![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Type of molecule found within a cell used to build protein polymers
|
Amino Acid
|
|
|
A series of biochemical reactions in which large complex molecules are synthesized from smaller precursors
|
Anabolic Pathway
|
|
|
A series of biochemical reactions in which large complex molecules are degraded into smaller, simpler products
|
Catabolic pathway
|
|
|
a long chain monocarboxylic acid that contains an even number of carbon atoms
|
fatty acid
|
|
|
a group of atoms that undergo characteristic reactions when attached to a carbon atom in an organic molecule or a biomolecule
|
functional group
|
|
|
molecules that possess few if any electonegative atoms; do not dissolve in water
|
hydrophobic
|
|
|
any of a group of biomolecules that are soluble in nonpolar solvents and insoluble in water
|
lipid
|
|
|
the sum total of all chemical reactions in an organism
|
metabolism
|
|
|
a macromolecule composed of nucleotides; DNA and RNA are nucleic acids
|
nucleic acid
|
|
|
an amide linkage in an amino acid polymer
|
peptide bond
|
|
|
the process in which single-stranded RNA with a a base sequence complementary to the temple strand of DNA is synthesized
|
Transcription
|
|
|
Protein synthesis; the process by which the genetic message carried by mRNA directs the synthesis of polypeptides with the aid of ribosomes and other cell constitituents
|
translation
|
|
|
Elements needed by living organisms in very low quantities
|
Trace elements
|
|
|
Large organic polymers.
|
Macromolecule
|
|
|
Large molecule consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
|
Polymer
|
|
|
Subunit or building block molecule of a polymer
|
Monomer
|
|
|
Polymerization reactions during which monomers are covalently linked, producing net removal of a water molecule for each covalent linkage
|
Condensation (dehydration) reactions
|
|
|
a chemic reaction that invovles the reaction of a molecule with water; the process by which molecules are broken into their constituents by adding water
|
Hydrolysis reactions
|
|
|
Simple sugar in which C, H and O occur in the ratio of (CH20)n, where n is at least 3
|
Monosaccharides
|
|
|
In this functional group, the terminal carbon forms a double bond with oxygen.
|
Aldehyde
|
|
|
In this functional group, the carbonyl group is within the carbon skeleton
|
Ketone
|
|
|
A double sugar that consists of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage.
|
Disaccharide
|
|
|
Covalent bond formed between two sugar monomers by a condensation reaction
|
Glycosidic linkage
|
|
|
Macromolecules that are polymers of a few hundred or thousand monosaccharides
|
Polysaccharides
|
|
|
Diverse group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water, but will dissolve in nonpolar solvents (e.g. ether, chloroform, benzene). Important groups are fats, phospholipids, waxes and steroids.
|
Lipids
|
|
|
A lipid composed of three fatty acids bonded to one glycerol by ester linkages (triacylglycerol)
|
Neutral fat
|
|
|
Bond formed between a hydroxyl group of glycerol and a carboxyl group of a fatty acid
|
Ester linkage
|
|
|
Compounds with molecular building blocks of glycerol, two fatty acids, a phosphate group and usually an additional small chemical group attached to the phosphate.
|
Phospholipids
|
|
|
a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence
|
polypeptide
|
|
|
Organic compounds which are complex polymers of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
|
Proteins
|
|
|
Organic molecules that store and transmit hereditary information
|
Nucleic acids
|
|
|
Polymer of nucleotides linked together and made of a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
|
Nucleic acid
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base characterized by a six-membered ring made up of carbon and nitrogen atoms
|
Pyrimidine
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base characterized by a five-membered ring fused to a six-membered ring
|
Purine
|
|
|
Pentose sugar found in DNA
|
deoxyribose
|
|
|
Pentose sugar found in RNA
|
ribose
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base + pentose + phosphate.
|
Nucleotide
|
|
|
A polymer of nucleotides joined by phosphodiester linkages between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next.
|
Polynucleotide
|
|
|
The branch of chemistry that specializes in the study of carbon compounds.
|
Organic chemistry
|
|
|
Molecules containing carbon are _________.
|
Organic molecules
|
|
|
Carbon can form ____ covalent bonds with a variety of atoms
|
four
|
|
|
Molecules containing only hydrogen and carbon.
|
Hydrocarbons
|
|
|
_________ are the components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
|
Functional groups
|
|
|
A functional group that consists of a hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn forms a polar covalent bond to carbon.
|
Hydroxyl group
|
|
|
Functional group found in alcohols.
|
Hydroxyl group
|
|
|
Functional group that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to oxygen.
|
Carbonyl group
|
|
|
When a carbonyl is within a carbon chain of a molecule it is a(n) _____
|
Ketone
|
|
|
When a carbonyl is on a terminal carbon of a molecule it is a(n) _____
|
Aldehyde
|
|
|
Functional group that consists of a carbon atom that is both double-bonded to an oxygen and single bonded to the oxygen of a hydroxyl group. Acts as an acid.
|
Carboxyl group
|
|
|
Functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogens and to the carbon skeleton. Acts as a base.
|
Amino group
|
|
|
Functional group that consists of an atom of sulfur bonded to an atom of hydrogen.
|
Sulfhydryl group (Thiol)
|
|
|
Functional group that forms disulfide bridges between two cysteine amino acids.
|
Sulfhydryl group
|
|
|
Functional group which is the dissociated form of phosphoric acid which consists of phosphorus bound to four oxygen atoms (three with single bonds and one with a double bond). Acts as an acid.
|
Phosphate group
|
|
|
Non-polar functional group that is a carbon and surrounding hydrogens.
|
Methyl group
|
|
|
What 6 elements make up 97% of the mass of living organisms?
|
CHONPS
|
|
|
Elements needed by the body in very low quantities are called _______ elements.
|
trace
|
|
|
Nucleotides are joined by ____ between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next.
|
phosphodiester linkages
|
|
|
In a cell, solid material is primarily ___ and the solvent is ____
|
organic
water |
|
|
A functional group in which something replaces the hydroxyl of a carboxyl
|
Acyl
|
|
|
The linkage that connects the phosphates of ATP
|
Phosphoanhydride
|
|
|
The peptide bond joining to amino acids is a ________ linkage
|
Amide
|
|
|
The linkage of two carbon with an oxygen linker
|
Ether
|
|
|
The capacity to do work - to move matter against opposing forces is _____.
|
Energy
|
|
|
Quantitative measure of disorder that is proportional to randomness (designated by the letter S).
|
Entropy
|
|
|
Those reactions that can occur without outside help. (Spontaneous processes/Nonspontaneous processes)
|
Spontaneous processes
|
|
|
Those reactions that can only occur if energy is added to a system. (Spontaneous processes/Nonspontaneous processes)
|
Nonspontaneous processes
|
|
|
Portion of a system's energy available to do work; is the difference between the total energy (enthalpy) and the energy not available for doing work (TS).
|
Free energy (G)
|
|
|
Formula for free energy
|
G = H - TS
|
|
|
Formula for free energy change
|
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
|
|
|
∆G is the symbol for _______.
|
Free energy
|
|
|
In the free energy equation, ∆H is the symbol for _______.
|
Enthalpy (total energy)
|
|
|
In the free energy equation, ∆S is the symbol for _______.
|
Entropy
|
|
|
In the free energy equation, T is the symbol for _______.
|
Temperature in Kelvin
|
|
|
A reaction that proceeds with a net loss of free energy.
|
Exergonic reaction
|
|
|
An ________ (endergonic/exergonic) reaction is one that releases free energy to its surroundings.
|
exergonic
|
|
|
Δ G of an exergonic reaction is _____
|
negative.
|
|
|
Amount of energy that reactant molecules must absorb to start a reaction.
|
Energy of activation
|
|
|
Unstable condition of reactant molecules that have absorbed sufficient free energy to react.
|
Transition state
|
|
|
An energy-requiring reaction that proceeds with a net gain of free energy.
|
Endergonic reaction
|
|
|
An _____ (endergonic/exergonic) reaction is one that requires free energy from its surroundings.
|
endergonic
|
|
|
Δ G of an endergonic reaction is ____
|
positive.
|
|
|
Reaction in which the rates of forward and backward reactions are equal and there is no change in the concentration of products or reactants.
|
Chemical Equilibrium
|
|
|
The Δ G of a reaction at equilibrium is ______
|
Zero
|
|
|
To do work, cells manage energy resources by energy coupling, the use of an ___ (endergonic/exergonic) process to drive an ____ (endergonic/exergonic) one
|
exergonic
endergonic |
|
|
Nucleoside triphosphate with unstable phosphate bonds that the cell hydrolyzes for energy to drive endergonic reactions.
|
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
|
|
|
The bonds between the phosphate groups of ATP’s tail can be broken by ____ reactions
|
hydrolysis
|
|
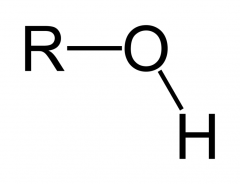
What is this functional group?
Type of molecule? |
Hydroxyl
Alcohol |
|
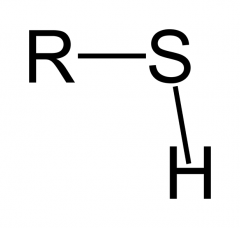
What is this functional group?
Type of molecule? |
Sulfhydryl
Thiol |
|
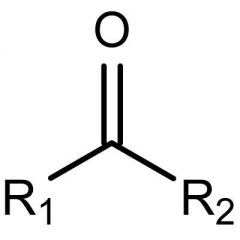
What is this functional group?
Type of molecule? |
Carbonyl
Ketone |
|
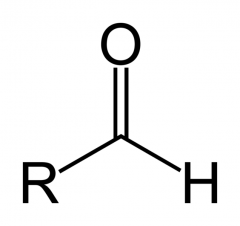
What is this functional group?
Type of molecule? |
carbonyl
aldehyde |
|
|
The four elements that make up most of the total weight of the human body?
|
carbon
oxygen hydrogen nitrogen |
|
|
Difference between organic and inorganic compounds?
|
organic compounds MUST contain carbon.
|
|
|
How is carbon such a special and important compound in living things?
|
it's very versatile.
has 4 outer valence electrons. can combine with many many other elements through covalent bonds, esp. with itself. |
|
|
The four major groups of organic compounds found in living things?
|
carbohydrates
lipids nucleic acids proteins |
|
|
What is simple sugar referred to as?
|
monosaccharides
|
|
|
Why are phospholipids important in the cell?
|
phosphlipids make up cell membranes
|
|
|
What are the four major types of lipids?
|
Fats
waxes phospholipids sterols |
|
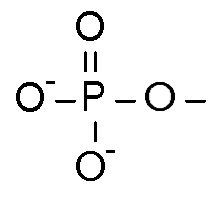
What is this functional group?
Where are these found? |
Phosphate
Nucleotides and phospholipids |
|
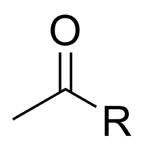
What is this functional group?
|
Acyl
|
|
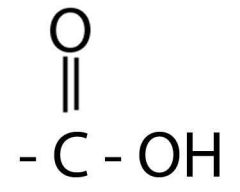
What is this functional group?
Where are these found? |
Carboxyl
Carboxylic acid |
|
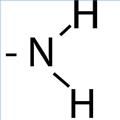
What is this functional group?
Where are these found? |
Amino
Amines |

