![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
3 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pyridine-Piperidine |
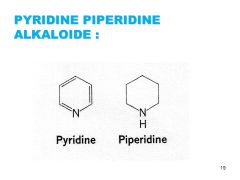
Single carbon ring containing one nitrogen atom (N). Poison hemlock (Apiaceae Conium maculatum) and tobacco (Solanaceae Nicotiana tabacum). Coniine causes paralysis, asphyxia and death is coniine, a single ring compound synthesized in the plant from octanoic acid. The closely-related water hemlock (Cicuta douglasii) contains cicutoxin, a terpenoid resin. Water hemlock is one of the most violently (convulsive) poisonous native plants in North America. If mistaken for a parsnip root, it acts directly on the central nervous system and is often fatal. The alkaloid in tobacco responsible for its highly addictive properties is nicotine, a mild stimulant of the central nervous system. In its pure form, nicotine is highly poisonous and is used as an insecticide. Nicotine is derived from nicotinic acid, a B-vitamin also known as niacin. Niacin prevents pellagra, a disease characterized by severe damage to the tongue, skin and digestive tract. Nicotinic acid is also converted into nicotinamide, a precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), a vital coenzyme required for photosynthesis. |
|
|
Tropanes |
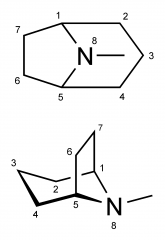
A common property of tropane alkaloids is a methylated nitrogen atom N-CH3 at one end of the molecule. This chemical structure is also found in the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which transmits impulses between nerves in the brain and neuromuscular junctions. Some of the most potent tropane alkaloids are atropine, hyoscyamine and scopolamine. These alkaloids affect the central nervous system, including nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord which control many direct body functions and the behavior of men and women. They may also affect the autonomic nervous system, which includes the regulation of internal organs, heartbeat, circulation and breathing. Tropane alkaloids are found in many other poisonous plants of the nightshade family (Solanaceae). The action of tropane alkaloids at the cellular level is complex and is related to their molecular structure, particularly the methylated nitrogen at one end of the molecule. This chemical structure is also found in the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which transmits impulses between nerves in the brain and neuromuscular junctions. The anesthetic properties of tropane alkaloids may relate to their interference with acetylcholine, perhaps by competing with it at the synaptic junctions, thus blocking or inhibiting nerve impulses. It is interesting to note that the infamous tropane alkaloid cocaine, from the leaves of the coca shrub (Erythroxylum coca--Erythroxylaceae), is also a local anesthetic when injected into skin or muscle tissue. This property led to the discovery and synthesis of the more potent compound, novocain, widely used in dentistry. |
|
|
cocaine |
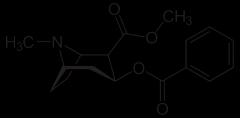
Cocaine is a white powder extracted from the dried leaves of the South American shrub Erythroxylon coca. It induces a sense of exhilaration in the user primarily by blocking the reuptake of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the midbrain. |

