![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Frequent & liquid stools
Usually on the right side of abdomen Sigmoid- |
Ileum (Ileostomy)
|
|
|
|
An ascending colostomy will show signs of what in the stool
|
frequent and liquid stools
|
|
|
|
When you see more solid formed stool
|
Transverse colostomy
|
|
|
|
When you see near normal stool
Usually on the left side of the abdomen |
Sigmoid colostomy
|
|
|
|
The organ that neutralizes acidic gastric contents
|
Duodenum
|
|
|
|
Major organ for nutrient absorption
|
Jejunum
|
|
|
|
responsible for nutrient absorption
|
lleum
|
|
|
|
What disease presents with abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and growth failure, has a slight increse for cancer
|
Chrones disease
|
|
|
|
What disease involves only the colon and the mainfest w/ diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and weight loss, high increase for cancer
|
Ulcerative colitis
|
|
|
|
you should never use an enema for irrigationof what
|
Colostomy
|
|
|
|
Anywhere along GI tract
Abdominal pain, diarrhea weight loss and growth failure Blood not visible if proximal disease |
Chrons disease
|
|
|
|
Colon only
Diarrhea, rectal bleeding, weight loss Blood usually visible |
Ulcerative colitis
|
|
|
|
Infection
|
Invasion- of tissues or cells by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses
|
|
|
|
Inflamation
|
Reaction- caused by an agent either living or nonliving
|
|
|
|
You have brief vasonconstriction and the release of histomines
|
Vascular response
|
|
|
|
what are the first WBC to respond
|
Neutrophils
|
|
|
|
Second to respond and are there by day three and last up to a week are
|
Monocytes
|
|
|
|
Contamination
|
Presence of non-replicating microorganisms on the wound surface
|
|
|
|
Critical coloinzation
|
Increased bio-burden to overwhelm the host. Poor healing, becomes invasive
|
|
|
|
Replicating bacteria without a host reaction or clinical signs and symptoms of infection
|
colonization
|
|
|
|
Acute Wound that is infected
|
Local inflammation
Pus formation - due to neutrophils Increased exudate |
|
|
|
Chronic Wound that is infected
|
Wounds are usually colonized and signs are more subtle
Changes in exudate, Increased pain in wound bed, change in color Delayed healing, Unhealthy granulation |
|
|
|
Healthy granulation tissue looks like?
|
Bright (beefy) red
|
|
|
|
What are the host defences
(protect the pt from infection) |
Intact skin barrier, good inflammatory responce (healthy)
|
|
|
|
Toxins (endotoxins)
|
Alter normal function of the cells host
|
|
|
|
Environmental factors
|
Some organisms can alter the environment in which they live so that the host’s immune system cannot locate them and/or has difficulty destroying them i.e. capsules, slime and moucus layers.
|
|
|
|
Factors that affect wound healing
|
necrotic tissue, your perfusion status, and the size and duration of the would
|
|
|
|
Obtaining a tissue biospy
|
Time consuming and costly
Risk of trauma and bacteremia Require special equipment Not within the scope of practice of RN’s time consuming, risk of trauma, and introducing bacteria in to the bloos stream |
|
|
|
needle aspiration
|
Painful
Invasive, painfull, expensive Not within the scope of practice for RN’s |
|
|
|
Swab Culture negatives
|
A concern about this is that cultures only reflect the surface colonizing bacteria
|
|
|
|
Swab culture positives
|
It is usefull guide to antibiotic therapy, it is with in the scope of the nurse.
|
|
|
|
Supplies for a cotton swab culture collection
|
cotton swab, sterile gloves, flush with NS or distilled water, debrive wound prior to collection.
|
|
|
|
Stage 1 Ulcer
|
Intact skin with non-blanchable redness of a localized area usually over a bony prominence
Darkly pigmented skin may not have visible blanching, it’s color may differ from surrounding areas |
|
|
|
Treatment for stage 1 Ulcer
|
No Vigorous massage
Pressure redistribution mattress Risk assessment on admission and daily Remove excess moisture Provide moisture barrier Turn every 2 hours Avoid friction and shear |
|
|
|
Stage II Ulcer
|
Partial thickness loss of dermis presenting as a shallow open ulcer with a red pink wound bed, without slough. May also present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister.
|
|
|
|
NonBlanchable Erythema
|
The ulcer appears as a defined area of redness that does not blanch (become pale) under applied light pressure.
|
|
|
|
Blanchable errythmia
|
Reddened area that turns pale under applied light pressure. NOT a Stage I pressure ulcer
|
|
|
|
What stage ulcer is this?
|
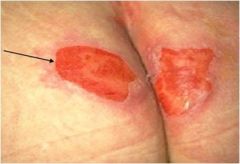
|
Stage 2
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a stage 2 ulcer
|
Pressure relief of site
Wound cleansing Moist wound healing: decreases pain, reduces infection, decreases cost and hours spent changes dressing |
|
|
|
What describes a stage three ulcer
|
Full thickness tissue loss. Subcutaneous fat may be visible but bone, tendon or muscle are not exposed. Slough may be present but does not obscure the depth of tissue loss. May include undermining and tunneling.
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a stage three ulcer
|
Pressure relief
Cleanse wound Provide moisture Absorb excess exudate Fill dead space |
|
|
|
Stage 4 pressure ulcer
|
Full thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon or muscle. Slough or eschar may be present on some parts of the wound bed. Often include undermining and tunneling.
|
|
|
|
Moist topical treatment and main goal for what?
|
A stage 2 ulcer healing?
|
|
|
|
Full thickness tissue loss in which the base of the ulcer is covered by slough (yellow, tan, gray, green or brown) and/or eschar (tan, brown or black) in the wound bed.
|
Unstageable
|
|
|
|
You will not see muscle, bone, tendon are not ecposed in what stage?
|
Stage 3
|
|
|
|
Undermining and tunneling may or will be included in determining what stage of ulcers
|
Stage 3 and stage 4
|
|
|
|
Purple or maroon localized area of discolored intact skin or blood-filled blister due to damage of underlying soft tissue from pressure and/or shear
|
Suspected deep tissue injury.
|
|

