![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
132 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
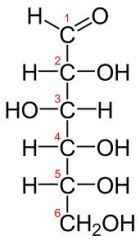
aldehyde or ketone? |
aldehyde
|
|
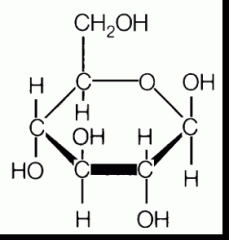
alpha or beta?
|
beta
|
|
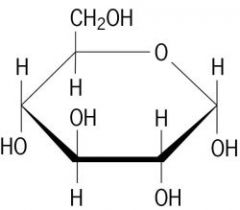
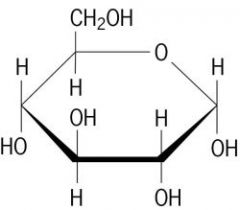
alpha or beta?
|
alpha
|
|
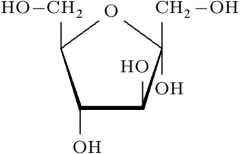
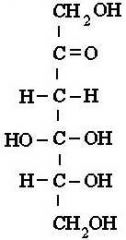
aldehyde or ketone?
|
ketone
|
|
aldehyde or ketone?
|
aldehyde
|
|
aldehyde or ketone?
|
ketone
|
|
|
Large organic polymers.
|
Macromolecule
|
|
|
Large molecule consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
|
Polymer
|
|
|
Subunit or building block molecule of a polymer
|
Monomer
|
|
|
Polymerization reactions during which monomers are covalently linked, producing net removal of a water molecule for each covalent linkage
|
Condensation (dehydration) reactions
|
|
|
A reaction process that breaks covalent bonds between monomers by the addition of water molecules.
|
Hydrolysis
|
|
|
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
|
Fuel and Building Material
|
|
|
Simple sugar in which C, H and O occur in the ratio of (CH20)
|
Monosaccharides
|
|
|
Terminal carbon forms a double bond with oxygen. (aldehyde/ketone)
|
Aldehyde
|
|
|
Carbonyl group is within the carbon skeleton. (aldehyde/ketone)
|
Ketone
|
|
|
six carbon monosaccharides are _________
|
hexose monosaccharides
|
|
|
three carbon monosaccharides are __________.
|
triose monosaccharides
|
|
|
five carbon monosaccharides are ___________.
|
pentose monosaccharides
|
|
|
A double sugar that consists of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage.
|
Disaccharide
|
|
|
Covalent bond formed between two sugar monomers by a condensation reaction
|
Glycosidic linkage
|
|
|
Macromolecules that are polymers of a few hundred or thousand monosaccharides
|
Polysaccharides |
|
|
Amylose and amylopectin are commonly called _______
|
Starch
|
|
|
Unbranched form of starch
|
Amylose
|
|
|
______ is the branched form of starch
|
Amylopectin
|
|
|
______ is the glucose polymer that is a storage polysaccharide in animals.
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
Linear unbranched polymer of D-glucose in Beta 1-4 linkages.
|
Cellulose
|
|
|
Linear unbranched polymer of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) in Beta 1-4 linkages.
|
Chitin
|
|
|
Diverse group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water, but will dissolve in nonpolar solvents
|
Lipids
|
|
|
A lipid composed of three fatty acids bonded to one glycerol by ester linkages (triacylglycerol)
|
Neutral fat
|
|
|
Bond formed between a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group which connects glycerol to fatty acids is called a __________ linkage.
|
Ester linkage
|
|
|
If there are no carbon-carbon double bonds, then the molecule is a _____ fatty acid with a hydrogen at every possible position.
|
Saturated
|
|
|
If there are one or more carbon-carbon double bonds, then the molecule is an _____ fatty acid — formed by the removal of hydrogen atoms from the carbon skeleton.
|
Unsaturated
|
|
|
What are the 3 major functions of fats?
|
1.energy storage. |
|
|
Compounds with molecular building blocks of glycerol, two fatty acids, a phosphate group and usually an additional small chemical group attached to the phosphate.
|
Phospholipids
|
|
|
Lipids which have four fused carbon rings with various functional groups attached.
|
Steroids
|
|
|
a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence
|
polypeptide |
|
|
Functioning organic compounds which are complex polymers of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
|
Proteins |
|
|
What are the functions of proteins?
|
1.Enzymes |
|
|
Building block molecule of a protein; most consist of an asymmetric carbon, termed the alpha carbon, which is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a variable R group (or side chain).
|
Amino acid
|
|
|
Polymer of many amino acids joined by peptide bonds.
|
Polypeptide chain |
|
|
Three-dimensional shape of a protein.
|
Protein conformation
|
|
|
Covalent bond formed by a condensation (dehydration) reaction that links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next.
|
Peptide bond
|
|
|
Functional conformation of a protein found under normal biological conditions.
|
native conformation
|
|
|
a protein's unique sequence of amino acids.
|
Primary protein structure
|
|
|
Regular, repeated folding of a protein's polypeptide backbone
|
Secondary protein structure
|
|
|
Secondary structure of a polypeptide that is a helical coil
|
Alpha helix
|
|
|
Secondary protein structure is stabilized by _____
|
hydrogen bonding along the backbone
|
|
|
Secondary protein structure which is a sheet of antiparallel chains folded into accordion pleats.
|
Beta pleated sheet
|
|
|
Irregular contortions of a protein due to bonding between side chains (R groups)
|
Tertiary structure
|
|
|
What bonds and forces stabilize tertiary protein structure?
|
1)hydrogen bonds among polar and/or charged areas 2)ionic bonds between charged R groups 3)hydrophobic interactions among hydrophobic R groups |
|
|
Structure that results from the interaction among several polypeptides (subunits) in a single protein.
|
Quaternary structure |
|
|
A process that alters a protein's native conformation and biological activity
|
Denaturation |
|
|
____________ store and transmit hereditary information
|
Nucleic acids |
|
|
_____________ determines a protein's unique sequence of amino acids.
|
DNA
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base characterized by a six-membered ring made up of carbon and nitrogen atoms
|
Pyrimidine
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base characterized by a five-membered ring fused to a six-membered ring
|
Purine
|
|
|
Pentose sugar found in DNA
|
deoxyribose
|
|
|
Pentose sugar found in RNA
|
ribose
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base + pentose sugar + phosphate. |
nucleotide |
|
|
A polymer of nucleotides joined by phosphodiester linkages between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next.
|
Polynucleotide |
|
|
Nucleotides are joined together by ___________ linkages between the sugar and the phosphate. |
phosphodiester |
|
|
Linear unbranched polymer of D-glucose in alpha 1-4 linkages.
|
Amylose
|
|
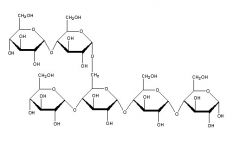
Which type of starch is this? |
amylopectin
|
|
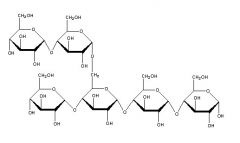
The branches formed in this polysaccharide are between carbon ____ of one glucose and carbon _____ of another glucose. These connections are _______ (alpha/beta). |
one |
|
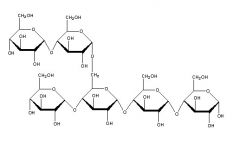
If the polysaccharide pictured above is from animals and is highly branched, it would be called ____________ |
glycogen |
|
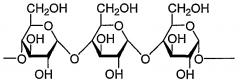
A polymer of glucose in this arrangement is called____________ |
amylose |
|
The linkages between the glucose monomers are ________ (alpha/beta). |
alpha
|
|
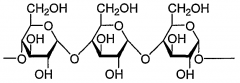
The linkages between the glucose monomers are ________ (alpha/beta). |
Beta
|
|
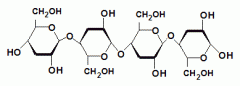
A polymer of glucose in this arrangement is called___________ |
Cellulose |
|
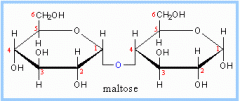
This is an example of a ___________
|
disaccharide
|
|
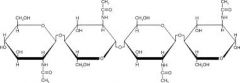
A polymer in this arrangement is called______. It is composed of _______. The monomers and are connected ____ (alpha/beta). |
Chitin |
|
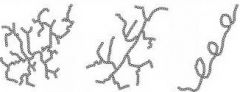
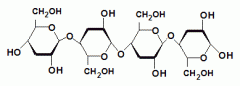
Name the polysaccharides depicted in the drawings.
|
Left to Right |
|
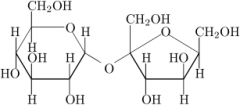
This is an example of a___________. The linkage between the monosaccharides is________(alpha/beta). |
disaccharide |
|
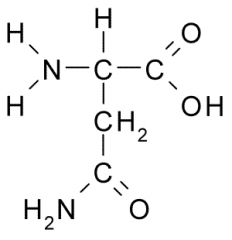
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
a. polar |
|
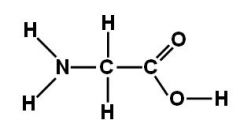
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
b. non-polar
|
|
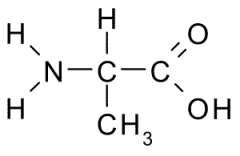
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
b. non-polar
|
|
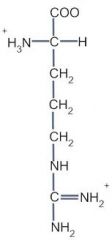
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
d. basic
|
|
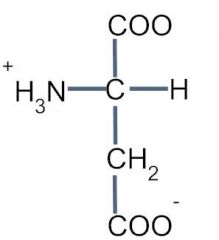
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
c. acidic
|
|
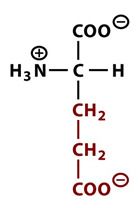
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
c. acidic
|
|
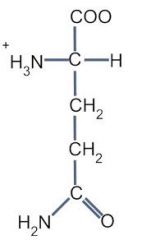
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
a. polar
|
|
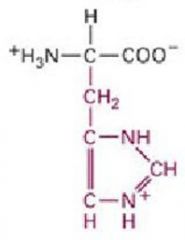
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
d. basic
|
|
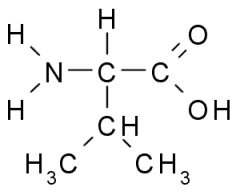
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
b. non-polar
|
|
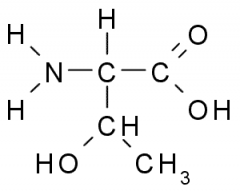
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
a. polar
|
|
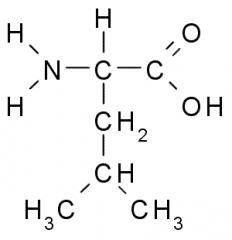
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
b. non-polar
|
|
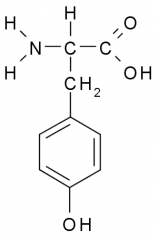
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
a. polar
|
|
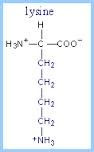
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
d. basic
|
|
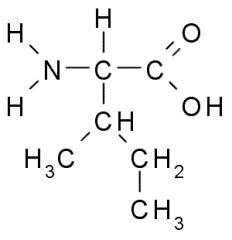
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
b. non-polar
|
|
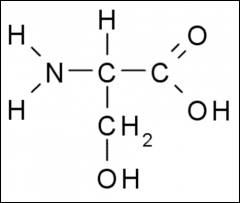
This amino acid is
a. polar b. non-polar c. acidic d. basic |
a. polar
|
|
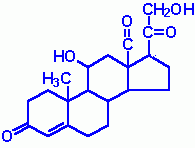
What type of molecule is this?
|
Steroid
|
|
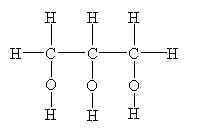
What is this molecule?
|
glycerol
|
|
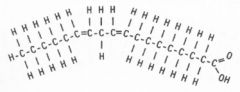
What type of molecule is this?
|
unsaturated Fatty acid
|
|
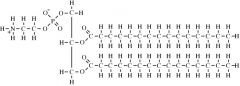
What type of molecule is this?
|
phospholipid
|
|
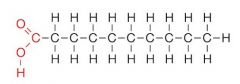
What type of molecule is this?
|
saturated fatty acid
|
|
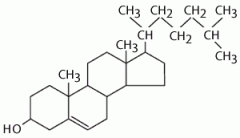
What type of molecule is this?
|
steroid
|
|
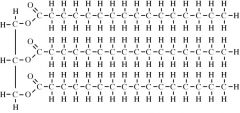
What type of molecule is this?
|
Fat (Triglyceride)
|
|
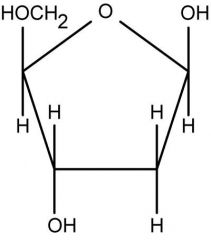
deoxyribose or ribose?
|
deoxyribose
|
|
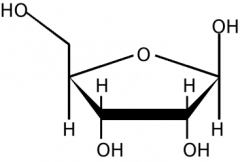
deoxyribose or ribose? |
ribose
|
|
|
The primary function of DNA is ___ |
Stores genetic information |
|
|
The primary function of RNA is ____ |
Protein synthesis |
|
|
Which nitrogenous base is found in DNA but not RNA? |
Thymine |
|
|
Which nitrogenous base is found in RNA but not DNA? |
Uracil |
|
|
________ is the process of making new DNA using a DNA template |
Replication |
|
|
___ is the process of making mRNA from a DNA template |
Transcription |
|
|
___ is the process of making of protein using the information from mRNA |
Translation |
|
|
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a unit of inheritance called a _____
|
Gene
|
|
|
Genes are made of ____, a nucleic acid made of monomers called ________ |
DNA nucleotide |
|
|
What are two types of nucleic acid? |
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Ribonucleic acid (RNA) |
|
|
Protein synthesis occurs on _____ |
Ribosomes
|
|
|
A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides called a _____ |
polynucleotide |
|
|
Polymer of nucleotides (polynucleotide) linked together and made of a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group is a ____ |
Nucleic acid
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base + pentose + phosphate.
|
Nucleotide
|
|
|
___ is a nitrogenous base characterized by a six-membered ring made up of carbon and nitrogen atoms
|
Pyrimidine
|
|
|
Name the three pyrimidine bases. |
C= cytosine U= uracil T= thymine |
|
|
____ is a nitrogenous base characterized by a five-membered ring fused to a six-membered ring
|
Purine
|
|
|
Name the purine bases. |
A= adenine G= guanine |
|
|
Name the pentose sugar found in DNA.
|
deoxyribose
|
|
|
Name the pentose sugar found in RNA. |
Ribose
|
|
|
A polymers of nucleotides are joined by _____ linkages |
phosphodiester
|
|
|
Phosphodiester linkages are between the ___ of one nucleotide and the ____ of the next. |
phosphate
pentose sugar |
|
|
_____ reactions between the OH group on the 3′ carbon of one nucleotide and OH group on the phosphate on the 5′ carbon on the next form the phosphodiester linkage. |
Dehydration (condensation)
|
|
|
Phosphodiester linkages create a ____ of sugar-phosphate units with nitrogenous bases as appendages |
backbone
|
|
|
DNA molecules have two polynucleotides spiraling around an imaginary axis, forming _____ |
double helix
|
|
|
In the DNA double helix, the two backbones run in opposite 5′→ 3′ directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as _____
|
antiparallel
|
|
|
Name the nitrogenous bases in DNA as they pair up and form hydrogen bonds. |
adenine (A) always with thymine (T)
guanine (G) always with cytosine (C) |
|
|
A=T and C=G this is called _____base pairing |
complementary |
|
|
RNA molecules usually exist as _____ polypeptide chains
|
single
|
|
|
In RNA, thymine is replaced by ____ so A and ___ pair |
Uracil U |
|
|
nucleotide |
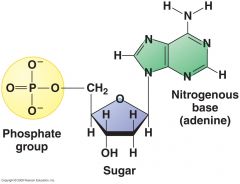
This monomer is called a ____ |
|
|
DNA. Look at the sugar. It is deoxyribose. |
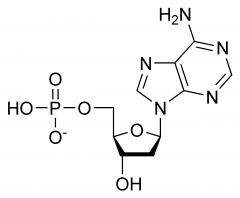
Would this nucleotide be found in DNA or RNA? |
|
|
RNA. Look at the sugar. It is ribose. |
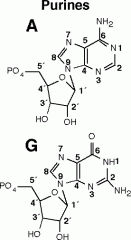
Would these nucleotides be found in DNA or RNA? |
|
|
purine |
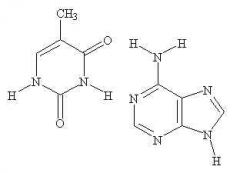
The nitrogenous base on the right is a ____ base |
|
|
pyrimidine |
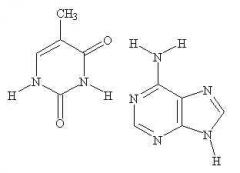
The nitrogenous base on the left is a ____ base |

