methionine proline |
|
|
polar
|
What do the following amino acids have in common:
serine threonine tyrosine asparagine glutamine cysteine aspartate glutamate histidine lysine arginine |
|
|
cysteine
|
Which amino acid has a sulfhydryl group, and is therefore able to form a disulfide bond?
|
|
|
essential amino acids
|
The following are required as an EXTERNAL source:
phenylalanine valine threonine tryptophan isoleucine methionine histidine arginine leucine lysine What category are they? |
|
|
nonessential amino acids
|
The following amino acids are synthesized by the body:
alanine asparagine aspartate cysteine glutamate glutamine glycine proline serine tyrosine What category are they? |
|
|
arginine
histidine |
Which amino acids are semi-essential (required more during childhood or to recover from diseased state)?
|
|
|
proline
|
Which is an IMINO acid due to its secondary amino group?
|
|
|
glycine
alanine valine leucine isoleucine |
Which amino acids are aliphatic?
|
|
|
serine
threonine |
Which amino acids contain a hydroxy group?
|
|
|
methionine
cysteine |
Which amino acids contain a sulfur group?
|
|
|
aspartic acid
glutamic acid glutamine asparagine |
Which amino acids are acidic (proton donors, negatively charged)?
|
|
|
arginine
lysine histidine |
Which amino acids are basic (proton acceptors, positively charged)?
|
|
|
aromatic
|
The following have what in common:
phenylalanine tyrosine tryptophan proline |
|
|
hydroxyl group
|
Which side chain group of serine helps in the activity of an enzyme active site?
|
|
|
glycine
|
Which amino acid is NOT chirally active (chirally inactive)?
|
|
|
isomerism
|
What is the phenomenon by which two or more compounds exhibit same molecular formula but differ in structural pattern?
|
|
|
L
|
Amino acids in proteins favor which stereo configuration?
|
|
|
D
|
The following are of what configuration:
antibiotics plant/bacterial cell walls |
|
|
alpha-carboxyl
alpha-amino |
What are the two common ionizable groups present in all amino acids?
|
|
|
ionizable group
|
The following are in what group?
extra carboxyl groups (beta, gamma) in aspartate and glutamate extra epsilon amino group in lysine guanido (guanidino) group in arginine imidazole group in histidine |
|
|
pKa
|
Negative log of dissociation constant, K (pH at which both protonated (undissociated) and unprotonated (dissociated) forms of acid group are present at equal concentration
|
|
|
buffer
|
Solution that resists change in pH following the addition of an acid or base (made by solutions of weak acids and their conjugate bases)
|
|
|
zwitterion
|
Ionic form of an amino acid contains equal number of positive and negative charges (net charge is zero)
|
|
|
henderson-hasselbalch equation
|
Equation that depicts relationship among pK, pH and concentration of acid and its conjugate base
|
|
|
sickle cell anemia
|
Substitution of polar glutamate by nonpolar valine at the 6th position in beta subunit of hemoglobin leads to what genetic disease
|
|
|
disulfide bonds
|
Albumin, a stabilizing blood protein, contains what type of bonds?
|
|
|
modified amino acids
|
Hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine in collagen and gamma-carboxyglutamate in clotting factors are what types of amino acids?
|
|
|
non protein amino acids
|
Beta alanine, ornithine, citrulline, homocysteine, homoserine, gamma amino butyric acid (GABA), and taurine are examples of what types of amino acids?
|
|
|
7.4
|
what is physiologic pH
|
|
|
energy production
neurotransmitters |
What are some functions of amino acids?
|
|
|
glucogenic
|
can produce glucose
|
|
|
ketogenic
|
can produce ketone bodies
|
|
|
alanine
|
ala
|
|
|
asparagine
|
asn
|
|
|
aspartate
|
asp
|
|
|
cysteine
|
cys
|
|
|
glutamate
|
glu
|
|
|
glutamine
|
gln
|
|
|
glycine
|
gly
|
|
|
proline
|
pro
|
|
|
serine
|
ser
|
|
|
tyrosine
|
tyr
|
|
|
isoleucine
|
ile
|
|
|
leucine
|
leu
|
|
|
lysine
|
lys
|
|
|
methionine
|
met
|
|
|
phenylalanine
|
phe
|
|
|
threonine
|
thr
|
|
|
tryptophan
|
trp
|
|
|
valine
|
val
|
|
|
arginine
|
arg
|
|
|
histidine
|
his
|
|
|
pK
|
pH at which both protonated and deprotonated forms of acid group are present at equal concentration
|
|
|
polyfunctional amino acids
|
have more than two dissociable groups
|

