![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define: Gross Income
as defined by the IRC |
Gross Income; except as otherwise provided in this subtitle, gross income means all income from whatever source derived
|
|
|
|
In the development of income tax law, a choice was made between two competing models, what are they?
|
1. Economic Income
2. Accounting Income |
|
|
|
How is Economic Income determined?
|
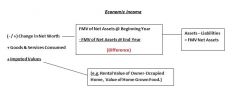
This model has been rejected by the supreme court
|
|
|
|
How is Accounting Income determined?
What is it based on? |
Accounting Income is based on the realization principle.
Income is not recognized until it is realized. |
|
|
|
What must happen for realization to occur?
|
1. An exchange of goods or services must take place between the accounting entity and some independent external group.
2. In the exchange the accounting entity must receive assets that are capable of being objectively valued. |
|
|
|
What is the most significant difference between Income Tax rules and Financial Accounting measurements?
|
Unearned (prepaid) income received by an accrual basis taxpayer often is taxed in the year of receipt. For financial accounting purposes, such prepayments are not treated as income until earned. Because of this and other differences, many corporations report fiinancial accounting income that is substantially different from the amounts reported for tax purposes.
|
|
|
|
Ostrich Corporation allows Bill, an employee, to use a company car for his vacation. Does Bill realize any income?
|
Unfortunately, Yes, Bill realizes INCOME equal to the rental value of the car for the time and mileage.
|
|
|
|
Terry owes $10,000 on a mortgage. The creditor accepts $8,000 in full satisfaction of the debt. What's significant here?
|
Well Terry just realized a gain. She realizes $2,000 of INCOME.
|
|
|
|
Martha is an attorney. She agrees to draft a will for Tom, a neighbor, who is a carpenter. In exchange, Tom repairs her back porch. Income Realization?
|
Yes, Martha and Tom both have gross income equal to the fair market value of the services they provide.
|
|
|
|
Define: Recovery of Capital Doctrine
|
No income is subject to tax until the taxpayer has recovered the capital invested.
In other words, Gross Receipts (ie selling price) must be reduced by the amount of the capital invested (plus or minus appropriate adjustments such as capital improvements and cost recovery allowances) in determining the amount of gross income subject to tax. |
|
|
|
Dave sold common stock for $15,000, he purchased it for $12,000. What is his Gross Income from this transaction?
|
$3,000
|
|
|
|
Define: Taxable Year
|
The annual period over which income is measured for income tax purposes. Most individuals use a calendar year, but many businesses use a fiscal year based on the natural business year.
|
|
|
|
Define: Accounting Method
|
The method under which income and expenses are determined for tax purposes. Important accounting methods include the cash basis and the accrual basis. Special methods are available for the reporting of gain on installment sales, recognition of income on construction projects (the completed contract and percentage of completion methods), and the valuation of inventories (last-in, first-out and first-in, first-out). §§ 446–474.
|
|
|
|
What are the three primary methods of accounting?
|
1. The cash receipts and disbursements method.
2. The accrual method 3. The hybrid method |
|
|
|
What is the Hybrid Method?
|
This is a combination of the cash and accrual methods of accounting
|
|
|
|
TRUE or FALSE
Except for certain small businesses, the accrual method is optional in determining income from the purchase and sale of inventory |
False
It is REQUIRED |
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
The IRS may prescribe the method of accounting if a taxpayer has not adopted a method or if the taxpayer's method does not clearly reflect income. |
TRUE
|
|
|
|
Explain: Cash Receipts Method
|
A method of accounting that reflects deductions as paid and income as received in any one tax year. However, deductions for prepaid expenses that benefit more than one tax year (e.g., prepaid rent and prepaid interest) usually must be spread over the period benefited rather than deducted in the year paid. § 446(c)(1).
|
|
|
|
Explain: Accrual Method
|
A method of accounting that reflects expenses incurred and income earned for any one tax year. In contrast to the cash basis of accounting, expenses need not be paid to be deductible, nor need income be received to be taxable. Unearned income (e.g., prepaid interest and rent) generally is taxed in the year of receipt regardless of the method of accounting used by the tax-payer. § 446(c)(2).
|
|
|
|
When is income earned under the accrual method?
|
1. all the events have occurred that fix the right to receive such income
2. the amount to be received can be determined with reasonable accuracy. |
|
|
|
Define: Claim of Right Doctrine
|
A judicially imposed doctrine applicable to both cash and accrual basis taxpayers that holds that an amount is includible in income upon actual or constructive receipt if the taxpayer has an UNRESTRICTED CLAIM to the payment. For the tax treatment of amounts repaid when previously included in income under the claim of right doctrine, see § 1341.
|
|
|
|
Income is Constructively Received under what 2 conditions?
|
1. The amount is made readily available to the taxpayer.
2. The taxpayer's actual receipt is not subject to substantial limitations or restrictions. |
|
|
|
Define Original Issue Discount
|

The difference is not considered to be original issue discount for tax purposes when it is less than one-fourth of 1 percent of the redemption price at maturity multiplied by the number of years to maturity. §§ 1272 and 1273(a)(3).
|
|
|
|
Amounts Received under an Obligation to Repay, is there income recognized here?
Why or Why Not (Be Specific)? |
There is no income recognized here because assets and liabilities increase at the same time.
|
|
|
|
What is the difference between prepaid income for tax purposes and financial accounting?
|
Prepaid income is a liability under financial accounting purposes and recognized immediately for tax purposes.
|
|
|
|
Under what provisions did the IRS acquiesce and allowed the accrual basis of accounting for tax purposes? (Specifically with Prepaid Income)
|
1. Deferral of Advance payments for Goods
2. Deferral of Advance payments for Services |
|
|
|
Explain: Fruit & Tree Metaphor
|
The courts have held that an individual who earns income from property or services (labor/work) cannot assign that income to another. For example, a father cannot assign his earnings from commissions to his child and escape income tax on those amounts.
|
|
|
|
The IRS acquiesced and allowed the accrual basis of accounting for tax purposes. But what did the IRS stipulate?
|
The IRS said that you must use the accrual basis accounting for your financial accounting purposes as well.
|
|
|
|
Explain: Assignment of Income
|
A procedure whereby a taxpayer attempts to avoid the recognition of income by assigning to another the property that generates the income. Such a procedure will not avoid the recognition of income by the taxpayer making the assignment if it can be said that the income was earned at the point of the transfer. In this case, usually referred to as an anticipatory assignment of income, the income will be taxed to the person who earns it.
|
|
|
|
According to the IRS, interest accrues...
|
Daily
|
|
|
|
What is the tax on qualified dividends?
HINT! for the old answer |
Dividend income now is taxed at the same marginal rate that is applicable to a net capital gain (i.e., 0% or 15%)
|
The tax rate on qualified dividends is 5% or 15% (depending on the individual's income tax rate). If the individual has a regular income tax rate of 25% or higher, then the qualified dividend tax rate is 15%. If the individual's income tax rate is less than 25%, then qualified dividends are taxed at the 5% rate.
|
|
|
Dividends are classified as qualified dividends and not ordinary income if ?
|
In order to be taxed as a qualified dividend, the investor "must have held the stock for more than 60 days during the 121-day period that begins 60 days before the ex-dividend date," as the IRS explains in Publication 550.
|
|
|
|
Are qualified dividends netted with capital losses?
|
No they are not! Because qualified dividends are not regarded as capital gains because you are perceived to be an owner of the company
|
|
|
|
A stock price usually increases or decreases after it goes ex-dvidend
|
decreases
|
|
|
|
What is the ex-dividend date?
|
The ex-dividend date (typically 2 trading days before the record date for U.S. securities) is the day on which all shares bought and sold no longer come attached with the right to be paid the most recently declared dividend.
|
|
|
|
A partner in a partnership firm withdraws 30K over the year and the business earns 70K among two people. What is the partners income?
|
It's 35K because the partnership is not a separate taxable entity.
|
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
A shareholder in an S Corporation must report his or her proportionate share of the corporation's income and deductions for the corporation's tax year whether or not any distributions are actually made to the shareholder by the corporation |
YES!
Yes it's a "corporation" but S corporations ELECT to be taxed like partnerships. |
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
The beneficiaries of estates and trusts generally are not taxed on income that actually is distributed or required to be distributed to them. |
FALSE
|
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Any income not taxed to the beneficiaries of an estate or trust is taxed to the estate or trust |
TRUE
|
|
|
|
The basic difference between common law and community property law centers around
|
the property rights of married persons
|
|
|
|
Read: Common Law Property System
|
In a common law system, each spouse owns whatever he or she earns.
|
|
|
|
Read: Community Law Property System
|
Under a community property system, one-half of the earnings of each spouse is considered owned by the other spouse. Assume, for example, Jeff and Alice are husband and wife and their only income is the $50,000 annual salary Jeff receives. If they live in New York (a common law state), the $50,000 salary belongs to Jeff. If, however, they live in Texas (a community property state), the $50,000 salary is owned one-half each by Jeff and Alice.
|
|
|
|
Are Alimony payments deductible for AGI by the payor?
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
Are Alimony payments included in gross income of the recipient?
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
A transfer of of property other than cash to a former spouse is a taxable event. |
FALSE
This is not a taxable event. There is not recognized gain or loss and the transferor is not entitled to a deduction. |
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Alimony can come in the form of different assets |
FALSE
Alimony must be cash payments |
|
|
|
Describe: Alimony Recapture
|
The amount of alimony that previously has been included in the gross income of the recipient and deducted by the payor that now is deducted by the recipient and included in the gross income of the payor as the result of front-loading. § 71(f).
|
|
|
|
Special rules apply to post 1986 agreement if payments in the first or second year exceed....
|
$15,000
|
|
|
|
In the third year, the payor, if excess alimony exist, then the payor must....
|
the payor must include the excess alimony payments for the first and second years in gross income.
|
|
|
|
Are child support payments income?
|
No
|
|
|
|
Are child support payments deductible by the payor?
|
No
|
|
|
|
Alimony of $500 is made to Grace, with a reduction to $300 when their child turns 21. What does this tell you?
|
That the child support must be $200 and is hidden within the alimony payments. Thus only $300 of the $500 alimony payment is deductible
|
|
|
|
Define: Below Market Loans
|
A below-market loan is a loan on which no interest is charged or on which interest is charged at a rate below the applicable federal rate.
Essentially, you're below the market rates. |
|
|
|
Since you aren't able to receive a non-interest bearing note from someone you gave an investment to for the same amount to reduce your taxes, what must you do?
|
You must use the federal rate applicable to the amount loaned. The person who gave the investment away in exchange for a note of the same price, must recognize interest income. As if he loaned the investment (instead of giving it away interest free as he had expected)
Remember that an interest income on one person's books is interest expense on another's. Thus the recipient of such a investment give, must report an investment expense |
|
|
|
No interest is imputed on total outstanding gift loans of (a) ___?____ or less, unless (b)....
|
a. $10,000
b. the loan proceeds are used to purchase income producing property. |
|
|
|
On loans of ___?___ between individuals (interest free) the imputed interest cannot exceed the brorrower's net investment income for the year.
|
$100,000
|
|
|
|
How do you computer net investment income?
|
Gross Income from all investments less the related expenese.
|
|
|
|
Consider, a borrower of a interest free loan between individuals, if the borrower's net investment income for the year does not exceed ___?___, no interest is imputed on loans of $100,000 or less
|
$1,000
|
|
|
|
Describe: Compensation Related Loan
|
Below-market loans between an employer and an employee or between an independent contractor and a person for whom the contractor provides services.
|
|

