![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Muscles of Facial Expression
|
-Part of the panniculus carnosus muscle layer
-Common embryological origin; 2nd Pharyngeal Arch -Common innervation; Facial Nerve (VII) -Have one attachment to bone and one to skin |
|
|
|
Functions of Muscles of Facial Expression
|
-Organised around orifices of face as sphincters/dilators
-Protective -Speech (opening mouth and raising eyebrows) |
|
|
|
Importance of Buccinator
|
-Keeps cheeks taut during mastication
-Anterior attachment important in denture fitting -Pterygomandibular Raphé landmark for IAN block |
|
|
|
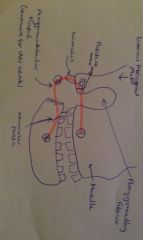
Attachments of Buccinator
|
-From 1st maxillary molar to palatine bone and lateral pterygoid plate
-Short ligaments from palatine bone to tip of hamulus -Pterygomandibular Raphé from tip of hamulus to retromolar fossa -Retromolar fossa, along oblique line then alveolar process to 1st mandibular molar |
|
|
|
Roles of Lip Muscle in Speech; Longitudinal
|
Lengthens vocal tract via:
-Lip protrusion -Labiodentalization (sound articulated by lower lip and upper teeth) |
|
|
|
Roles of Lip Muscles in Speech; Latitudinal
|
Widen lips via:
-Horizontal or vertical expansion -Horizontal or vertical constriction |
|
|
|
Facial Nerve (VII)
|
-Emerges from stylomastoid foramen
-Enters parotid gland -Provides motor innervation to facial muscles -Branch to posterior digastric & stylohyoid |
|
|
|
SCALP (S outermost layer//P Innermost layer)
|
-Skin with hair follicles
-Connective tissue with blood vessels -Aponeurosis of occipitofrontalis (layers of flat tendons that join muscles to the bones) -Loose sub-aponeurotic connective tissue (fatty tissue) -Pericranium (layer of connective tissue surrounding the cranium) |
|
|
|
Venous Sinuses
|
-Present in skulls
-Veins in scalp communicate through foramina in skull with venous channels -No veins as no muscles in walls |
|
|
|
Sensory Innervation of the Face
|
-Trigeminal Nerve (V)
-Has 3 divisions -Each exit at different foramen |
|
|
|
Divisions of Trigeminal Nerve; Ophthalmic (V1)
|
-Exits through supraorbital foramen
-Supplies eye (cornea, iris, ciliary body, lacrimal gland, conjunctiva) -Supplies skin of eyelid, eyebrows, forehead and nose -Supplies part of mucous membrane of nasal cavity |
|
|
|
Divisions of Trigeminal Nerve; Maxillary (V2)
|
-Exits through infraorbital foramen
-Supplies some teeth (maxillary) -Supplies the skin of the midface -Supplies the nasal cavity -Supplies the sinuses -Supplies the palate |
|
|
|
Divisions of Trigeminal Nerve; Mandibular (V3)
|
-Exits through foramen ovale
-Supplies the muscles of mastication -Supplies the mandibular teeth -Supplies the lower lip and chin -Supplies mylohyoid, anterior digastric, anterior 2/3rd of tongue, inside of cheek (buccal mucosa) -Supplies skin of temporal region and auricula |
|
|
|
Muscles of Mastication
|
-Muscles that raise the mandible
-Common embryological origin; 1st Pharyngeal Arch -Innervated by V2 |
|
|
|
Masseter Muscle
|
-Arises from zygomatic arch
-Multipennate (central tendon branches into 2 or more tendons) -Powerful elevator of mandible as sloped fibres perpendicular to molar teeth -Attach to outer surface of mandible |
|
|
|
Temporalis Muscle
|
-Covered by temporalis fascia
-Bipennate -Attached to temporal fossa from temporal line to temporal crest and to temporal fascia -Attached inferiorly to coronoid process & anterior ramus down to retromolar fossa -Muscle elevates and retracts mandible |
|
|
|
Parotid Gland
|
-Largest of salivary gland
-Mainly serous -Duct opens near 2nd maxillary molar -Lies between ramus of mandible and sternocleidomastoid -Enclosed within deep cervical fascia;parotid capsule |
|
|
|
5 Branches of Facial Nerve (VII)
|
-Temporal
-Zygomatic -Buccal -Mandibular -Cervical |
The Zante Bad Males Chunder
|
|
|
Branches of Facial Nerve; Temporalis
|
Innervates the Frontalis
|
|
|
|
Branches of Facial Nerve; Zygomatic
|
Innervates muscle of the eye
|
|
|
|
Branches of Facial Nerve; Buccal
|
Innervates Buccinator and lower lip
|
|
|
|
Branches of Facial Nerve; Mandibular
|
Innervates lower lip
|
|
|
|
Branches of Facial Nerve; Cervical
|
Innervates platysma of neck
|
|
|
|
Blood Supply to Face; Facial Artery
|
Gives off the following branches:
-Submental artery -Inferior Labial artery -Superior Labial artery -External Nasal artery -Angular artery |
|
|
|
Blood Supply to Face; Transverse Facial Artery
|
-Branches from the superficial temporal artery
-Runs across face -Supplies parotid gland, parotid duct & masseter |
|
|
|
Blood Supply to Face; External Carotid Artery
|
Branches:
-Superior Thyroid Artery -Ascending Pharyngeal Artery -Lingual Artery -Facial Artery -Occipital Artery -Posterior Auricular Artery -Maxilary Artery -Superficial Temporal Artery |
Some Anatomists Like Fenwicks Others Prefer Marks & Spencers
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Superior Thyroid Artery
|
Supplies the Larynx and Thyroid Gland
|
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Ascending Pharyngeal Artery
|
-Supplies the base of the skull
|
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Lingual Artery
|
Supplies Oral Floor and Tongue
|
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Facial Artery
|
Several branches which supply the face
|
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Occipital Artery
|
Several branches which supply sternocleidomastoid, mastoid...
|
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Posterior Auricular Artery
|
Supplies the auricle and scalp
|
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Maxillary Artery
|
Supplies the deep structures of the face
|
|
|
|
Branches of External Carotid Artery; Superficial Temporal Artery
|
Supplies part of the face and scalp
|
|
|
|
Venous Drainage of Face
|
-Facial Vein
-Retromandibular vein anterior division -Internal Jugular Vein |
|
|
|
Venous Drainage of Face; Facial Vein
|
Formed by confluence of:
-Supratrochlear/Frontal vein -Supraorbital vein -Angular Vein -Superior Labial Vein -Inferior Labial Vein -Deep Facial Vein |
|
|
|
Venous Drainage of Face; Retromandibular Vein Anterior Division
|
Formed by confluence of:
-Maxillary Vein -Superficial Temporal Vein Joins facial vein to form common facial vein |
|
|
|
Venous Drainage of Face; Retromandibular Vein Posterior Division
|
-Travels underneath internal jugular vein
-Joins posterior auricular vein to form external jugular vein |
|
|
|
Venous Drainage of Face; Internal Jugular Vein
|
Drains blood from:
-The brain -The face (Common facial vein) -The neck (pharyngeal, superior thyroid, middle thyroid) |
|
|
|
Relationships of Parotid Gland; Within
|
-Facial nerve (stylomastoid fo.)
-External Carotid Artery -Retromandibular Vein |
|
|
|
Relationships of Parotid Gland; Deep
|
-Postero-medial: Sternocleidomastoid & posterior digastric
-Antero-medial: Mandible, masseter, posterior digastric & stylohyoid -Intermediate: Styloid apparatus, int. carotid artery, int. jugular vein, IX, X, XI & XII |
|
|
|
Relationships of Parotid Gland; Superficial
|
-Fascia
-Skin |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Eye; Orbicularis Oculi
|
3 portions:
-Palpebral (the Lower eyelid) -Orbital (the Upper eyelid) -Lacrimal (the Middle of eyelid) |
|
|
|
Orbicularis Oculi;Palpebral Portion
|
Involved in light blinking/during sleep
|
|
|
|
Orbicularis Oculi; Orbital Portion
|
Involved in heavy blinking at high light intensities
|
|
|
|
Orbicularis Oculi: Lacrimal Portion
|
Involved in holding lid against eyeball for even distribution & removal of tears
|
|
|
|
Muscles of The Nose; Nasalis
|
2 Main Portions:
-Transverse/Compressor Naris -Alar/Dilator Naris |
|
|
|
Nasalis; Compressor Naris Portion
|
-Arises from upper portion of canine ridge of maxilla
-Functions to compress the nostrils |
|
|
|
Nasalis; Dilator Naris Portion
|
-Arises from the nasal region of the maxilla inserting into skin of nostril
-Function to flare/dilate the nostril |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Nose;Procerus
|
-Located around the nasal bone/lateral nasal cartilage (just above nose)
-Function to produce wrinkles at bridge of nose |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Nose;Levator Labii Superioris (angular head)
|
-Also functions to flares the nostril
|
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Orbicularis Oris
|
-Present within the upper and lower lips
-Fibres originate from parts of other facial muscles that converge on mouth |
|
|
|
Orbicularis Oris Function
|
-Compress lips against anterior teeth
-Closing the mouth -Protruding the lips |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Zygomatic Minor Muscle
|
-Elevates the portion of the lip it is inserted
-Drags the external angles of the lips with it slightly |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Zygomatic Major Muscle
|
-Lifts upward and laterally the corners of the mouth
|
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Levator Angular Oris
|
-Located in canine fossa of maxilla
-Functions in elevating angle of mouth |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Levator Labii Superioris
|
-Elevates the upper lip
|
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Depressor Angular Oris
|
-Found on oblique line of mandible
-Depresses the angles of the mouth |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Depressor Labii Inferioris
|
-Also found on oblique line of mandible
-Depresses the lower lip |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Mouth; Mentalis
|
-Located at incisive fossa of the mandible
-Protrudes the lower lip |
|
|
|
Muscles of The Cheek; Buccinator
|
-Presses the cheek against the vestibular surfaces of the molar teeth aiding mastication
-Prevents cheeks from expanding when expelling air |
|

