![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What effect does hyperventilation have on K?
|
decreases it-driven intracellularly
|
|
|
A pt with BP of 110/60 has a brady rythmn. Does this need tx'd?
|
No-no hemodynamic issue
|
|
|
Which of the following indicate a dysrythmia that needs treated?
A. hemodynamic compromise B. a harbinger of a worse dysrythmia C. cant be corrected by removing cause D. Lets hope my pts never have nay |
A, B, C
|
|
|
What % of dysrythmias in aneshtetized pts need treated?
|
1%
|
|
|
What % of anesthetized pts have dysrythmias?
|
15-85%
|
|
|
Automaticity definition?
|
Ability to spontaneously generate actionpotential
|
|
|
Enhanced automatcity does which of the following?
A. brings the RMP closer to TP B. ^ slope of phase 4 C. depolarized the TP D. hyperpolarizes the RMP |
A, B. ( it actually depola. the RMP and hyperpol the TP)
"The end result: Increased HR" |
|
|
depressing the automaticity does what to the RMP and TP?
|
makes them further apart
-decreases slope of phase 4 -Hyperpolarizes the RMP -Depolarizes the TP "End result: Decreases HR" |
|
|
Cardiac muscle APs are also known as?
A. fast APs B. Na+ mediated APs C. Ca+ mediated APs D. phase 4 APs |
a, b
|
|
|
Pacemaker cells APs are also known as?
A. Slow APs B. Ca+ mediated APs C. Na+ mediated APs D. phase 4 APs |
A, B, D
|
|
|
Excitability is defined as?
|
ability of a cardiac cell to respons to stimulation by depolarizing
|
|
|
The SNS does what to excitability?
A. Increases B. decreases |
A
|
|
|
The PSNS does what to excitability?
A. increases B. decreases |
B
|
|
|
The refractory period of the heart is:
A. beginning of QRS to top of T B. phases 0, 1, 2 and early 3 C. the time when a stimulus, no matter how strong, does not elicit a depolarization |
All are correct
( the absolute refractory period) |
|
|
Which receptors are responsible for increasing automaticity?
A. B1 B. B2 C. alpha D. Dopmine |
A
|
|
|
Conduction is defined as?
|
ability to cause adjoining cell to depolarize and the speed at which this happens
|
|
|
reexcitation is what?
|
SAME impulse comes back and reexcites cardiac tissue
|
|
|
Two things are necessary for reexcitation to occur:
|
1. imbalance between conduction and refractoriness
2. unidirectional block |
|
|
Reexcitation is the mechanism for which kind of dysrythmias?
A. bradycardic B. tachycardic C. ventricular |
B
|
|
|
chamber enlargement leads to reexcitation by:
|
elongating the conduction pathway
|
|
|
MI can lead to reexcitation by:
|
decreasing the velocity of conduction of cardiac implulse
|
|
|
Ischemia does what to AP?
|
prolongs it
|
|
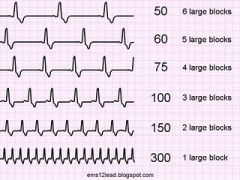
|
to determine rate
|
|
|
A QRS of <0.12 means the impulse originates where?
|
above the ventricles
|
|
|
A QRS or >0.12 means what?
|
IVCD or BBB
|
|
|
Atrial and nodal rythms are very common in anesthetized pts. Why?
|
Volatile agents are Na channel blockers
|
|
|
Which lead is best used to assess for flutter waves?
|
Lead II
|
|
|
Which lead is best to assess for ischemia?
|
V5
|
|
|
What is the most common dysrythmia under general anesthesia?
|
accelerated junctional
|
|
|
Which of the following drugs should you never give to a WPW pt?
A. lidocaine B. sux C. verapamil D. cardizem E. digoxin |
C, D, E
(all CCBs are out, so is dig) |
|
|
The only electrical connection between the atrial tissue and ventricular tissue in the heart is?
|
the AV bundle ( goes through valve ring)
|
|
|
The Na-K pump depends on what other electrolyte to function properly?
|
Mag
(that is why we use Mag for dysrythmias-membrane stabilizer) |
|
|
The #1 cause of PEA in general anesthesia is?
|
hypovolemia
|
|
|
Which lead is best to look at for determining BBB?
|
V1
|
|
|
If you determine a pt has a LBBB, what does that mean for dx'ing anterior MI?
|
You cant dx an ant MI if LBBB present
|
|
|
RBBB has a classic pattern of?
|
M pattern ( can be unequal, though)
|
|
|
* broad QRS > .11 seconds
* rSR' pattern in V1 * broad terminal S wave in Leads I, aVL and V6 * there may be secondary T wave changes (inversion) |
RBBB criteria
|
|
|
You have a new MI pt. They develop a new RBBB during your shift. Should you be worried?
|
Yes, new RBBB is highly indicative of 3rd deg. HB -be ready to pace.
|
|
|
You see a QS complex in V1. Can you dx MI from this EKG pattern?
|
No
|
|
|
Which BBB is this: R or L
* QRS>.12 no sEPtal q waves in I and V6 QS in V1 secondary T inversion in I & V6 |
LBBB
|
|
|
Myocardial ischemia shows what on a 12 lead?
|
classically-symmetrical T wave changes
|
|
|
Myocardial injury shows what on a 12 lead?
|
ST changes
|
|
|
Myocardial infarction shows what on a 12 lead?
|
Q wave changes
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most common type of MI? Why?
A. Trasmural B. subendocardial |
B. 2 reasons:
1. subendo region is furthest away from takeoff of arterial supply. 2. subendo region has LV pushing back against it. |
|
|
Systolic dysfunction is:
A. inability to contract B. has a decreased EF C. inability to relax D. has normal EF |
A, B
|
|
|
Diastolic dysfunction is:
A. inability to relax B. can have normal EF C. involves ventrticles inability to accept volume D. AKA "supply ischemia" |
A, B, C.
known as demand ischemia |
|
|
Angina is a reliable indicator of myocardial ischemia. T or F?
|
F-affected by neuropathy from DM
|
|
|
EKG changes are an early sign of ischemia. T or F?
|
F-actually late sign
|
|
|
List the following in order of occurence in the ischemia cascade:
angina EKG changes systolic dysfuntion diastolic dysfunction switch to anaerobic metabolism hemodynamic changes |
switch to anaerobic metabolism
diastolic dysfunction systolic dysfunction hemodynamic changes EKG changes angina |
|
|
catecholamines can do which of the following?
A. induce tachycardia-decreases filling time(and coronary perfusion B. inhibit platelet aggregation C. cause coronary vasoconstriction |
All are correct
|
|
|
the most sensitive test to detect ischemia is:
A. 12 lead B. Holter monitor C. echo D. PAC |
C. wall motion abnormalities
|
|
|
Which leads show the inferior wall of LV?
|
II, III, aVF
|
|
|
Which leads are the lateral leads?
|
1, aVL, V5, V6
|
|
|
which leads are right heart or septal leads?
|
V1, V2
|
|
|
Which leads are anterior leads?
|
V1-4, wiht V3 and V4 the main ones
|
|
|
Which leads is best for detecting dysrythmias?
|
Lead II
|
|
|
How much change from baseline is suggestive of ischemia in a spontaneously breathing pt?
|
1 mm elevation from baseline
|
|
|
reciprocal changes are:
A. in leaads facing away from affected area of heart B. a mirror image of indicative changes C. in leads facing the affected area of the heart |
A, B
|
|
|
Which is worse: ST elevation or ST depression?
|
ST elevation
|
|
|
How can you detect possible posterior MI from a 12 lead?
|
V1 R wave > or = 6mm or >=S wave
V2 R wave >or=15mm or 1.5 x's S wave |
|
|
Which coronary artery supplies inferior wall? Which leads do you look at?
|
RCA, II, III, aVF
|
|
|
Which coronary artery supplies the anterior wall? Which leads do you look at?
|
LAD, V3, V4
|
|
|
Which coronary feeds the lateral wall? which leads do you look at?
|
circumflex-I, aVL, V5, V6
|
|
|
Which is the correct term for complete interruption of blood supply leading to myocardial cell death?
A. injury B. ischemia C. infarction |
C
|
|
|
Which is the correct term for prolonged interruption of blood supply leading to disruption of myocardial cell membrane integrity?
A. injury B. infarction C. ischemia |
A
|
|
|
Which is the correct term for temporary interruption in blood supply?
A. infarction B. ischemia C. injury |
B
|
|
|
To determine injury, look at what?
|
T waves
|
|
|
To determine ischemia look at what?
|
ST segments
|
|
|
To determine infarct look at what?
|
Q waves
|
|
|
Inferior MI has which complications?
A. VT/VF B. SA node blocks C. AV node blocks |
B, C
|
|
|
Posterior MI involves which coronary artery?
|
PDA branch of RCA
|

