![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
For hysteroscopy procedures, what type of anesthetic techniques may be used?
a. regional b. general c. local d.all of the above. |
D.
|
|
|
When using regional anesthesia for a hysteroscopy procedure what level of spinal block is required?
|
T 10 so that blockade of the hypogastric nerve is achieved.
T 10= umbilicus |
|
|
Paracervical block may otherwise be known as what type of block?
|
Pudendal nerve block
|
|
|
What type of airway device is usually sufficient for hysteroscopy procedures if general anesthesia is used?
|
LMA if warranted by patient health history. Do not need muscle relaxation for these cases.
|
|
|
Post operative pain from hysteroscopy is generally minimal but patients may complain of pain radiating where?
|
To the shoulder......from CO2 insufflation used during the procedure.
|
|
|
True or False: Hysteroscopy patients will likely need anti-emetic prophylaxis?
|
True as this is a GYN procedure. I like to remember the 5 receptor sites for PONV by the pneumonic DASH. Dopamine, antichoinergic, serotonin, and histamine- Marcy
|
|
|
During hysteroscopy Toradol may be used for what reason?
|
To provide relaxation of the fallopian tube openings (os) in the uterus.
|
|
|
Toradol is an NSAID that works by inhibiting prostaglandins and COX pathways but you must be cautious of what complication that can result from this medicine in hysteroscopy procedures?
|
Bleeding.
|
|
|
Potential complications resulting from Hysteroscopy procedures include which of the following? ( more than 1 answer)
a. PONV b.lithotomy position (compartment syndrome, nerve damage etc.) c. uterine perforation d. reaction to distention medium e. bowel rupture f. increased FRC |
A-E True
F false- FRC is reduced due to diaphragm being pushed cephalad. |
|
|
Statement: Reactions to distention medium used for hysteroscopy include anaphylaxis to hyskon (rare), fluid embolus, pulmonay edema, bleeding issues (DIC, platelet dysfunction)
|
.
|
|
|
Signs of a fluid embolus during hysteroscopy include which of the following: Choose all that apply.
a. gradual increase in ETCO2 b.gradual decrease in ETCO2 c. more output than input of fluid d. more input than output of fluid e. fluid that is ran in without pressure f. fluid that is ran in under pressure. |
B, F, D
|
|
|
True or False: Uterine perforation or bowel rupture may result if the patient coughs while the surgeon is working in this area and the signs are often immediate
|
False: The first part of the statement is true....however the signs of perforation may not occur until later when there is blood loss into the abdomen or intrabdominal free air present on radiography,
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
pic
|
|
|
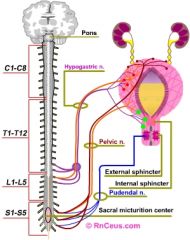
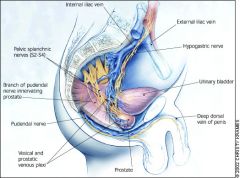
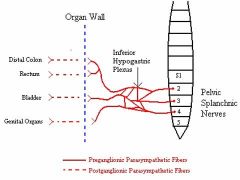
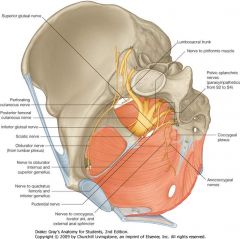
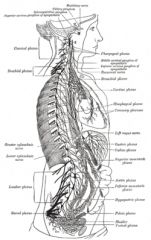
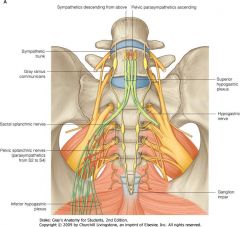
What 3 sympathetic nerves innervate the following Organs?
What spinal level do they originate from? -distal fallopian tube -Upper Ureter -Ovaries |
Aortic plexus
superior mesenteric plexus renal plexus T9-T10 |
|
|
What nerves innervate the following organs?
And, what spinal level do the nerves originate from? -Perineum -Vulva -Lower and upper vagina -Cervix and Low uterus -Posterior urethra -Trigone -Lower ureter -Rectosigmoid colon |
Pudendal nerve
inguinal nerve gentiofemoral nerve posterior femoral nerve pelvic and parasympathetic nerves S2-S4 |
|
|
The following organs are innervated by?
Where do they originate from? -uterine fundus -proximal third fallopian tube -broad ligament -upper bladder -cecum, appendix and terminal large bowel |
sympathetic nerves via hypogastric plexus
T11-T12 |
|
|
The cause of compartmetn syndrome in lithotomy position is?
|
decreased blood flow leads to swelling of tissue in enclosed space
|
|
|
What is the formula for determining flow gradient in lithotomy position?
|
0.7 mmHg per every 1 cm elevation above level of BP measurement
|
|
|
What can we do to reduce leg compartment pressures?
|
use SCDs
|
|
|
True OR False: All the following anesthesia types can be used for GYN laparoscopy procedures:
1. GETA with muscle relaxant 2. LMA (in short cases) 3. Neuraxial |
True
|
|
|
In GYN laparoscopic procedures and the use of LMA technique, nurse anesthetists should use caution and select patient carefully due to ____________
|
the risk of aspiration with this technique.
|
|
|
In neuraxial anesthesia, shoulder pain is related to irritation of the _____________and the _________ ___________
|
diaphragm and the phrenic nerve
|
|
|
Examination of the endometrial cavity usually for abnormal bleeding and lesions is called:
|
Hysteroscopy
|
|
|
what is the purpose of the distention media used during a hysteroscopic procedure?
|
To enable a better view.
|
|
|
Name examples of distention media that can be used in hysteroscopy.
|
-CO2
-Sorbitol in water -LR/NS -Dextran 70 (Hyskon) |
|
|
T/F: Uterine perforation is a complication assoc with hysteroscopy.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
Which of the following is not an indication for a laparotomy?
a. abd hysterectomy b. pelvic exoneration c. fertility procedures d. emergent surg for bleeding e. D&C |
E is not an indication
|
|
|
Why is neuraxial anesthesia contraindicated for a laparotomy in an unstable pt?
a. b/c sympathetic blockade of neuraxial b. b/c of need to control airway c. b/c risk for aspiration d. takes too long to do |
A
|
|
|
Statement: The pregnant female is considered to have a full stomach beginning at 10-14wks gestation.
|
.
|
|
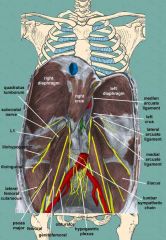
|
Hypogastric plexus
|
|
|
GYN surgical approaches:
A. Lapraroscopy B. Hysteroscopy C. Laparotomy D. Perineal Abcess |
GYN surgical approaches:
A. Lapraroscopy B. Hysteroscopy C. Laparotomy D. Perineal Abcess |
|
|
GYN Laparoscopy surgery Types
A. Diagnostic B. Endometriosis C. Ectopic Pregnancy D. Myomectomy E. Hysterectomy F. Orchiectomy |
A. Diagnostic
B. Endometriosis C. Ectopic Pregnancy D. Myomectomy E. Hysterectomy |
|
|
T/F - GYN Laparoscopy usually elective cases in old sick females
|
F - GYN Laparoscopy usually elective cases in YOUNG HEALTHY females
|
|
|
T/F - GYN laparoscopy will have CO insufflation.
|
F - GYN laparoscopy will have CO2 insufflation.
|
|
|
T/F - GYN laparoscopy may be done in lithotomy position.
|
T
|
|
|
T/F - GYN Laparoscopy requires muscle relaxation reversal after induction.
|
F - Usually requires muscle relaxation for abdominal insufflation.
|

