![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Linear Equation |
Equation that forms a line |
Obvious |
|
|
Standard form formula |
Ax + By = C |
|
|
|
Standard form rules |
a. A must be greater than or = to 0 b. A, B and C must be integers C. The constant C is always to be itself d. GCF of l |
4 of them |
|
|
Linear Function |
Function for which the graph is a line |
It's all in the wording |
|
|
Parent Function |
F(x) = x |
|
|
|
Family of graphs |
A group of graphs with one or more similar characteristics |
|
|
|
Root of the equation |
Any value that makes an equation true |
|
|
|
0s of the function |
X intercept |
F (x)= 0 |
|
|
Rate of change |
Ratio that describes how much one quantity changes in respect to another |
|
|
|
Rate of change formula |
Change in y/ the change in x |
|
|
|
Delta |
Means change |
|
|
|
Slope |
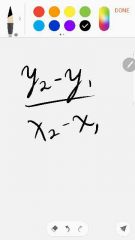
Slope can represented as k or m |
Rise / run |
|
|
Direct variation |
Y =kx , k is for constant |
|
|
|
The same 3 |
0 of function = roots = x intercept |
|
|
|
Sequence |
Set of #s in a specific order |
|
|
|
Terms |
#s in the sequence |
|
|
|
Arithmetic sequence |
A numerical pattern that increases or decreases @ a constant rate |
|
|
|
Common difference d |
The difference between terms |
|
|
|
Nth term of a sequence |

|
|
|
|
Inductive reasoning |
Using to derive a general rule after observing many events |
|
|
|
Deductive Reasoning |
Is when you come to a conclusion by accepting facts |
Sherlock Holmes |
|
|
Proportional relationship |
Linear Equation the goes through the origin |
00 |
|
|
Nonproportional relationship |
The linear equation does not go through 00 |
|
|
|
Integers |
+ and - whole numbers |
|
|
|
To find the intercept |
If x, y =0 vise versa |
|

