![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adapted Education |
An individualized program of physical and motor fitness, fundamental motor skills and patterns, and skills in aquatics, dance, individual and group games, and sports that are designed to meet the unique needs of individuals. |
|
|
Key Features of Adapted Physical Education |
Individualized, long term, active, meets unique needs. Empower individuals to take control of their lives, take responsibility for themselves and others. Outcomes related to cognitive, affective, and psychomoter domains as affected elements. |
|
|
Adapted Physical Activity |
Service delivery, pedagogy, coaching, training, or empowerment. -All ages -Various settings available (not just school based) -Provided by various qualified professionals |
|
|
Adaption |
Assessing and managing variables and services to meet unique needs and achieve desired outcomes. Considers variables that can be changed, tasks, persons, and environment. |
|
|
Modification |
Alter or lower the criteria that the student must meet in order to be considered successful. |
|
|
Accomodation |
Providing access, removing barriers, or minimizing limitations in order to facilitate a student's achievement of the same goals as peers. |
|
|
Supports |
Supplementary resources and airs that are provided to enable students with disabilities to be educated with nondisabled peers. |
|
|
What is the difference between Adapted and Adaptive? |
Adapted: education or service delivery -Verb denoting the process of modifying -Adjective referring to a program or serve delivery outcome.
Adaptive: Behaviours -Adjective that describes client behaviours in occupational therapy. |
|
|
What are the 3 plans associated with Adapted Physical Education? |
IEP: Individualized education program IFSP: Individualized family service plan IPEP: Individualized physical education program. |
|
|
Adapted Sport |
Sport modified or created to meet the unique needs of individuals. |
|
|
Aims and Goals for an Adapted Physical Education Program |
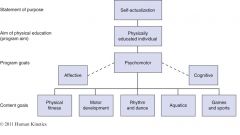
|
|
|
The first National Standard for PE |
Demonstrates competency in motor skills and movement patterns needed to perform a variety of physical activities. |
|
|
The second National Standard for PE |
Demonstrates understanding of movement concepts, principles, strategies, and tactics as they apply to the learning and performance of physical activities. |
|
|
The third National Standard for PE |
Participates regularly in physical activity. |
|
|
The fourth National Standard for PE |
Achieves and maintains a health-enhancing level of physical fitness. |
|
|
The fifth National Standard for PE |
Exhibits responsible personal and social behaviour the respects self and others in physical activity settings. |
|
|
The sixth National Standard for PE |
Values physical activity for health, enjoyment, challenge, self-expression, and social interaction. |
|
|
Impairments |
Problems in body function and structures. |
|
|
Disabilities |
Activity limitations. |
|
|
Restrictions |
Barriers to participation caused by person- environments, interactions, and handicaps. |
|
|
Handicaps |
A term no longer used by the WHO |
|
|
Quadriplegia |
Paralysis of all four limbs, the trunk, and many organ functions, like blood pressure and respiration. |
|
|
Paraplegia |
Paralysis of the lower limbs, and depending on the level of damage the trunk and alterations of organ function. |
|
|
Diplegia and Triplegia |
Condition where two or three limbs are more involved than others. |
|
|
Hemiplegia |
Loss of sensation and or movement on either the right or left side of the body. |
|
|
Functional Walking |
The ability to walk with assistive devices like crutches, walkers, and canes. |
|
|
Prothesis |
Refers to an external artificial body part. |
|
|
Orthosis |
Refers to a brace or splint. |
|
|
Congential Time-of-Onset |
Disability present at birth. |
|
|
Acquired Time of Onset |
Disability occurs after birth. |
|
|
Guidelines to Speaking and Writing to Individuals with Disabilities |
-Avoid reference to disability. -Avoid viewing those who succeed as super-human. -Do not sensationalize a person with disabilities by saying "Afflicted with" or "victim of". -Avoid labeling people into groups, eg. "the deaf". -Use first-person terminology. - Avoid using emotional descriptors. -Emphasize abilities -Avoid implying disease when discussing disabilities. |
|
|
Experiential Education |
Learning by doing. |
|
|
Reflective thinking |
Analyzing beliefs, effects of actions, and acquiring attitudes of open mindedness. |
|
|
Benefits of Hands-on Experience |
Greater perceived competence. Better attitudes towards inclusion. Difficult to measure actual competance. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of friendships or partnerships? |
Any kind of collaboration. Both parties share power. Benefit to the same extent. Respect and value one another equally. Experience mutual satisfaction and enjoyment. |
|
|
Eugenics |
Movement to improve gene pool. Sterilization. Marriages by feeble minded forbidden. People favoured euthanasia of defective infants. WWII- Nazi Germany conducted a widespread euthanization and sterilization of anyone believed to be inferior.
|
|
|
Read Slides..... |
24-31 |

