![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the ssx of acne? |
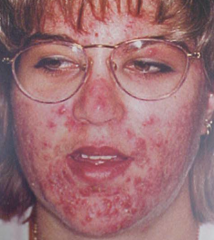
1. Chronic inflammation of the pilosebaceous units of skin |
|
|
What is the key lesion in acne? |
1. Comedo--- enlarged and plugged hair follicle 2. Open=blackhead 2. Closed=whitehead |
|
|
How do you grade acne? |
0= no acne 1= mild acne, comedos, papules, few pustules 2=moderate acne, multiple papules and pustules 3=moderately severe, multiple comedos, papules, and pustules 4= severe, multiple comedos, papules, pustules |
|
|
What is the principal bacterium behind acne? Characteristics? |
1. P. acnes--- metabolizes sebum to FFAs 2. Anaerobic |
|
|
What are the characteristics of comedo inflammation? |
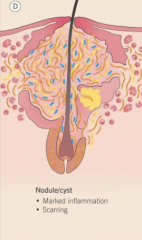
1. Nodule formed when comedo shatters 2. Remnants extruded into tissue 3. Can lead to chronic granuloma |
|
|
What is the etiology of neonatal acne? Infants? |
1. Neonatal= comedonal 2. Infants= inflammatory |
|
|
Does diet influence acne? |
1. No evidence suggests that dietary habits influence acne |
|
|
How do you tx acne vulgaris? |
1. Benzoyl peroxide 2. Topical abx 3. Retinoids 4. OCs 5. Salicyclic acid
Tx must last 8-12 weeks |
|
|
What abx can be used to tx acne? |
1. Doxycycline 2. Minocycline-- most effective, significant SE 3. Erythromycin 4. Clindamycin 5. Sulfonamides |
|
|
What is the clinical use of isotretinoin? |
1. Severe acne 2. Poorly responsive acne to other tx |
|
|
What are the complications of isotretinoin? |
1. Pregnancy category X 2. HyperTG 3. Dry skin, lips, and eyes 4. Joint pains |
|
|
What are the ssx of acne conglobata? |
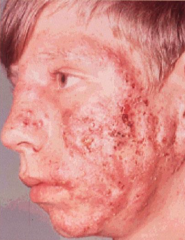
1. Severe variant of acne 2. Large, multiple comedones, abscesses, sinus tracts |
|
|
How do you tx acne conglobata? |
1. Isotretinoin |
|
|
What are the aspects of the follicular occlusion triad? |
1. Acne conglobata 2. Hidradenitis suppurativa 3. Dissecting cellulitis |
|
|
What is the mechanism of light tx to tx acne? |
1. Triggers proliferation of porphyrins 2. Porphyrins attach to P. acnes, destroys bacteria |
|
|
What are the ssx of rosacea? |
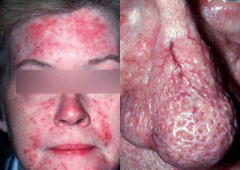
1. Chronic inflammatory dermatologic disorder 2. Redness w/ pustules, papules, telangiectasia, and hypertrophy of sebaceous glands |
|
|
What is stage I rosacea? |

1. Flusher/blusher 2. Nose/cheeks 3. Few telangiectasias, though they become more prominent 4. Persistent erythema |
|
|
What is stage II rosacea? |
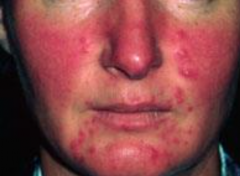
1. Papules and pustules begin 2. Increased erythema and telangiectasias |
|
|
What is stage III rosacea? |
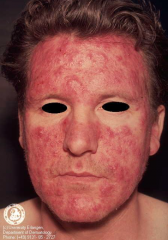
1. Dense erythema 2. Papules, pustules, nodules 3. Diffuse telangiectasias 4. Plaque-like edema |
|
|
What factors can provoke flushing in rosacea? |
1. Extreme temperatures 2. Spicy foods 3. Alcoholic or hot beverages 4. Exercise 5. Stronge emotions 6. Hormonal fluctuations |
|
|
What are the ssx of rhinophyma? |
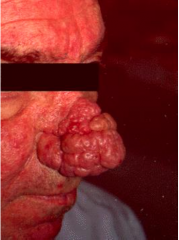
1. Progressive increase in connective tissue, sebaceous gland hyperplasia, ecstatic veins, and chronic deep inflammation |
|
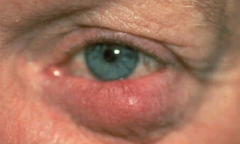
|
1. Ocular rosacea |
|
|
How do you tx rosacea? |
1. Sunscreen 2. Topical fsulfacetamide 3. Metronidazole 4. TCN, Doxy, minocycline |
|
|
How do you tx severe rosacea? |
1. Oral metronidazole 2. Clonidine for flushing 3. Prednisione 4. Isotretinoin |
|
|
What are the ssx of hidradenitis suppurativa? |
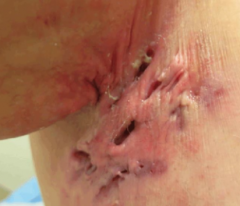
1. Intertiginous skin with terminal hairs--- tender, firm red nodules 2. Fluctuant suppuration sinus tract formation |
|
|
What are the complications of hidradenitis suppurativa? |
1. Interstitial keratitis 2. SCC 3. Fistulas 4. Anemia |
|
|
What is the MCC of hidradenitis suppurativa? |
1. Follicular hyperkeratosis leads to rupture of follicular epithelium 2. Inflammation engulfs apocrine gland 3. 2o bacterial infections |
|
|
How do you tx hidradenitis suppurativa? |
NO CURE
1. Friction reduction--- weight loss 2. Topical abx soaps 3. Oral abx 4. Isotretinoin |
|
|
What are the ssx of scabies? |
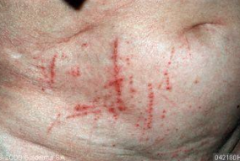
1. Severe itch 2. Mostly at night 3. Thread-like irregular line with tiny vesicle |
|
|
How do you tx scabies? |
1. Permethrin 2. Ivermectin |

