![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Generic cytotoxic drugs |
- Kills cells that proliferate, non-selectively
-Typical adverse side effects are in areas of high proliferation: Bone Marrow (immunosuppression, anemia, thrombocytopenia), GI Tract (diarrhea, vomiting), Hair follicles, Gonads, Wound healing, fetus, injection site |
|
|
Methotrexate |
- Folic Acid Analog inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (prevents formation of the methyl donor for thymidylate synthetase)
- Decrease dTMP leads to decreased DNA synthesis
- Reversible with Luecovorin rescue |
|
|
Vincristine (Oncovorin) |
- Inhibits microtubule formation and arrests cells at the M-phase
- FX: peripheral neuropathy which is dose dependent
- Part of MOPP (Hodgkins) and CHOP therapy (Non-Hodgkins) |
|
|
Paclitaxel |
- Hyperstabilizes polymerized microtubules in M phase so that mitotic spindle cannot breakdown
- Prevents anaphase
- Used in ovarian and breast carcinomas |
|
|
Mechlorethamine |
- Nitrogen mustard that cross links DNA
- Treatment for Hodgkin's lymphoma (myelosuppressive qualities)
- Part of MOPP therapy |
|
|
Cisplatin |
- Two activated Cl- arms can cross-link DNA
- FX: renal insufficiency and ototoxicity |
|
|
Cyclophosphamide |
- Taken orally as a prodrug
- P450 metabolism makes toxic metabolites - Alkylating Phosphoramide Mustard (cross links DNA) and Acrolein (causes hemorrhagic cystitis)
- High doses can cause dangerously low WBC levels
- Part of CMF therapy (breast cancer) |
|
|
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) |
- Topoisomerase II inhibitor prevents DNA untangling after crossover
- FX: impaired cardiac contractility because it also chelates iron and causes mitochondrial DNA damage (topoisomerase inhibition does not apply to myocytes because they don't proliferate)
- Women mores susceptible than men at lower doses |
|
|
5-fluorouracil (5-FU) |
- Pyrimidine analog (looks like dUMP but is FdUMP) binds thymidylate synthase and gets "stuck"
- Leucovorin (FH4) enhancement: FH4 is converted to CH2-THF methyl donor that complexes to form more stable thymidylate synthetase that can be inhibited by 5-FU) |
|
|
MOPP |
- Treatment for Hodgkins lymphoma
Mechlorethamine, alkylating agent Oncovin (vincristine), mitotic spindle poison Procarbizine, alkylating agent Prednisone, corticosteroid
|
|
|
CHOP |
- Treatment for Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma
Cyclophosphamide, alkylating agent Hydroxydaunorubicin (doxorubicin/adriamycin), TOP II inhibitor Oncovin (vincristine) , mitotic spindle poison Prednisone, corticosteroid |
|
|
CMF |
- Treatment for breast cancer
• Cyclophosphamide, alkylating agent • 5-FU, antimetabolite |
|
|
AC |
-Treatment for breast cancer
• Adriamycin, Top II inhibitor |
|
|
FOLFIRI |
-Treatment for colon and pancreatic cancer
• 5-FU, antimetabolite • Leucovorin, similar to FH4 • Irinotecan, Top II inhibitor |
|
|
Bevacizumab |
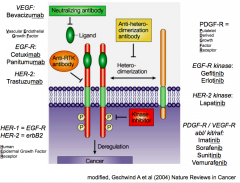
- Targets VEGF (ligand) and inhibits angiogenesis
- Used against solid tumors (colorectal, renal cell carcinomas)
- FX:1/4 pts get hypertension because VEGF helps blood vessels relax |
|
|
Rituximab |
- Monoclonal antibody against CD20 found on most B cell neoplasms
- Used in conjunction with CHOP
- Increased risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) |
|
|
Vemurafinib |
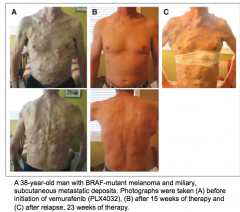
- Targets BRAF signaling molecule - V600E mutation in bRAF
- Treatment against melanoma
- Acquired drug resistance so tumors can come back on the skin |
|
|
Cetuximab |
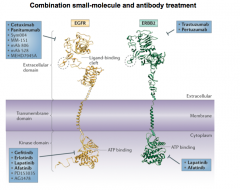
- Targets EFR-R (aka HER-1) but is only appropriate for WT KRAS (tyrosine kinase) patients
- Treatment for Colorectal cancer along with FOLFIRI
- FX: GI tract/cutaneous tissue |
|
|
Trastuzumab |
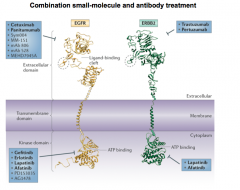
- Targets HER-2; often used in connection with CAP
- Restores outcome of breast cancer to those who are HER-2 negative
- FX: cardiac (HER-2 used for maintenance)
|
|
|
Gefitinib |
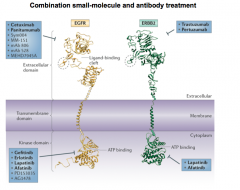
- Targets Tyrosine Kinase portion of EFGR
- T790M mutants are drug resistant
- Efficacy requires skin side effects (dose-dependent)
- Treats Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer |
|
|
Erlotinib |
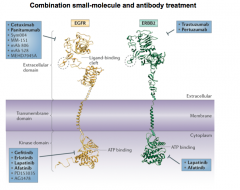
- Targets Tyrosine Kinase portion of EFGR
- T790M mutants are drug resistant
- Efficacy requires skin side effects (dose-dependent)
- Treats Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer |
|
|
Imatinib |
- Targets Abl, kit, PDGF-R to prevent constitutive tyrosine kinase
- Treatment for CML
- Drug resistance |
|
|
Lapatinib |
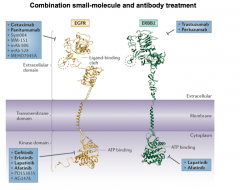
- Targets Tyrosine Kinase portion of HER-2
- T790M mutants are drug resistant
- Efficacy requires skin side effects (dose-dependent)
- Treats Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer |
|
|
Ipilimumab |
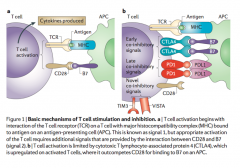
Immune cell target
-Blocking antibody used in melanoma patients
- Ab targets CTLA-4 (inhibitory receptor) on T cells and prevents B7 binding --> causes up regulation of T cell activation
- FX: hyper activation of immune system --> autoimmune symptoms (dermatologic, GI, endocrine) |
|
|
Lambrolizumab and Nivolumab |
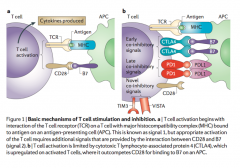
Immune cell target
- Targets PD-1 on T cell and prevents PD-L1 (tumor cell) from binding
- Prevents programmed death of T cell when it encounters a tumor cell
|
|
|
Azathioprine |
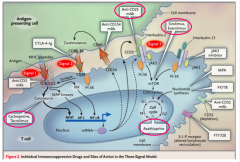
IMMUNOSUPPRESSANT
- It's active metabolite mercaptopurine gets incorporated into DNA and RNA
- Interferes with T cell cycle |
|
|
Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus |
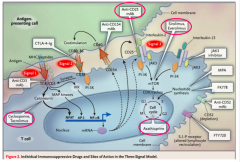
IMMUNOSUPPRESSANT - Blocks calcineurin signaling (of IL-2 receptor) to inhibit T cell activation
- FX: nephrotoxicity |
|
|
Sirolimus (Rapamycin) |
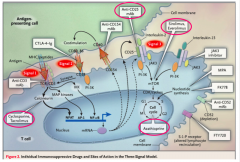
IMMUNOSUPPRESSANT
-Binds mTOR and interferes with T cell signaling in the cell cycle |
|
|
Basiliximab and Daclizumab |
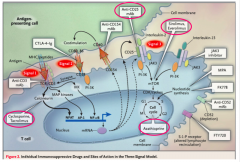
IMMUNOSUPPRESSANT
- Antibody inhibits T-cell activation by binding the IL-2 receptor (CD25) |
|
|
CTLA-4 Agonist |
- Opposite of Ipilimumab
- Inhibits T cell proliferation by providing the co-inhibitory signal (normally what B7 does) |
|
|
Irinotecan (and etoposide) |
- Topoisomerase II inhibitor used in colon cancer
- Unlike Doxorubicin, does not impair cardiac contractility |
|
|
Bortezomib |
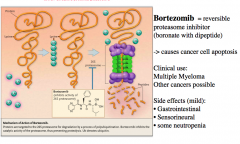
- Reversible proteasome inhibitor that causes cancer apoptosis
- Treatment for Multiple Myeloma
- Mild side effects |
|
|
Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitors |
- Usually designed to inhibit intracellular kinases that are often mutated in cancer
- Easier to make than mAb but can cause more non-specific side effects |
|
|
NSAIDS - analgesic only |
Acetaminophen (4 hr) - otc Ketorolac tromethamine (4-6 hr) - p
|
|
|
NSAIDS - analgesic and anti-inflammatory |
Aspirin/other salicylates (4 hrs) Ibuprofen (4 hr) Naproxen (12 hr) Ketoprofen (3-4 hr) Diflunisal (12 hr) - p Rofecoxib (12-16 hr) - p and withdrawn |
|
|
NSAIDS - anti-inflammatory only |
Indomethacin (4-8 hr) - p Sulindac (12 hr) - p Celecoxib (12 hr) - p |
|
|
OTC NSAIDS |
Acetaminophen Aspirin Ibuprofen Naproxen Ketoprofen |
|
|
Acetaminophen |
Poor anti-inflammatory:
1) <20% bound to proteins --> no accumulation at inflammatory site
2) Weak COX inhibitor (still effective as analgesic against inflammatory pain)
Detox: via hepatic glutathione-S-transferase (hepatic toxicity if overdose) |
|
|
Celecoxib |
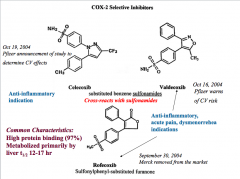
- COX 2 inhibitor - Can cross-react with sulfonamides (allergic reaction) and cause GI bleeding - Good for treating Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis -FDA: no proven reduction in ulcer complications compared to other NSAIDs
|
|
|
Aspirin |
- Salicylate
- Reaches analgesic ceiling at ~650 mg (shallow dose response curve)
- Additive analgesic effect when added to codeine (Empirin)
- Should not be given to children recovering from viral infection (can cause Reyes syndrome)
- Only approved NSAID for prophylactic low-dose use in patients with unstable angina, Post-MI, or at risk for MI (IRREVERSIBLE Cox inhibitor --> platelets can't overcome to make TXA2 but endothelial cells can to make PGI2) |
|
|
Indomethacin |
- Acetic Acid
- AI only but has a similar analgesic ceiling to aspirin
- Most potent NSAID (0.1 vs Aspirin 164) but has the same anti-inflammatory properties
- Used to treat Patent ductus arteriosus in neonates
|
|
|
Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Ketoprofen |
- Proprionic Acids; greater analgesic ceilings than aspirin
- Most effective NSAIDs against dysmenorrhea
- Ketoprofen > Ibuprofen in GI bleeding
- Naproxen > Ibuprofen > Ketoprofen in half life |
|
|
Adjuvant NSAID Therapies to prevent GI effects |
Ranitidine, Cimetidine = H2 receptor antagonists
Sucralfate = gel coating to protect stomach
Misoprostol (methylated PGE2) = Restore GI PGs -- only one shown to significantly decrease GI ulcers
|
|
|
Sulindac Sulfoxide |
- Acetic Acid
- AI only but has a similar analgesic ceiling to aspirin
- Slower onset than aspirin but matches analgesic ceiling
- Active metabolite, Sulindac Sulfide, converted back to prodrug for renal sparing |
|
|
Diflunisal |
- Salicylate
- Higher analgesic ceiling and higher half-life compared to aspirin |
|
|
Rofecoxib |
- COX 2 selective inhibitor; similar analgesic and AI efficacies to other NSAIDs
- Withdrawn for cardiotoxic side effects |
|
|
Ketorolac |
- IM, IV, or oral
- Acetic Acid
- Analgesic only; comparable ceiling to morphine if given intramuscularly, ibuprofen if given orally
- Short term pain management only - short half life
- Does not cause respiratory depression as seen with morphine and other narcotics |
|
|
Aspirin overdose |
- Normal: 80% conjugated and excreted by liver
- Prolonged doses: elimination takes on zero order kinetics --> liver excretion saturates and kidney excretion rises --> half-life greater than 12 hours
- CNS sx first: tinnitus, centrally induced respiratory alkalosis, uncoupling of oxidate phosphorylation
- Treatment: increasing pH of urine (b/c aspirin is a weak acid) will help increase renal excretion rate |
|
|
Aminoglutethimide |
- Blocks all steroid synthesis at first step (cholesterol -> pregnenolone) |
|
|
Metyrapone |
- Inhibits 11B-hydroxylase activity which stops glucocorticoid and minerocorticoid synthesis but not androgen
- Should induce an increase in ACTH (diagnostic for if something is wrong) |
|
|
Dexamethasone |
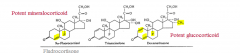
- Potent glucocorticoid because of its substitutions (fluorine, 2 double bonds, and methyl group) |
|
|
9α-Fludrocortisone |
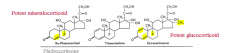
- Potent minerocorticoid because it doesn't have a substituted methyl group and only has one double bond
- Treatment for Addison's disease along with cortisol
|
|
|
Short-acting Glucocorticoids (in order of Anti-inflammatory activity) |
8-12 hours
Prednisolone (5)> Prednisone (4)> Hydrocortisone (1)> Cortisone (0.8)
Prednisolone and Prednisone has least salt-retaining activity (0.3) |
|
|
Intermediate-acting Glucocorticoids |
12-36 hours
Triamcinolone (5 anti-inflammatory, 0 salt retaining) |
|
|
Long-acting Glucocorticoids |
36-72 hours
Dexamethasone (30=AI, 0=SR) |
|
|
Fludrocortisone |
8-12 hour minerocorticoid (10=AI, 250=SR) |

