![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
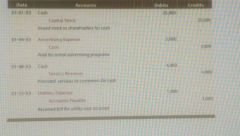
General Journal |
The tool businesses use to record each material financial transaction, in a format that enables a manager to quickly scan it and identify what transpired in a given period of time. |
|
|
|
Formatting Rules |
1. Record the date, 2. Record the name of the account that is being debited or credited, 3. In the Doc. No. column, record either the invoice number or check number, if applicable, 4. Record the dollar amount to be debited from the account in the Debit column, 5. Record credits in the credit column, 6. For every debit and credit recorded, note the respective account number in the Post Ref. column (called "posting to the general ledger"), 7. Some businesses record a short explanation of the transaction after the last credit. |
These help managers analyze and describe what has happened to the business financially. |
|
|
Revenue |
The money made from goods sold or services rendered by a business. |
Also known as sales |
|
|
Expenses |
The cost of goods and services used up in the process of obtaining revenue. |
can be associated with finance. |
|
|
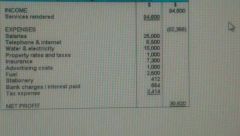
Income Statement |
A financial statement that measures a company's financial performance over a specific accounting period. |
|
|
|
Matching Principle |
The principle that requires a company to match expenses with related revenues in order to report a company's profitability during a specific time interval; an important accounting rule business owners should keep in mind when recording sales and expenses; If a cost cannot be linked to revenues or to an accounting period, the expense is recorded immediately. |
[Example] Advertising is an expense that helps make potential customers aware of your business, which in turn helps increase sales. |
|
|
Accounts Receivable |
Money owed by customers (individuals or corporations) in exchange for goods or services that have been delivered or used but not yet paid for. |
(A/R) involves selling on account |
|
|
Accounts Payable |
An entity's short-term debits to its creditors; as it grows, you credit it each time. |
(A/P) involves purchasing on account |
|
|
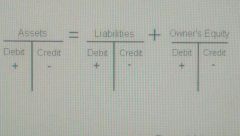
Debit or Credit a Sale or Expense Transaction |
A sale would help increase owners' equity (recorded as credit) An expense decreases owners' equity (recorded as a debit) A withdrawal (dividend) from the company decreases owners' equity (recorded as a debit) Investment of capital stock would increase owners' equity (recorded as a credit) |
|

