![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the benefits of Decentralization in Organizations? |
1.Lower-level managers gain experience in decision making. 2.Top manage free to concentrate on strategy 3.Decision making authority leads to job satisfaction 4.Lower level decisions often based on better information 5.Lower level managers can respond quickly to customers |
|
|
What are disadvantages of Decentralization in Organizations? |
1. lower level managers may make decisions without seeing the "Big Picture" 2. May be a lack of coordination among autonomous managers 3. lower level manager's objectives may not be those of the organization 4. may be difficult to spread innovation ideas in the organization |
|
|
What is a segment? |
any part or activity of an organization where a manager seeks cost, revenue, or profit data. Examples: individual store sales territory service center |
|
|
What are the two keys to building a segment income statement? Explain what they are for. |
Contribution Format: used to separate fixed from variable costs and allows calculations of CM Traceable Fixed Costs separate from common fixed costs: Allows the calculation of a segment margin. |
|
|
What are Traceable costs? |
Costs that appear because of the existence of a particular segment. Disappears over time if that segment disappeared. |
|
|
What are common costs? |
Costs that appear because of the overall operation of the company. Does not disappear if any segment disappears. Do not allocate common costs to segment |
|
|
What is Segment Margin? |
The best gauge of long-run profitability of a segment. Traceable fixed costs - CM |
|
|
What some hindrances to proper cost assignment? |
1.Commission of some costs in assignment process 2.Assignment to segments of costs are are really common costs of the entire organization. 3. Use of inappropriate methods for allocating costs among segments |
|
|
What are Omission of costs? |
Costs assigned to a segment should include all costs attributable to that segment from the company's entire value chain. The value chain is the whole line from designing to customer service. |
|
|
What are two ways that companies incorrectly handle traceable fixed expenses on segmented income statements? |
1. They may not trace fixed expenses to segments even when it is feasible to do so. 2. they may use inappropriate allocation bases to allocate traceable fixed expenses to segments. |
|
|
Name two reasons why common costs should not be arbitrarily allocated. |
1.this practice may make a profitable business segment appear to be unprofitable. 2. Allocating common fixed costs forces managers to be heal accountable for costs they cannot control |
|
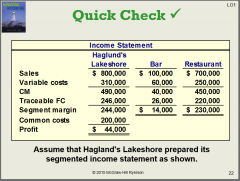
Howmuch of the common fixed cost of $200,000 can be avoided by eliminating thebar?a.None of it.b.Some of it.c.All of it. |
a. None of it Common costs do not go away with one segment going away |
|
|
Supposesquare feet is used as the basis for allocating the common fixed cost of$200,000. How much would be allocated to the bar if the bar occupies 1,000square feet and the restaurant 9,000 square feet?a.$20,000b.$30,000c.$40,000d.$50,000 |
a. $20,000 1000 is 10% of the square footage. 200000*0.10 = $20000 |
|
|
What is a Responsibility centre? |
any part of an organization whose manager has control over and is accountable for cost, profit or investment |
|
|
What are the 3 primary types of Responsibility centre? Explain each. |
Cost centres: segment where manager controls costs, but not revenue or investment funds Profit centres: segment where manager has control of BOTH costs and revenues but not investment funds inventment centres: segment where manager has control over costs,revenue and investments in operating assets. |
|
|
What is Return on investment? (definition and equation) |
metric used to measure performance of departments in relative terms. It calculates departments' return on their average operating assets. ROI = Operating income/ average operating assets operating income = income before interest and taxes average operating assets= cash, accounts receivable, inventory, etc.. |
|
|
What are the benefits of Net Book Value (NBV)? |
consistent with how plant and equipment are reports on balance sheet consistent with calculation of operating income, which includes depreciation as an operating expense |
|
|
What are the benefits of Gross cost? |
Eliminates age of equipment and method of depreciation as factors in RIO calculations Does not discourage replacement of old, worn-out equipement |
|
|
Useful Formulas Write on sheet |
ROI = operating income/ average operating assets Margin = operating income/sales Turnover = sales/ average operating assets ROI = Margin x Turnover |
|
|
What are the 3 ways to increase ROI? |
Increase Sales Reduce Operating Expenses Reduce Operating Assets |
|

|
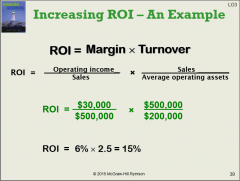
If another wuestion changes values, just sub those values into their proper spot, recalculate |
|
|
What are the criticisms of ROI? |
absense of balance scorecard = not knowing how to increase ROI Managers often inherit many committed costs over which they have no control Manager evaluated on ROI may reject profitable investment opportunities. |
|
|
What is Residual Income? (Definition and equation) |
Definition: net operating income of a department or investment center. Equation: Residual income = operating income - (Average operating assets x minimum required rate of return) |
|

|

|
|
|
RedmondAwnings, a division of Wrap-up Corp., has an operating income of $60,000 andaverage operating assets of $300,000. The required rate of return for thecompany is 15%. What is the division’s ROI?a.25%b. 5%c.15%d.20% |
ROI = operating income/ average operating assets 60,000/300,000 = 0.20 = 20% d. 20% |
|
|
RedmondAwnings, a division of Wrap-up Corp., has an operating income of $60,000 andaverage operating assets of $300,000. The required rate of return for thecompany is 15%. What is the division’s residual income?a.$240,000b.$ 45,000c.$ 15,000d.$ 51,000 |
Residual Income= operating income - (average operating assets * minimum rate f return) 60,000 - (300,000 * 0.15) = 15,000 c.$15,000 |
|
|
True or False: Residual Income cannot compare performance of divisions of different sizes? |
True: If the division are of different sizes it cannot compare their performances (Redundant sentence) |
|
|
What arae some criticisms of Residual Income? |
RI is based on historical accounting data which can lead to inflated amount for residual income in periods of rising prices RI does not indicate what earning should be Calculating RI requires numerous adjustments to GAAP increasing the cost of preparing information RI does not incorporate important leading non-financial indicators |

