![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
innervation of abdoinal wall
|
T7-L1, thoracoabdominal nerves
|
|
|
Lymph drainage
|
above umbilical- anteior axillary
below- inguinal nodes |
|
|
external abdominal oblique
|
bilateral contraction, movement to opposite side
|
|
|
inguinal ligament
|
lower edge of aponeurosis
|
|
|
arcuate line
|
where rectus sheeth ends
|
|
|
upper 3/4th
|
rectus sheeth conmpletes covers rectus abdominal muscles
|
|
|
lower 1/4th
|
aponeorosis is deficient posteriorly
|
|
|
iternal thoarcic artery
|
ends at 6th IC space, becomes musculophrenic and epigastric
|
|
|
falciform
|
sickle shaped
|
|
|
Hesselbachs triangle
|
rectus abdominus, lateral inferfior epigastric vessels, inguinal ligament
|
|
|
conjoint tendon
|
aponeorosis of transverse and interior tendon= fuse on lower 1/4 of rectus sheath, provdies support
|
|
|
superficial inguinal ring in external abdominal aponerousis
|
in external abdominal aponerousis
more medial |
|
|
deep inguinal ring
|
in transversilis fascia, above midpoitn of inguinal lifament, more lateral
|
|
|
direct inguinal hernias
|
pass medially to vessels and perforate through ahsselbacks traingle
|
|
|
indirect hernias
|
pass laterally to vessels and can esacpe through the inguinal canal
follows course of testicular descent |
|
|
why do testes descent into the scrotum?
|
need correct temperautre for production of sperm
|
|
|
gubernaculum
|
guides descent of testes
|
|
|
processes vaginalis
|
future layers of the scrotum
|
|
|
hydrocoele
|
fluid develops in unclosed part of processus vaginalis
|
|
|
incomplete indirect inguinal hernia
|
distal part of PV is closed, but proximal is not, tunica vaginalis not continuous with peritoneal cavity, intestine simply pushes down on closed processus vaginalis
|
|
|
indirect inguinal hernia
|
intestine pushes into unclosed processus vaginalis . herniates inside spermatic cord and into the scrotum
|
|
|
indirect congenital inguinal hernia
|
intestine pushes into unclosed processes vaginalis. herniates inside spermatic cord and is lateral to inferior apigastric vessels. goes into direct canal.
|
|
|
spermatic cord
|
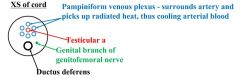
pampin- cools to produce sperm, tesicular artery
|
|
|
Chryptorchid
|
undescended tsticle that remains in the abdominal cavity, most commonly in the inguinal canal, NOT confused with retractile testis which results from very strong cremaster muscle
|
|
|
Ectopic Testes
|
tests lie in abnormal position after passing through inguinal canal: iterstitial (superficial to externatl oblique aponerosis), medial thigh, perneum or contrlateral due to abnormal attachment of gubernaculum
|
|
|
- Visceral peritoneum
|
sensitive only to stretch and pressure- experienced only as dull and generalized pain
|
|
|
- Parietal peritoneum
|
innervated by spinal nerves and pain is over precise dermatome
o Localized pain |
|
|
Greater/lesser sac
|
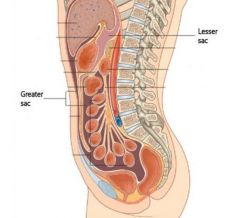
lesser sac- omental bursa, extension of the peritoneal cavity posterior to the stomach
greater sac- rest of peritoneal cavity divided by trasnverse colon/greater omentum |
|
|
compartments and regions
|
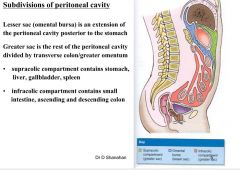
supracolic compartment - stomach , liver, gallbladders, spleen
infracolic- small intestine, ascending and descending colon |
|
|
rectouterine pouch of Douglas
|
between rectum and uterus
|
|
|
vesicouterine pouch
|
bladder and uterus
|
|
|
hepatourinal pouch
|
separates liver from right kidney
directly continuous with right lateral paracolic gutter |
|
|
falciform ligament
|
divides liver anatomically into right and left half, connects liver to anterior abdominal wall
|
|
|
round ligament
|
remnant of umbilical vein. connected to the free end of the falciform ligament and IVC
|
|
|
coronary ligaments
|
peritoneal reflections that hold liver to the inferior portion of diaphragm
|
|
|
triangular ligaments
|
hold liver to diaphragm
|
|
|
median umbilica ligament
|
attaches bladder to anterior abdominal wall
remnant of fetal umbilical arteries |
|
|
lateral umbilical
|
overlie inferior epigastric a and v
|
|
|
greater omentim
|
covers small and large intestines
|
|
|
gastrocolic ligament
|
greater curvature of stomach to hilum of spleen
|
|
|
splenorenal
|
wall of general peritoneal cavity comes into contact with omental bursa between left kidney and spleen, tail of pancreas
|
|
|
lesser omentum
|
extends from liver to lesser curvature of stomach and beginning of duodenum
|
|
|
ligament of treitz
|
fold of peritoneum containg muscle fibers surrounding the duodenojejnual junction and important to locate duodenojejunal junction
connects the 4th part of the duodenum to the diaphragm (suspensory muscle of the duodenum) |
|
|
intraperitoneal
|
elements of gastroinestinal system suspended form abdonimal wall by mesenteries,
|
|
|
retroperitoneal
|
not suspended in abdominal cavity by mesentery, lie bwetween parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall
|
|
|
ectopic pregnancy
|
abdominopelvic cavity-can have abdominopelvic infections and pregnancy that is not implanted in the uterus
|
|
|
where does air go in the peritoneal cavity?
|
usually to highest point , below diaphragm and above the liver!!!
|
|
|
perforation in first part of duodenum
|
effects proper hepatic artery
|
|
|
coeliac trunk
|
lower esophagus to upper 1/2 of duodenum at T12
|
|
|
superior mesenteric
|
midgut, lower 1/2 of duodenum to left colic flexure- at L1
|
|
|
inferior mesenteric artery
|
hindgut(left colic flexure to upper rectum) L3
|

