![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four main mechanisms of antibiotic resistance? |
Inactivation Altered target/overproduction of target Reduced accumulation (decreased uptake/increased efflux) Bypassing of antibiotic sensitive process |
|
|
Define intrinsic resistance |
Inherent features of the bacterial species, usually expressed by chromosomal genes |
|
|
Define acquired resistance |
Resistant features caused by mutations in chromosomal genes, or acquisitions of plasmids/transposons |
|
|
Define plasmid |
Extra-chromosomal genetic elements that replicate independently of the chromosome |
|
|
Define transposon |
Mobile genetic elements capable of transferring themselves from one DNA molecule to another Not capable of independent replication Recognition seq. at end of transposon for transposases |
|
|
Describe the contribution of plasmids to antibiotic resistance |
Transferred from cell-cell by conjugation Carry antibiotic resistant genes Plasmid may be lost in absence of antibiotic |
|
|
Which plasmids (small/large) are conjugative? |
Large plasmids are conjugative |
|
|
Describe the contribution of transposons to antibiotic resistance |
Central region of transposon often carries antibiotic resistance genes Can transpose into plasmids and spread |
|
|
Describe the range of resistance exchange |
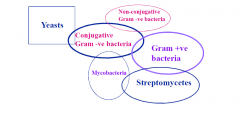
Not every organism can pass resistance directly |
|
|
Describe resistance to Sulphonamides - Chromosomal encoded |
Hyperproduction of PABA Mutation in DHPS DHPS lowers affinity for sulphonamides |
|
|
Describe resistance to Sulphonamides - Plasmid encoded |
Duplication of DHPS enzyme Binds Sulphonamides 10000x less effectively |
|
|
Describe resistance to Quinolones |
Chromosomal encoded only gyrA mutations confer Nalidixic acid resistance N-terminal mutations in DNA gyrase reduce affinity of binding gyrB mutations confer Nalidix acid + Ciprofloxacin resistance aa substitutions reduce affinity of binding |
|
|
Describe resistance to Aminoglycosides |
Plasmid/transposon encoded Enzymatic modification of the antibiotic, decreasing uptake |
|
|
What are the three classes of enzymes that confer resistance to Aminoglycosides? |
Acetyltransferases (AAC) Adenyltransferases (AAD) Phosphotransferases (APH) |
|
|
Describe resistance to Tetracycline |
Plasmid/transposon encoded Membrane proteins mediating energy-dependent efflux |
|
|
Describe resistance to Vancomycin |
Inducible/Transposon encoded Vancomycin binds to D-Ala-D-Ala of murein precursors Resistant strains synthesise D-Ala-D-Lac |
|
|
Describe resistance to Beta-Lactams |
Reductions in permeability (altered porins) Alteration of target (PBP) Enzymatic inactivation (beta-lactamse) |
|
|
What strategies are available for counteracting resistance? |
Development of new antibiotics Enzyme inhibitors Limiting antibiotic use Reduction in preventable HAIs Education |

