![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
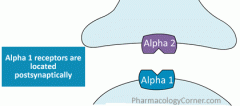
alpha 1 receptors
|
|
|
|
alpha 1 receptor activation
|
|
|
|
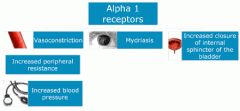
Effects of alpha 1 receptor
|
1. vascular smooth muscle: vasoconstriction, increase in PVR
2. Mydriasis: mediated by both alpha 1 and alpha 2 3. genitourinary tract smooth muscle: alpha 1A located at external sphincter of the bladder (improves urinary flow) |
|
|
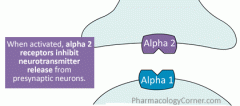
alpha 2 receptors
|
|
|
|
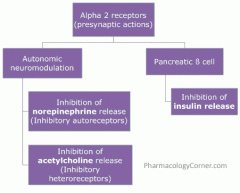
alpha 2 receptor location
|
|
|
|
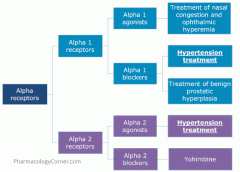
drugs affecting alpha receptors
|
|
|
|
alpha 2 receptors work mainly as
|
autoreceptors to mediate feedback inhibition of sympathetic transmission
|
|
|
alpha 1 agonists
|
VASOCONSTRICTION
reduce edema and inflammation |
|
|
alpha 1 agonist drugs
|
decongestant drugs: naphazoline, phenylephrine, propylhexedrine
|
|
|
alpha 1 antagonists
|
VASODILATION
decrease PVR treatment of HTN |
|
|
alpha 1 antagonist drugs
|
prazosin
|
|
|
alpha 1A antagonist for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
|
tamsulosin
|
|
|
tamsulosin has decreased incidence of
|
orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
alpha 2 agonists
|
inhibit sympathetic outflow from CNS
|
|
|
treatment of HTN and symptoms associated with opiod withdrawal
|
clonidine
|
|
|
treatment of HTN during pregnancy
|
alpha-methyldopa
precursor to alpha-methylnorepinephrine |
|
|
alpha 2 antagonists
|
yohimibine blocks alpha 2 leading to increased release of NE with subsequent stimulation of cardiac beta 1 receptors and peripheral vasculature alpha 1 receptors
used to be used to treat erectile dysfunction |
|
|
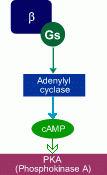
structure of beta receptors
|
|
|
|
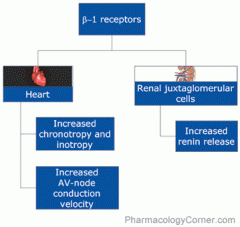
beta 1 receptors
|
|
|
|
rank order in terms of potency of response for beta receptors
|
isoproternol> epi> NE
|
|
|
division of beta receptors is made based on their
|
affinities to adrenergic agonists and antagonists
|
|
|
beta 1 receptors
|
increase chronotropy (HR) and inotropy (force of contraction)
(inotropy is increased phosphorylation of Ca2+ channels) increase in AV node conduction velocity kidney: yuxtaglomerular cells where receptor activation causes renin release |
|
|
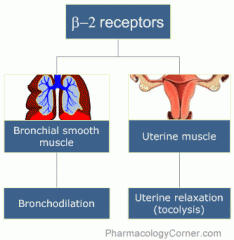
beta 2 receptors
|
|
|
|
beta 2 agonists
|
bronchodilation
treatment of asthma and COPD salbutamol, albuterol, tertbutaline |
|
|
tocolytic drug
|
ritodrine
|
|
|
beta 2 receptors
|
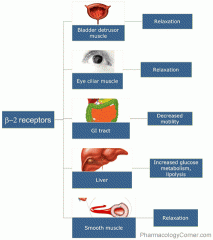
|
|
|
system that activates bladder constriction
|
parasympathetic
|
|
|
drugs that act on _ receptors used in treatment of urinary retention
|
muscarinic
bethanechol |
|
|
beta 2 induce vasodilation in
|
liver and muscle
|

