![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Perez argues that each great technology surge occurs in two phases, punctuated by a |
The two phases are the initial installation period (1 point) followed by the subsequent |
|
|
Explain the PSIDR model of malware propagation: what do the states S, I, D, & R |
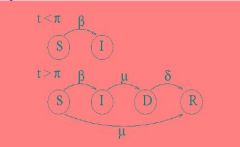
S=Susceptible; I=Infected; D=Detected; R=Removed; pi= signature delay time; mu=
|
|
|
With reference to the PSIDR model, explain how the HP Virus Throttle can be an |
HP Virus Throttle works by greatly reducing the infection rate (but not actually reducing |
|
|
What does it mean for π to be negative in the PSIDR model? |
If pi<0 then the patch is produced before the exploit (1 point) – e.g. when a vulnerability |
|
|
What is the “vulnerabilities market”, why does it exist, and who are the participants |
The “vulnerabilities market” exists because it costs time and money to identify software |
|
|
What is a Freemium Game? |
Freemium games are offered to consumers as free to install and play the basic game, but advanced features and or faster progress are made by in-game purchases, thereby providing revenue to the game developer/publisher (1 point |
|
|
What is Gold Farming? |
.Gold-farming is when people are employed and paid to play MMO games on behalf of a third party.
.in poor countries possible to earn more money in virtual world.
.reported that at least 500,000 people work as
.Gold farmers are often paid to generate ingame currency (for later sale to end-users)
. or to create/capture in-game items
. or to increase the experience/level of a player ("power leveling")
. countermeasures: ignoring/permitting it. Actively hosting it to make money
.counter Measures: nerfing, banning, disruption, patches, attacks, forced develuation
|
|
|
Briefly give a real world example of a digital product with positive network |
This is a ‘freemium’ model. Adobe acrobat uses this: the reader is given away free, to |
|
|
Describe the topology of the Spotify P2P network and give two reasons why this |
The network is based on (two) central servers that act as trackers for clients. Random |
|
|
Essay questions: points to mention? |
Environmental Impact |
|
|
Give 2 different ways a provider of a free service can make money from it. |
Sell complementary goods, eg Red Hat Linux selling support contracts. |
|
|
What is the 'freemium' business model? Why is it economically important for |
A company provides a basic free version of a digital product, and a premium version |
|
|
Define a Peer-to-Peer distributed system. How does a hybrid P2P system differ from |
A computer network which uses diverse connectivity between participants in a network
Gnutella: Peers act as equals, merging the roles of the client and the server. |
|
|
Explain how the HP Virus Throttle algorithm works |
Virus comes in, tries to spread itself throughout the network. .doesn't stop virus from entering, just limits it leaving .notices if lots of connections are opened, reduces the amount of connections. .notifices an authority .doesn't need signature of virus (polymorphic and space filler viruses).
|
|
|
Describe the BitTorrent P2P architecture. How does BitTorrent handle the problem of |
BitTorrent client software communicates with a tracker to find other computers running |
|
|
What is a Vickrey auction. |
A Vickrey, or sealed-price second bid, auction requires all bidders to specify a single bid |
|
|
Carlotta Perez argues that there have been five major technology surges since |
• Industrial Revolution 1770-1829 |

