![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Linear Equation |
Equation for a straight line y=mx+b y=2x+1 5x=6+3y y/2=3-x |
|
|
Quadratic Equation |
Quad means square,must have x2 Standard form ax2+ bx + c = 0 2x2+5x+3=0 2(x2-2x)=5 |
|
|
Polynomial |
Poly=many,nomial=terms, many terms 4xy2+3x-5 this has 3 terms 5xy2-3x+5y4-3 |
|
|
Rational equation |
An expression that is the ratio of 2 polynomials |
|
|
Simplifying |
Making things as simple as can be |
|
|
Factoring |
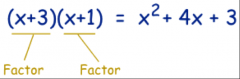
Finding what tomultiply together to get an expression,"splitting" an expression into a multiplication of simpler expressions |
|
|
Function f(x) |
Likea machine that has an input and an output, and the output is related somehow tothe input |
|
|
DomainVs. Range |
Domain:The set of all first elements of ordered pairs (x-coordinates) The set ofx-values that give rise to real y-value Range:difference between the largest & smallest values {(2, –3), (4, 6),(3, –1), (6, 6), (2, 3)} domain: {2, 3, 4, 6} range: {–3, –1, 3, 6} |
|
|
Exponential Growth y(t) = a * e |
Some things grow (getbigger) exponentially At 1yr old it is e1,at 10yrs it is e10 |
|
|
Exponential Decay y(t) = a * ekt |
Some things decay (getsmaller) exponentially |
|
|
Slope y = mx+b |
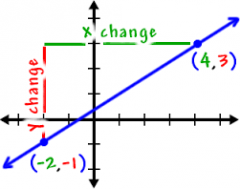
Slope = Change in Y Change in X |
|
|
x-intercept |
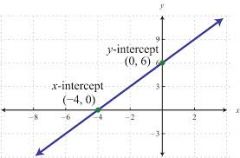
Where the graph crossesthe x-axis |
|
|
y-intercept |
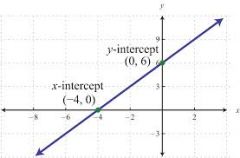
Where the graph crossesthe x-axis |
|
|
Linear Function y = a=bx is now... f(x) = a=bx |
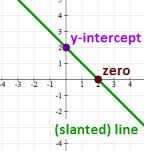
Graph is a straightline One independent (x) andone dependent (y), a is the constant term or y-int. |
|
|
Exponential function |
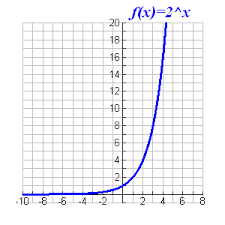
F(x) – ax a is any value greater than 0,never crosses the x-axis, always passes through (0,1) |
|
|
Logarithm function f(x) = loga(x) |
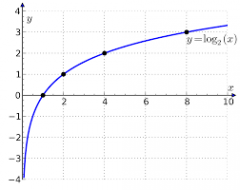
Any value greater than0 except 1, always on the positive side and never passes the y-axis, alwaysintersects the x-axis at x=1 (1,0) |
|
|
Quadratic Function |
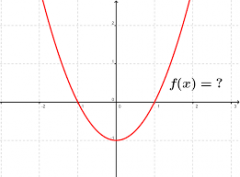
The form f(x) = ax2+ bx + c, where a, b, and c are numbers that are not equal to 0. The graph of aquadratic function is a curve called a parabola which may open upward ordownward and vary in "width" or "steepness", but they allhave the same basic "U" shape. |
|
|
Rational Function |
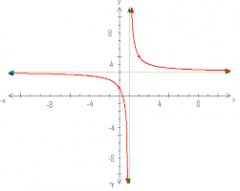
Any function that canbe defined by a rational fraction, i.e. an algebraic fraction such that boththe numerator and the denominator are polynomials. |
|
|
Trigonometric Function |
Functions of an angle that relate the angles of a triangle to the lengthsof its sides. |

