![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
163 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
bronchoscopy
|
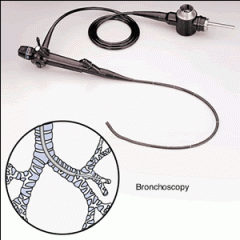
a visual examination of the bronchial tubes with a fiberoptic or rigid endoscope—can be used to identify the source of secretions.
|
|
|
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
|
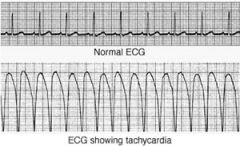
record of electricity of the heart
|
|
|
Subgastric ( Sub/gastr/ic)
|
Pertaining to below the stomach
|
|
|
laparoscopy = lap-ah-ROS-ko-pe
|
process of viewing the interior of the abdomen
|
|
|
prognosis
|
The prediction about the outcome of an illness or treatment
|
|
|
resection
|
removal (excision) of an organ or other body structure
|
|
|
gastroscopy
|
process of visually examining the stomach
|
|
|
bronchography
|
radiographic examination of the bronchi after the installation of a radiopaque medium
|
|
|
biopsy
|
process of viewing living tissue under a microscope
|
|
|
gastrectomy
|
excision (removal) of the stomach
|
|
|
laparotomy
|
incision of the abdomen (exploratory surgery)
|
|
|
nephrectomy
|
excision (removal) of the kidney
|
|
|
osteotomy
|
incision (to cut into) of a bone
|
|
|
enterocolostomy
|
new surgical connection between parts of the small intestine and colon; anastomosis
|
|
|
arthrogram
|
x-ray of a joint
|
|
|
arthrotomy
|
an incision of a joint
|
|
|
colonoscopy
|
visual examination of the colon
|
|
|
autopsy
|
examination of a dead body to determine the cause of death
|
|
|
transurethral resection (TURP)
|
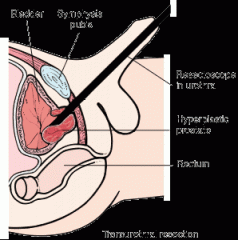
removal of portions of the prostate gland through the urethra. an electrical hot-loop destroys prostatic tissue, and these portions of the gland are then removed. (procedure is called TURP). treatment for BHP Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BHP)
|
|
|
gastrotomy
|
incision of the stomach. (cut into or operate)
|
|
|
cystoscopy
|
process of visually examining the urinary bladder
|
|
|
colonography
|
image of the colon
|
|
|
cholecystectomy
|
removal of the gallbladder
|
|
|
enterocolostomy
|
creating a new opening between the small intestine and the large intestine.
|
|
|
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
|
a record of electricity in the brain
|
|
|
endoscopy
|
process of visually examining (using an endoscope) within the body.
|
|
|
neurotomy
|
incision of the nerves
|
|
|
radiotherapy
|
radiation therapy
|
|
|
electrocardiography (ECG)
|
Diagnosis of rhythmic irregularities of the heart. records/ heart's/ electric activity
|
|
|
Stress Test
|
ECG combined with blood pressure monitoring and heart rate measurements to show the heart's response to physical exertion (usually on a treadmill)
|
|
|
Holter monitor
|
is a portable electrocardiographic device that can be worn to provide an extended recording of the heart's activity
|
|
|
cardiac catheterization
|
involves guiding a flexible catheter via a vein or artery into the heart to detect blood flow and pressure.
|
|
|
angiography
|
Angiography is the process of obtaining a radiographic image (–graphy) of blood vessels (angi/o) following injection of contrast dye.
|
|
|
cardiac catheter ablation
|
a therapeutic procedure in which catherization is used to actually destroy abnormal tissue that is causing arrhythmias.
|
|
|
echocardiography (ECHO)
|
the use of high-frequency sound (echo–) waves to show the structure and movement of the heart (cardi/o).
|
|
|
MUGA scan
|
images the motion of heart wall muscles using radioactive chemicals.
|
|
|
serum enzyme tests
|
used to detect Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
|
|
|
Lipid tests
|
used to detect Coronary artery disease (CAD). to screen for risk factors such as high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood.
|
|
|
lipoprotein electrophoresis
|
lipoproteins (which are combinations of fat and protein) are physically separated in a blood sample. This separation allows the lab to analyze the presence of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) vs. HDL (high-density lipoprotein).
|
|
|
technetium 99m
|
Nuclear imaging. Sestamibi scan—helps assess coronary blood flow and myocardial viability.
|
|
|
thallium stress testing
|
assesses blood flow to the myocardium during exercise after injection of the radioisotope thallium 201.
|
|
|
Positron emission tomography (PET)
|
is also used to identify areas of ischemia and infarction by the injection of radioactive chemicals that release radioactive particles. When these particles reach the heart, cross-sectional images can be taken to show blood flow and heart muscle activity.
|
|
|
defibrillation (cardioversion)
|
passing brief discharges of electricity across the chest.
|
|
|
thrombolytic therapy
|
can prevent heart attacks by using drugs to dissolve clots before they lead to heart attack. This is called thrombolytic therapy (thromb/o = clot; –lytic = to reduce or destroy).
|
|
|
cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
|
an emergency procedure that uses manual (by hand) chest compression's in an effort to restart the heartbeat and breathing of a person whose heart has stopped in cardiac arrest.
|
|
|
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
|
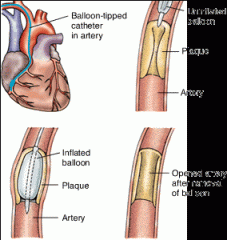
or balloon angioplasty—is a repair procedure (–plasty) in which a balloon-tipped catheter and a mesh-like device called a stent are threaded into a coronary artery to dilate the clogged vessel (angi/o).
|
|
|
lipoprotein tests
|
lipoproteins (which are combinations of fat and protein) are physically separated in a blood sample. This separation allows the lab to analyze the presence of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) versus HDL (high-density lipoprotein).
|
|
|
coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
|
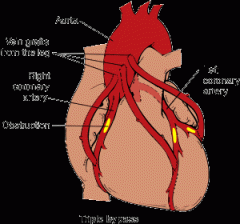
surgical procedure, a blood vessel is grafted onto one of the coronary arteries to bypass the area of occlusion.
|
|
|
endarterectomy
|
the fatty deposits are surgically removed (–ectomy) from the innermost (end–) lining of the artery (arter/o)
|
|
|
thrombolytic
|
therapy that uses drug injections to dissolve clots before they have a chance to cause a heart attack.
|
|
|
abdominal ultrasound
|
a procedure in which sound waves beamed into the abdomen produce images of organs (like the gallbladder)
|
|
|
computed tomography (CT scan)
|
a radiographic procedure thatt produces computerized images representing cross-sectional slices of tissue structure; a painless, noninvasive technique that is 100 times more sensitive than conventional radiography.
|
|
|
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
|
image of the body with magnetic and radio waves. Organs are seen in three planes: Coronal (front to back), sagittal (side to side), and transverse (cross section)
|
|
|
barium tests
|
in which a barium mixture is introduced into the GI tract and then x-ray pictures are obtained (lower and upper GI)
|
|
|
lower GI (gastrointestinal) series
|
(barium enema, or BE)
|
|
|
upper GI (gastrointestinal) series
|
(or barium swallow)
|
|
|
Endoscopic ultrasound
|
a procedure that produces images of intestinal wall layers by use of an endoscope with an attached ultrasound probe. Used for detection of tumors and cystic growths and for determining stage of malignant tumors.
|
|
|
cholangiography
|
a radiographic examination of the bile ducts (cholangi/o) after a contrast material is injected either through the liver or through a catheter.
|
|
|
Hemoccult® test
|
which involves testing the feces for blood
|
|
|
stool culture
|
which examines the feces for microorganisms)
|
|
|
liver function tests (LFTs)
|
liver enzyme tests, measure the presence of liver enzymes such as ALT (alanine transaminase) and AST (aspartate transaminase) in the blood.
|
|
|
Endoscopy
|
is the visual examination (-scopy) within (endo-) any hollow organ using an instrument called, in its most basic form, an endoscope (shown here)
|
|
|
esophagoscopy
|
visually examining the esophagus by inserting an esophagoscope
|
|
|
gastroscopy
|
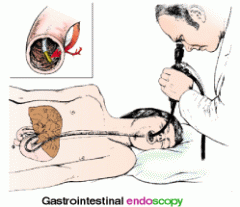
visually examining the stomach by inserting a gastroscope into the mouth and eased down the esophagus into the stomach (see illustration).
|
|
|
sigmoidoscopy
|
used to look at the walls of her sigmoid colon (sigmoid/o)
|
|
|
colonoscopy
|
examination of the entire colon (colon/o) using a more elongated endoscope
|
|
|
virtual colonoscopy, or CT colonography
|
two- and three-dimensional images of the colon are produced using CT scans, MRIs and computers
|
|
|
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
|
a contrast medium is injected via a catheter tube through the mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, and then into the bile ducts.
|
|
|
colostomy
|
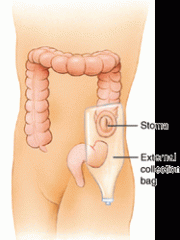
which is an artificial opening (–stomy) into the colon through the abdominal wall, used for the passage of stool, especially in cancer of the colon
|
|
|
ileostomy
|
is the surgical creation of a new opening from the ileum (ile/o) to the outside of the body
|
|
|
Anastomosis
|
is the surgical creation of an opening between two gastrointestinal organs—such as between the stomach and a section of the intestine.
|
|
|
cholecystectomy
|
traditional surgery to remove the gallbladder
|
|
|
laparoscopic cholecystectomy
|
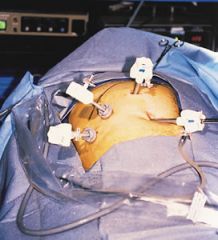
involves gallbladder removal through visual examination of the interior (–scopy) of the abdomen by means of a laparoscope inserted through one or more small incisions in the abdominal wall (lapar/o).
|
|
|
fasting blood sugar (FBS)
|
measures the body's ability to break down and utilize glucose
|
|
|
glucose tolerance test (GTT)
|
measures the body's response to a concentrated glucose solution.
|
|
|
hormone tests
|
measure the amount of ADH, cortisol, growth hormone (GH), or parathyroid hormone in the blood
|
|
|
radioimmunoassay studies (RIA)
|
tag and detect hormones in the blood
|
|
|
thyroid function tests (TFT)
|
measure the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. assess triiodothyronine T3, T4, and calcitonin levels in the blood
|
|
|
radioactive iodine uptake
|
involves administering iodine and assessing the amount absorbed by the gland. In hyperthyroidism, absorption of iodine is increased
|
|
|
thyroid scan
|
produces a visual image of thyroid after a radioactive substance has been given to the patient
|
|
|
exophthalmometry
|
measures the forward displacement of the eyes in Graves disease.
|
|
|
pregnancy test
|
measures the hCG hormone (human chorionic gonadotropin) which is found in the blood and urine or pregnant women
|
|
|
Mammography
|
an x-ray imaging of the breast (mamm/o)
|
|
|
Pap smear
|
a test in which the physician removes a sample of cervical and vaginal secretions for microscopic analysis to detect any presence of disease.
|
|
|
Hysterosalpingography
|
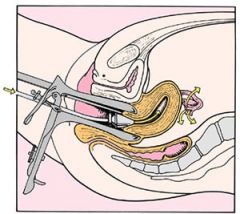
a diagnostic test that involves the x-ray imaging of the uterus (hyster/o) and fallopian tubes (salping/o) following the injection of contrast dye.
|
|
|
colposcopy
|
visual examination of the vagina and cervix using a small magnifying instrument
|
|
|
pelvic ultrasonography
|
the process of imaging deep body structures by measuring and recording sound waves—which is also used to detect leiomyomas
|
|
|
Transvaginal ultrasound
|
uses a transducer placed in the vaginal canal, to obtain a sharper image of internal structures than the transabdominal approach.
|
|
|
Conization
|
removal of a cone-shaped section of the cervix, is used if the doctor wants to examine a section for biopsy (bi/o = life; –opsy = view of).
|
|
|
Uterine artery embolization
|
used to shrink the size of the tumors by injecting tiny pellets into the artery to block blood flow to the fibroids
|
|
|
myomectomy
|
excision of the fibroid
|
|
|
cryosurgery
|
the use of liquid nitrogen to freeze (cry/o = cold) and destroy damaged tissue.
|
|
|
ELISA - (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
|
a test that screens for antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
|
|
|
Western blot test
|
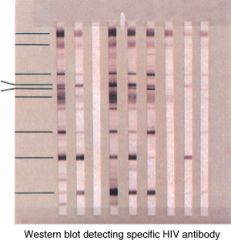
a blood test that also detects antibodies to specific antigens like HIV. more precise than ELISA
|
|
|
lymphangiography
|
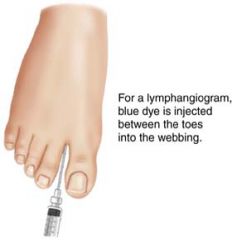
the lymph nodes and lymph vessels (lymphangi/o) are x-rayed after the injection of contrast medium into the lymphatic system. (injected between the toes in the webbing)
|
|
|
Chemotherapy
|
involves the use of powerful drugs to kill the cancer cells, as well as viruses like HIV
|
|
|
Radiotherapy
|
uses high-dose radiation to destroy malignant lesions
|
|
|
HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy)
|
slows progression of lymphatic system disorders such as AIDS
|
|
|
vasectomy
|
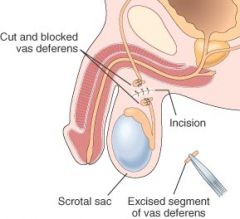
a surgical procedure that produces sterilization by closing off the vas deferens (vas/o) on each side to prevent sperm from being released with semen.
|
|
|
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
|
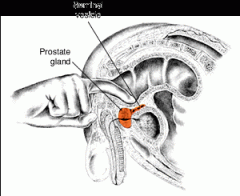
Through the rectal wall, the physician can palpate Frank's prostate for nodules or enlargement.
|
|
|
prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test
|
tests for elevated levels of protein produced by the prostate. Indicates cancer or disorder with the prostate.
|
|
|
semen analysis
|
the number, shape, and motility of sperm cells is analyzed.
|
|
|
Orchiopexy
|
surgical procedure done in infancy to repair cryptorchism (undescended testicles)
|
|
|
photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP)
|
use of lasers to destroy prostatic tissue
|
|
|
Arthrography
|
x-ray imaging of the joints
|
|
|
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
|
measures the rate at which red blood cells fall to the bottom of a test tube. High sedimentation rates can indicate rheumatoid arthritis.
|
|
|
range of motion (ROM) tests
|
the physician maneuvers a joint to assess flexibility or stiffness.
|
|
|
uric acid test
|
used to measure uric acid. high levels are a strong indicator of gout.
|
|
|
bone density test
|
uses low-energy x-rays of the skeleton to detect areas of bone deficiency
|
|
|
bone scan
|
involves the IV injection of a radioactive substance into bone to measure its uptake using a special scanning device
|
|
|
disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)
|
drugs used in treatment for Rheumatoid arthritis.
|
|
|
arthrocentesis
|
Surgical puncture to remove fluid from a joint
|
|
|
laminectomy
|
involves removing all or part of the protruding disk
|
|
|
endoscopic diskectomy
|
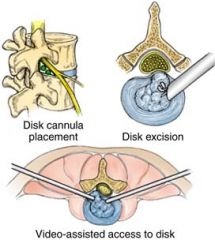
removal of a disk by aspirating it through a tube inserted through the skin
|
|
|
microscopic diskectomy
|
an incision only one to two inches long, with the surgical field visualized with an operating microscope.
|
|
|
Arthroplasty
|
surgical repair of a joint (arthr/o = joint; –plasty = surgical repair).
|
|
|
physical therapy (PT)
|
treatment of disorders to rehabilitate patients after illness or injury. ie. exercise, massage, manipulation, hydrotherapy, and light therapy.
|
|
|
lumbar puncture
|
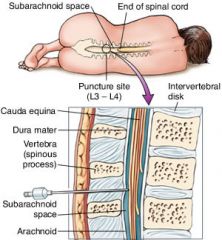
fluid is withdrawn by inserting a needle into the spinal (spin/o) cavity
|
|
|
cerebral angiography
|
x-ray images are taken of these blood vessels (angi/o) with the help of a contrast material injected into an artery
|
|
|
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
|
analysis of the fluid from a lumbar puncture. (spinal fluid)
|
|
|
Stereotactic radiosurgery
|
involves locating a target in the brain, then using a high-energy radiation beam (gamma knife) to destroy the tissue
|
|
|
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator (TENS)
|
delivers stimulation to nerves to relieve acute and chronic pain.
|
|
|
sputum culture (or sputum tests)
|
cultivation of microorganisms from sputum (bacterial analysis)
|
|
|
tuberculin test
|
administered via skin puncture or injection to test for TB
|
|
|
chest x-ray (CXR)
|
radiographic image of the chest obtained to evaluate the lungs and the heart. aka. chest radiograph
|
|
|
pulmonary angiography
|
x-ray images of the lung's blood vessels are taken after they are injected with contrast material
|
|
|
ventilation and perfusion scan (VQ)
|
air flow (ventilation) and blood supply (perfusion) are traced using a radioactive material that is injected or inhaled.
|
|
|
laryngoscopy
|
visual examination of the larynx (laryng/o) using a larynogoscope.
|
|
|
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
|
used to measure the ventilation mechanics of the lung (airway function, lung volume, and capacity of the lungs to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently). These help diagnose the disease and determine the extent of airway obstruction.
|
|
|
spirometer
|

an instrument that measures and records the volume of inhaled and exhaled air.
|
|
|
tracheostomy
|
an opening into the trachea through the neck can allow insertion of a tube to create an airway
|
|
|
lobectomy
|
an incision (–tomy) into the chest to remove a portion (lobe, lob/o) of a lung.
|
|
|
thoracotomy
|
an incision (–tomy) into the chest to remove a lung (pneumonectomy)
|
|
|
thoracocentesis
(also called thoracentesis) |
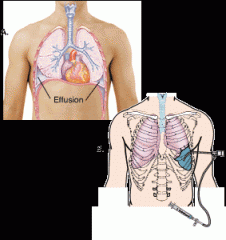
(right image) a surgical puncture to remove fluid (–centesis) from the pleural space in the chest (thorac/o)
|
|
|
positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP)
|
mechanical ventilation--helps with breathing through a machine or device
|
|
|
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure)
|
used in serious cases of sleep apnea. Used to deliver air into the airway
|
|
|
metered dose inhaler (MDI)
|
a device that delivers a specific amount of medication to the lungs, in the form of a short burst of aerosolized medicine
|
|
|
endotracheal intubation
|
the insertion and placement of a tube through the nose or mouth into the pharynx, larynx, and trachea—is sometimes performed to prevent aspiration, to establish an airway, or for placement on a respirator. (during surgery or when the patient is unconscious)
|
|
|
pneumonectomy
|
surgery to remove a lung
|
|
|
audiometer
|
measures hearing loss
|
|
|
ophthalmoscopy
|
a visual examination of the interior of the eye
|
|
|
otoscopy
|
a visual examination of the ear (ot/o)
|
|
|
tuning fork test
|
using an instrument to produce a constant pitch when struck to test for bone or air conduction hearing loss
|
|
|
fluorescein angiography
|
involves injection of dye to watch the movement of blood in the eye to detect retinopathy or macular degeneration of the retina
|
|
|
aspiration
|
insertion of a hollow needle to withdraw the lens tissue—followed by irrigation of the anterior chamber
|
|
|
Phacoemulsification
|
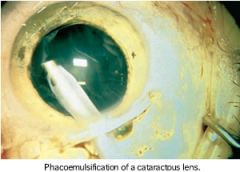
the use of ultrasonic vibration to break up the lens (phac/o) of the eye
|
|
|
slit-lamp examination or slit-lamp microscopy
|
an instrument that combines a microscope and a light source, allowing magnified examination of the eye's interior.
|
|
|
urinalysis (UA)
|
a physical, microscopic or chemical examination or urine
|
|
|
creatinine clearance test (Ccr)
|
measures the rate at which creatinine concentration in a blood sample is excreted in the urine over a 24-hour period
|
|
|
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
|
used to document stages of kidney disease
|
|
|
Urography
|
the x-ray, or radiologic, imaging of the urinary tract after injecting contrast material
|
|
|
pyelography
|
the x-ray, or radiologic, imaging of the urinary tract and the renal pelvis after injecting contrast material
|
|
|
retrograde pyelogram (RP)
|
the use of a radioisotope study can reveal the presence of obstructions in the kidney using contrast medium via a catheter into the urethra and bladder; the images taken are of the urethra, bladder, and ureters.
|
|
|
Cystoscopy
|
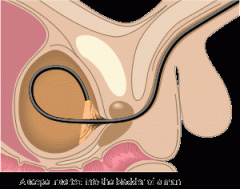
visual examination of the urinary bladder (cyst/o) using a specialized type of endoscope called a cystoscope.
|
|
|
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
|
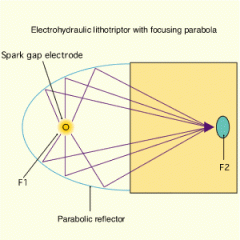
uses shock waves to break a kidney stone into small pieces that can more easily travel through the urinary tract and pass from the body.
|
|
|
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
|
A test used to determine how much urea and nitrogen have accumulated in the blood (uremia) is the urea
|
|
|
kidney, ureter, and bladder (KUB)
|
imaging series, along with an MRI, which helps confirm the diagnosis of acute or chronic renal failure. showing the kidneys, ureters, and bladder
|
|
|
dialysis
|
removing wastes from the blood by machine
|
|
|
Hemodialysis (HD)
|
the use of an artificial kidney machine
|
|
|
peritoneal dialysis
|
involves the introduction of a peritoneal catheter and a special solution (via IV bag) into the abdomen. The wastes pass into the fluid from the bloodstream and are then drained from the body
|
|
|
continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD
|
an indwelling cathetar permits fluid to drain into and out of the peritoneal cavity to cleanse the blood.
|
|
|
renal transplant
|
the implantation of a donor kidney
|
|
|
Lithotripsy
|
in which shock waves crush (–tripsy) the kidney stones for easier, eventual passage from the body with urine.
|

