![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Air Pollution |
Various chemicals added to the atmosphere by natural events or human activities in high enough concentrations to be harmful |
|
|
|
Primary Air Pollutant |
A harmful substance that is emitted directly into the atmosphere |
Soot or carbon monoxide are examples of this |
|
|
Secondary Air Pollutant |
A harmful substance formed in the atmosphere when a primary pollutant reacts with substances normally found in the atmosphere or with other air pollutants |
Ozone and sulfur trioxide are secondary air pollutants |
|
|
Ozone |
A form of gas considered a pollutant in the troposphere, but essential for screening out UV radiation in the stratosphere |
|
|
|
Hazardous Air Pollutants |
Air pollutants that are potentially harmful and may pose long term health risks to people who live and work around chemical factories, incinerators, or other facilities that produce/use them |
Air toxics |
|
|
Photochemical Smog |
A brownish-orange haze formed by chemical reactions involving sunlight, nitrogen oxide, and hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
Temperature Inversion |
A deviation from the normal temperature distribution in the atmosphere, resulting in a layer of cold air temporarily trapped near the ground by a warmer, upper layer |
|
|
|
Emphysema |
A disease in which the air sacs in the lungs become irreversibly distended, decreasing the efficiency of respiration |
|
|
|
Chronic Bronchitis |
A disease in which the air passages of the lungs become permanently inflamed |
|
|
|
Vapor Recovery |
The removal of unburned gasoline vapors from gas containers, including underground tanks at gas stations and automobile gas tanks |
|
|
|
Ultraviolet Radiation |
The part of the electromagnetic spectrum with wavelengths just shorter than visible light |
|
|
|
Stratospheric Ozone Thinning |
The accelerated destruction of ozone in the stratosphere by human produced chlorine and bromine containing chemicals |
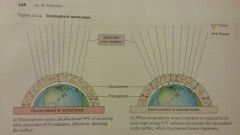
|
|
|
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) |
Human made organic compounds of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine that had many industrial and commercial applications that were banned because they attack the stratospheric ozone layer |
Aerosol cans |
|
|
Acid Deposition |
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acids that return to the surface as either dry or wet deposition |
|
|
|
Wet Deposition |
Sulfuric and nitric acids in precipitation |
|
|
|
Dry Deposition |
Dry sulfuric-acid and nitric-acid containing particles that settle out of the air |
|
|
|
pH Scale |
Scale of values between 0 and 14, with 0 being the most acidic, 14 being the most basic, and 7 being neutral |
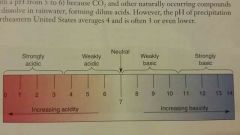
|
|
|
Global Distillation Effect |
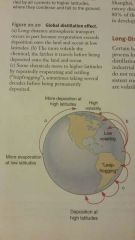
The process whereby volatile chemicals evaporate from land as far away as the tropics and are carried by air currents to higher latitudes, where they condense and fall to the ground |
|

