![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Aspartic Acid |
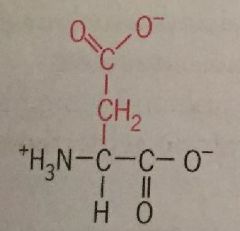
Asp Polar Charged |
|
|
Glutamic Acid |
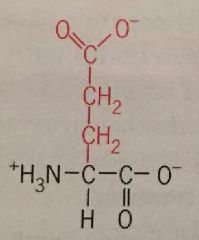
Glu Polar Charged |
|
|
Lysine |
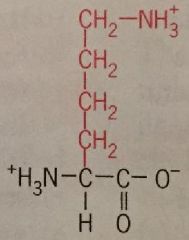
Lys Polar Charged |
|
|
Arginine |
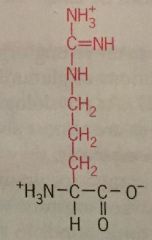
Arg Polar Charged |
|
|
Histidine |
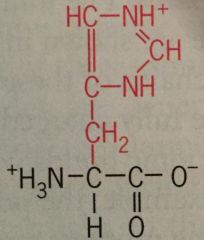
His Polar Charged |
|
|
Serine |
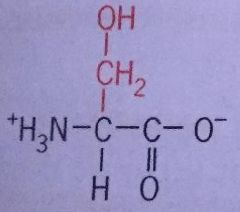
Ser Polar Uncharged |
|
|
Threonine |
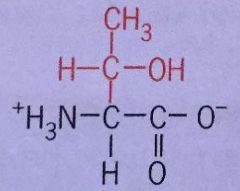
Thr Polar Uncharged |
|
|
Glutamine |
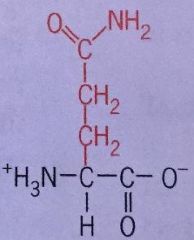
Gln Polar Uncharged |
|
|
Asparagine |
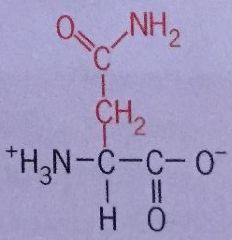
Asn Polar Uncharged |
|
|
Tyrosine |
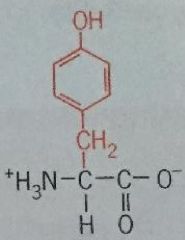
Tyr Polar Uncharged |
|
|
Alanine |
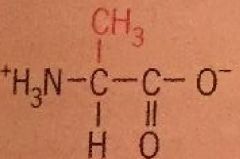
Ala Nonpolar |
|
|
Valine |
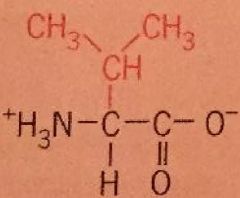
Val Nonpolar |
|
|
Leucine |
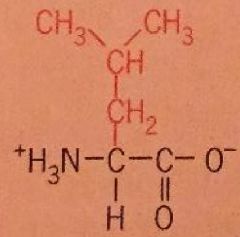
Leu Nonpolar |
|
|
Isoleucine |
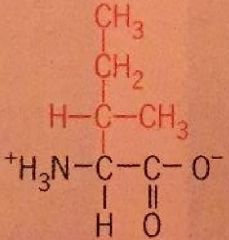
Ile Nonpolar |
|
|
Methionine |
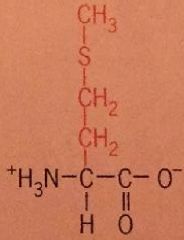
Met Nonpolar |
|
|
Phenylalanine |
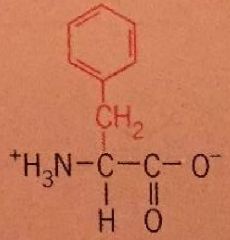
Phe Nonpolar |
|
|
Tryptophan |
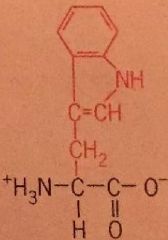
Trp Nonpolar |
|
|
Glycine |
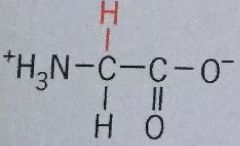
Gly Can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environment, can reside where two polypeptides come in close contact
|
|
|
Cysteine |
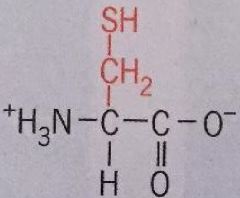
Cys Has polar uncharged character, forms covalent bond with another of its self to form disulfide link
|
|
|
Proline |
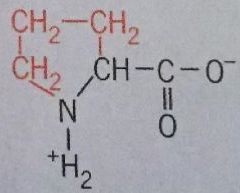
Pro Though it has hydrophobic character, creates kinks in polypeptide chains and disrupts secondary structure |
|
|
Polar Charged |
-Hydrophilic side chains have fully charges -Act as acids or bases -Side chains often form ionic bonds -Involved in reactions
|
|
|
Polar Uncharged |
-Hydrophilic side chains have partial charges -Participate in reactions -Form H bonds -Associate with water |
|
|
Nonpolar |
-Hydrophobic side chains (mostly C or H) -Form inner core of soluble proteins (buried from aq medium) -Associate with lipid bilayer |

