![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
159 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Emmetropia |
Eye focus light precisely on the retina |
|
|
Myopia |
(nearsighted) light rays focus in front of the retina |
|
|
Hyperopia |
(farsighted) when light reaches retina the object is not in focus |
|
|
Astigmatism |
Light rays focus on multiple points on the retina |
|
|
Presbyopia |
When the crystalline lens is no longer able to change shape and focus on objects At different distances |
|
|
Compound myopic astigmatism |
Both sphere and cylinder are myopic or minus power(compounds) ex: -2.00 -.75 x180 |
|
|
Compound hyperopic astigmatism |
Adding the sphere and cylinder together results in a hyperopic value, the added value and the original sphere value are both hyperopic. Ex: +2.00 -.75x180 |
|
|
Mixed astigmatism |
When adding the sphere and cylinder together the original sphere power and the added value have different signs. Resulting in one being myopic and the other hyperopic. Ex: +1.00-1.25x180 |
|
|
One meter=___in |
39.37 |
|
|
One cm= ____ in |
.39 in |
|
|
2.5 cm =____in |
1in |
|
|
One mm=____ in |
.4in |
|
|
25 mm=____in |
1in |
|
|
UVC rays |
Absorbed by atmosphere 200nm-290nm |
|
|
UVB |
Source of sunburns 290nm-315nm |
|
|
UVA |
Associated with skin aging. 315nm-389nm |
|
|
Light reflection Grass and soil Sand Water Snow |
10% 15% 25% 80% |
|
|
Index of refraction |
Relationship between the speed of light in air and the speed of light in a medium. |
|
|
Speed of light |
186,000 miles per second |
|
|
Angle of incidence |
Angle of incoming ready of light |
|
|
Angle of reflection |
Angle at which the ray leaves the surface |
|
|
Angle of refraction |
Angle that light rays take as they travel through a medium |
|
|
Where is light directed in a prism |
Base |
|
|
Average blink rate |
7to12 times per minute |
|
|
Medial rectus |
Tword the nose |
|
|
Lateral rectus |
Away from the nose |
|
|
Superior rectus |
Upward |
|
|
Inferior rectus |
Downward |
|
|
Superior oblique |
Top of the eye tword the nose |
|
|
Inferior oblique |
Top of the eye away from the nose |
|
|
Cornea |
Clear, outer portion of the eye |
|
|
Total eye refractive power |
60D |
|
|
Cornea refractive power |
2/3 |
|
|
Crystalline lens refractive power |
1/3 15-16D |
|
|
Iris |
Colored part of eye. Controls light inside eye. Devides the front and back of eye |
|
|
Pupil |
Center of iris. Light ray pass through to get to retina |
|
|
Crystalline lens |
Transparent located behind the iris. |
|
|
Ciliary muscles |
(Zonular fibers) shape the lens to focus light on the retina. |
|
|
How zonular fibers work |
Zonules relax, ciliary body contract, causes crystalline lens to thicken. (Ability to see up close) Zonules contract,ciliary body relax, causes crystalline lens to thin.(ability to see far away) |
|
|
Accommodation |
Ability of crystalline lens to change to allow eye to focus |
|
|
Aphakic |
Without crystalline lens |
|
|
Pseudophakic |
With an intraocular implant |
|
|
OD |
Oculus dexter |
|
|
OS |
Oculus sinister |
|
|
OU |
oculus uterque |
|
|
Visible light |
380nm and 750nm |
|
|
Optical center |
Single point on lens where light may pass without being refracted Plus lens-where bases meet Minus lens-where apex meet |
|
|
Plus lens |
Magnify Against the motion Weaker when closer to the eye Pincushion distortion Converge light Thicker in center Correct hyperopia |
|
|
Minus lens |
Minify Becomes stronger when closer to eye Barrel distortion Diverge light Thinner in center Correct myopia |
|
|
Vertex distance |
Distance glasses are from eye |
|
|
Three types of aberrations |
Spherical Marginal Distortion |
|
|
Spherical aberration |
Parallel light rays enter, peripheral rays focus sooner than center rays |
|
|
Marginal aberrations |
Small bundle of light strikes lens from an angle. Astigmatism is created. |
|
|
Distortion aberration |
As rays approach lens edge, magnification,or minification increases and distorts the image |
|
|
How to measure base curve |
Lens clock |
|
|
Major reference point |
Point where the prism equals the amount prescribed |
|
|
Cancelling prism |
Base in &base out Base up &base up Base down &base down |
|
|
Compounding prism |
Base in &base in Base out & base out Base up & base down |
|
|
Specific gravity |
Density of material |
|
|
ABBE value |
Chromatic aberrations in material. Occur because color components have different wavelengths Higher value=lower amount aberrations |
|
|
Reflectance |
%of light reflected from highly polished surface |
|
|
Transmittance |
Amount of light that passes through a material. In our case measures how much uva |
|
|
Characteristics Cr39 |
Good Optics, half weight of glass, more impact-resistant than glass, can have scratch resistant, easy to tint and UV coat. Good for Rx less than+/-2.00 |
|
|
Characteristics Polycarbonate |
Highly impact-resistant, thinner and lighter than CR 39, can block UV rays, can be scratch resistant, tinting difficult |
|
|
Characteristics Trivex |
Strong, light, impact-resistant, built-in UV protection, can be made without scratch coating, easily tinted and AR coated |
|
|
Characteristics Hi-index |
Index of refraction higher than 1.58 thinner and lighter than plastic, good Optics, built-in UV protection, these curves can be ground thinner reducing lens thickness, easy to tint, requires AR coating |
|
|
Characteristics Glass |
Scratch resistant, heavier and shatter more easily |
|
|
Index of refraction |
Indicates how much the material will bend or refract light |
|
|
ASTM |
American Society for testing materials |
|
|
FTC |
Federal Trade Commission promotes consumer protection and elimination and prevention of anticompetitive business prices |
|
|
Lensometer Rectle (target) |

Prism scale with series of circles used to Center lens |
|
|
Lensometer Prism dial |
Used to measure prism |
|
|
Lensometer Marking device |
Ink blotting mechanism used to Mark Optical centers |
|
|
Lensometer Lens holder |
Spring-loaded arm used to hold lens in place |
|
|
Lensometer Lens table |
Adjustable straight metal shelf Warframe rest to make sure axis reading is correct |
|
|
Lensometer Power Wheel (power drum) |
Large wheel used to find power of Lens marked with powers ranging from -20 to +20 diopters. Black numbers r+ powers and red numbers are negative powers |
|
|
Lensometer elevation level |
Changes angle of lensometer |
|
|
Lensometer Axis wheel |
Large Wheel Marked from 0 degrees to 180 degrees used to find access location |
|
|
What do sphere lines look like on a lensometer |
3 thin close lines |
|
|
What do cylinder lines look like on a lensometer |
Three widely spaced lines |
|
|
How do you determine if the lens is spherical on a lensometer |
If both sets of lines are in sharp focus at the same time |
|
|
How can you tell if a lens is a spherocylindrical lens on the lensometer |
It's both sets of lines are not in focus at the same time |
|
|
How Can you tell if a prismatic lens is centered on the lensometer |
When lines are located on indicator rings at point that matches prescribed prism |
|
|
Anti reflective coating |
Improves light transmission to almost 100%. improve night driving |
|
|
Grey tint |
Do not distort colors. Reduce overall brightness.Do not distort colors.Comfortable to wear for an extended period Of time. Comfortable to wear for an extended period Of time. |
|
|
Brown tint |
Reduce glare.Absorb higher frequency colors.Increase contrast.Good for emerging cataracts,Hazy Days, tasks that require contrast |
|
|
Green tint |
Filter some blue light and glare.Great contrast and good color balance.Good for tennis, golf, driving.Best absorption of infrared wavelengths. |
|
|
Yellow, gold, orange tint |
Reduce blue light.Good for skiing, cycling, shooting. Provide maximum contrast.Good for overcast days and low light driving |
|
|
Red tint |
Increase contrast.Good for fishing in early morning, late evening hours.Good for low lighting conditions |
|
|
Purple and Rose tint |
Good contrast against a green or blue background.Good for hunting water skiing, snow, snowmobilers.Pink good for computer users |
|
|
Melanin tint |
Melanin is additive.Selectively block Violet and high-energy blue light. And to provide high contrast without altering colors.Golfers and low-vision patients |
|
|
Blue tint |
Can be used in most lighting conditions.Good for tennis, golfers, snowmobiling, shooting green targets.Can add more glare |
|
|
Mirror tint |
Reflex mirror reduce light transmission by 20 to 30%.Designed for bright sunlight conditions such as water activities and cycling |
|
|
Round face frame selection |
Use rectangular frame shapes that are whiter than longer.Do not use round frame shapes |
|
|
Oval shape frame selection |
Use frames as wide or a little wider than the broadest part of the face |
|
|
Oblong face frame selection |
Use wider frames, overal, decorative or contrasting temples |
|
|
Triangular face frame selection |
Detailing on the top half of the eyeglasses use frames that are wide at the bottom or rimless styles |
|
|
Diamond shape frame selection |
Use frames with detailing or distinctive browline Use oval or cat eye shapes |
|
|
Square shape frame selection |
Use Narrow, oval shaped frame styles with more width then depth |
|
|
Saddle bridge |
Plastic Bridge, distributes weight evenly across the nose, no room for adjustment |
|
|
Modified saddle bridge |
Plastic Bridge, fixed nose pads, more room for adjustment |
|
|
Keyhole bridge |
Plastic Bridge, looks like a keyhole, weight is supported by side pads |
|
|
Pad bridge |
Used with Metal Frames, nose pads attached by metal arm, frame does not touch the face |
|
|
Metal saddle bridge |
Used with Metal Frames, frame rests directly on the nose |
|
|
Eye wire or rim |
Frame that goes around the lens |
|
|
Boxing system |
An imaginary box containing the lens is used to determine the length and depth of the lens |
|
|
"A" measurement |
Horizontal measurement across the lens part of the boxing system |
|
|
"B" measurement |
Vertical measurement. add 1 millimeter for Groove. part of the boxing system |
|
|
Effective diameter |

Geometric Center geometric Center to longest outermost Edge Times by 2 |
|
|
Darrin or 180 degree line |
Halfway between the top and bottom of the Len |
|
|
Geometric center, box center |
Where A and B measurements meet |
|
|
Frame difference, Len difference |
Difference between the A&B measurements |
|
|
DBC |
Measure from far left side of one lens opening too far left side of other opening |
|
|
End pieces |

Attach temples to the frame front |
|
|
Hinges |

Hold temples to frame front |
|
|
Butt portion |

Closest to the front |
|
|
Bend |

Where the temple goes over the ear |
|
|
Shaft |

Between the butt portion and bend |
|
|
Skull temple |
Most common style |
|
|
Library temples |
Straight with no Bend, great for constant off and on wear |
|
|
Cable style temples |
Wrap around the ear, great for kids and active people to prevent eye glasses from slipping |
|
|
Plastic frame |
Zyl Cost-effective, lightweight colorful easy to adjust, easier to break and can burn it overheated |
|
|
Optyl frame |
Vacuum injected epoxy resin, available in Many Colors, memory capable, cost-effective, hypoallergenic, lightweight |
|
|
Metal frame |
Fitting flexibility, lighter softer appearance |
|
|
MONEL |
Mixture of metals, most widely used, flexible, corrosion resistant |
|
|
Titanium |
Lightweight, durable and strong, corrosion resistant, comes in many colors, not all are hundred percent titanium |
|
|
Beryllium |
Lower-cost, good for high skin acidity or salt water exposure, available in colors, lightweight and strong, easy to adjust |
|
|
Stainless steel |
Lightweight, low toxicity, great strength, hypoallergenic, Iowa of Steel and chromium, most are 10 to 30% chromium, resist corrosion |
|
|
Aluminum |
Lightweight, highly corrosion-resistant, commercial aluminum with silicon and iron is hard and strong |
|
|
Nose pad frontal angle |

Closer together at the top than at the bottom, mirrors the shape of the nose, each pad should be at same height and same distance from eyewire |
|
|
Splay or spread angle |
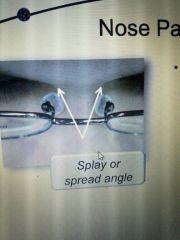
Front edges are closer than back edges. And her mirror slope of the nose.Flat Bridges have wide splays |
|
|
Vertical angle Nose pads |
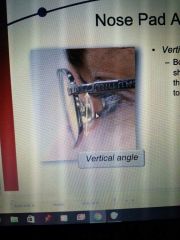
Bottom edges should be closer to the other than top |
|
|
Hexagon wrench |

|
|
|
Angling pliers |
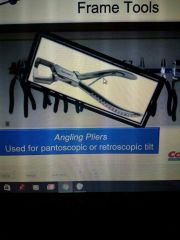
|
|
|
Corneal abrasion |
A break in the corneal epithelium.Can heal very quickly.Symptoms: pain, light sensitivity, excessive tearing |
|
|
Keraticonus |
Progressive, non inflammatory condition.Cornea thins and bulges forward |
|
|
Corneal ulcer |
Loss of epithelium enter may be caused by bacterial, single, viral infection or injury |
|
|
Corneal infiltrate |
Collection of white blood cells that form as a result of an inflammatory condition |
|
|
Neovasvularization |
Cause because cornea lacks oxygen.Cornea swells |
|
|
Conjunctivitis |
Inflammation of the conjunctiva Causes can be bacterial, viral, fungal or allergic |
|
|
Pinguecula |
Yellowish,triangular,thickening of bulbar conjunctiva Do not affect Vision, but can affect fit of contact lenses |
|
|
Pterigium |
Triangular fold of growing membrane Can continue to advance over visual access and distort vision |
|
|
Subconjunctival hemorrhage |
Blood between the conjunctiva and sclera Goes away on its own |
|
|
Ectropion |
Lower lid pulls away from the globe Most common in older adults |
|
|
Entripion |
Upper or lower lid turns in tword eye Not very common |
|
|
Ptosis |
Droopinh of the upper lid |
|
|
Chalazion |
Inflammation of the meibomian or Zeiss gland on eye lid Similar to a stye
|
|
|
Stye (hordeolum) |
Nodules that form on the eyelids as a result of blocked Zeis or meibomian gland |
|
|
Giant papillary conjunctivitis (gpc) |
Most often associated with soft contact lenses. Caused by the mechanical rubbing of palpebral conjunctiva |
|
|
Cataracts |
Condition that occurs when the crystalline lens becomes cloudy |
|
|
Antimetropia |
Patient who is myopic in one eye and hyperopic in other |
|
|
Aniseikonia |
Image seen by one eye is larger than the image seen by the other eye |
|
|
Anisometropia |
When eyes have unequal refractive powers |
|
|
Strabismus |
Occurs when one or both eyes turn in,out,up or down Caused by poor eye muscle control |
|
|
Retinal detachment |
Occular emergency Retina can die and unless there is immediate medical intervention Vision can be lost forever |
|
|
Glaucoma |
Condition in which increased internal pressure of the eye damages the optic nerve |
|
|
Macular degeneration |
Degenerative condition of the macula caused by hardening of the arteries that feed the macula |
|
|
Retinitis pigmentosa |
Progressive, inherited retinal dystrophy affecting the rods, cones or retinal pigment epithelium |
|
|
Aniseikonia |
Image seen in one eye is larger that seen in other |

