![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Just after decolorizer is applied acid-fast bacteria will appear ___ and non-acid bacteria will appear ______. |
Fushcia and colorless
|
|
|
After brilliant green is applied as counter stain, acid-fast bacteria will appear _____ while non-acid bacteria appear _____. |
Fuschia and green
|
|
|
Cellular morphology and appearance mycobacterium after the acid-fast stain is ____ |
Fuchsia bacilli |
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus after acid-fast stain is ____ |
Clusters of green cocci |
|
|
E. Coli is Gram ______ (negative/positive) |
negative |
|
|
Most critical step of gram stain is ___ |
Decolorization
|
|
|
If you forgot counter stain at end of stain procedure, gram neg would appear ______ and gram positive would appear _______ |
Colorless purple |
|
|
Cellular morphology and Gram reaction for Staphylococcus aureus |
Gram-positive staphylococci |
|
|
Why is it important crystal violet be contrasting color to safranin |
Difference in color between the two stains allows you to differentiate between gram negative and gram positive cells by observing the color of organism |
|
|
Microscopic morphology of Micrococcus luteus? |
Gram positive tetrads and staphylococci |
|
|
Purpose of allowing bacteria smear to dry when placed on slide |
Drying helps remove excess water to ensure optimal heat fix
|
|
|
Chains of spherically shaped bacteria are called _____. |
streptococci |
|
|
Clusters of spherically shaped bacteria are ____
|
Staphylococci |
|
|
Chains of rod-shaped bacteria are ____
|
Streptobacilli |
|
|
Decolorizing agent in spore stain is ____ |
Water
|
|
|
Name two genera of bacteria that are acid-fast. |
Mycobacterium Nocardia |
|
|
______ bacteria retain carbol fuchsin after acid-alcohol, ______ are decolorized |
Acid-fast non-acid fast |
|
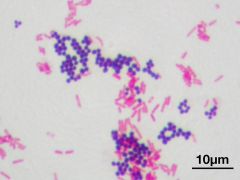
The bacilli in this stin are gram ____ and the cocci are gram ____ |
Gram negative (pink) |
|
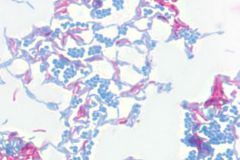
The fushcia cells are acid-fast ____ and the blue-green cells are acid-fast _____. |
Acid-fast positive (pink) Acid-fast negative (blue-green) |
|

These bacteria are acid-fast _____. |
Acid-fast negative (fushcia) |
|
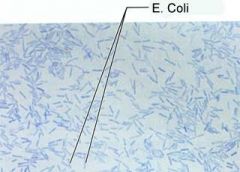
These bacteria are acid-fast _____. |
Acid-fast negative (bluish-green) |
|
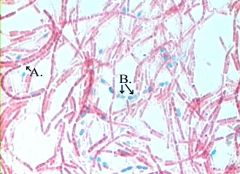
Does this organism have endospores? |
Endospore positive (green endospores) with pink vegetative cells |
|
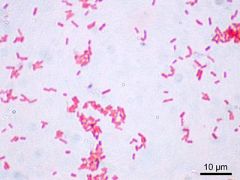
Does this organism have endospores? |
Endospore negative |
|
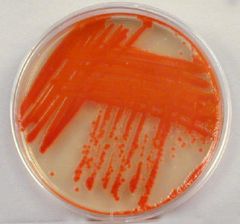
1. The genus of this organism is ____. 2. Describe the colonial morphology. |
1. Serratia (culture media) |
|
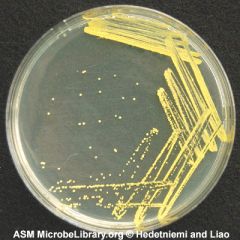
1. The genus of this organism is ____. 2. Describe the colonial morphology. |
1. Micrococcus (culture media) |
|
|
Fomite
|
Object or substance capable of carrying infectious organisms |
|
|
Aseptically |
Performed under sterile conditions
|
|
|
Density terms? |
Opaque, transparent, or translucent
|
|
|
Consistency terms? |
Butyrous, mucoid, dull, dry, or powdery
|
|
|
Texture terms? |
Smooth, rough, wrinkled, glistening, or irredescent
|
|
|
Colony forming unit- CFU |
Viable bacteria yields one colony |
|
|
TFTC means ___ |
Too few to count
|
|
|
TNTC means ___ |
Too numerous to count
|
|
|
Define nosocomial infection |
Infection development favored by a hospital environment
|
|
|
List the Gram stain reagents, time, and purpose |
Crystal violet (primary stain)- 60 sec Gram's iodine (mordant)-60 sec. ethyl alcohol (decolorizer) 10-15 sec safranin (counter stain) 30 sec |
|
|
List the Acid-fast reagents, purpose, and time |
Carbol fuchsin (primary stain) 5 min acid-alcohol (decolorizer) 30 sec brilliant green (counter stain) 2 min |
|
|
List the endospore stain reagents and time |
Malachite green (endospore stain) -steam 5 min safranin (vegetative stain)- 1 min |
|
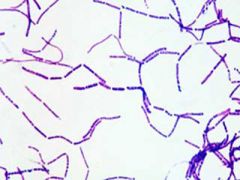
1. Describe the microscopic morphology. 2. Name the organism we have seen in lab that could have been used to make this slide. |
1. Gram positive streptobacilli 2. Bacillus cereus
|
|
|
Mycobacterium is acid–fast ___ (positive/negative) and ____ shaped |
Positive bacillus |
|
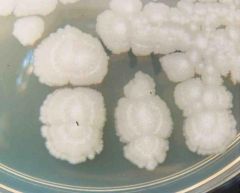
1. The genus of this organism is ____. 2. Describe the colonial morphology. |
1. Bacillus 2. Beige, dry, rough, opaque, large, flat, irregular |

