![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the anatomy of the urinary tract? |
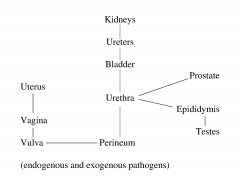
|
|
|
What are risk factors for UTIs? |
Pregnancy Age Females Indwelling catheters |
|
|
Describe asymptomatic bacteriuria |
No adverse outcomes on follow up More common in the elderly/catheterised |
|
|
Describe the ascending route of pathogenesis |
Bacteria ascend through urinary tract via: Intestinal Flora - Selection of uropathogenic strains Vaginal/Peri-urethral Colonisation - Diarrhoea, oestrogen deficiency, spermicides, antibiotics Urodynamics - Poor flow/structure Ascent - Motile flagellae, adherence |
|
|
Describe the haematogenous route of pathogenesis |
Infection of UT through kidneys |
|
|
What bacterial factors can make UTIs more likely? |
Type 1 Fimbriae - Bind to mannose containing epithelial receptors P- Fimbriae - Bind to Gal-Gal receptors on surface of epithelial cells |
|
|
What is Tamm Horsfall protein? |
A mannose containing protein that binds and allows for the flushing of bacteria |
|
|
Why is urine anti-bacterial? |
Urea is cidal/static pH is v. low (hippuric acid) Flow pushes bacteria out |
|
|
Define secretor status |
Some people secrete blood group antigens in their saliva, semun, vaginal secretions etc. Can trick bacteria |
|
|
What are the most common pathogens causing UTIs? |
Escherichia coli S. saprophyticus |
|
|
What are less common pathogens causing UTIs? |
Proteus Pseudomonas Klebsiella Enterobacter Enterococcus S. aureus |
|
|
Define Cystitis |
An infection of the lower urinary tract (bladder) |
|
|
Define Pyelonephritis |
An infection of the upper urinary tract (kidneys) |
|
|
Describe the symptoms of Cystitis |
Dysuria, frequency, urgency Suprapubic pain/tenderness Haematuria Fever Cloudy, smelly urine |
|
|
Describe the symptoms of Pyelonephritis |
Loin pain/tenderness Fever Nausea/vomiting +/- lower tract symptoms |
|
|
What is a occasional presentation of UTIs in children <2? |
Failure to thrive due to recurrent infections |
|
|
What is an occasional presentation of UTIs in the elderly? |
Increased confusion 'Off legs' |
|
|
What is UTI diagnosis based on? |
History/Examination Urinalysis (mid-stream urine) |
|
|
What are positive indicators in urine dipstick tests? |
Nitrite - Formed by action of bacterial nitrate reductase in enterobacteriae (enterococci do not possess nitrate reductase) Leucocyte Esterase - Chemical conversion of an ester |
|
|
What can give false negatives in urine dipstick tests? |
Presence of blood Nitrofurantoin, Rifampicin Bilirubin Ascorbic acid |
|
|
What can give false positives in urine dipstick tests? |
Co-amoxiclav |
|
|
What are M/C signs for UTIs? |
Pyuria >100 leukocytes/ml Culture >10^5 organisms/ml |
|
|
What is the management of asymptomatic UTIs? |
If culture is positive repeat and watch for development of symptoms IF PREGNANT NEEDS TREATING |
|
|
What is the management of symptomatic UTIs? |
Empirical treatment |
|
|
Describe non-specific therapy for UTIs? |
Fluid re-hydration Lowering urinary pH Analgesia not recommended |
|
|
What is a compromising factor in antimicrobial chemotherapy for UTIs? |
Ability to reach high concentrations in urine modified by renal failure |
|
|
What two antibiotics are most commonly prescribed in UTIs? |
Trimethoprim Nitrofurantoin |
|
|
What i.v. antibiotics are useful in treating UTIs? |
i.v Tazocin i.v. Gentamicin |
|
|
What is the time course of treatment? |
Cystitis - 3 days (10-14 in young men) Pyelonephritis - 10-14 days |
|
|
What are the four possible outcomes of treatment? |
Cure (-ve culture 1-2wks post treatment) Persistence (bacteruria after 48h) Relapse (within 1-2wks, same organism) Reinfection (diff. bacterium) |
|
|
What are the main presentations of STIs? |
Genital ulcers Genital discharge Suprapubic pain Other lesions |
|
|
What is the presentation of Herpes Simplex 2? |
Painful ulcers with local lymphadenopathy Recurrent |
|
|
What is the management of HS2? |
Confirm diagnosis with PCR Treat with aciclovir (5x daily) |
|
|
What is the pathogenic organism that causes Syphillis? |
Treponema Pallidum |
|
|
What are the four categories of Syphilis? |
Primary Latency Secondary Tertiary |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of primary syphilis |
Chancre, non-painful, heals spontaneously, local lymphadenopathy |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of secondary sphyilis |
Many different presentations: Macular, coppery rash (palms + soles) Core generalised lymphadenopathy Condylomata lata Can become latent |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of tertiary spyhillis |
Neurospyhillis Infection of the aortic arch |
|
|
How is Syphilis diagnosed? |
Dark ground microscopy Serology (EIA, VDRL, TPPA) |
|
|
What is the treatment for Syphilis? - Early (primary, secondary, early latent) |
Benzathine penicillin G (2.4 mill units, single dose) Procaine penicllin (2.4 mill units + probenicid for 14 days) Doxycycline (100mg b.d. for 15 days) |
|
|
What is the treatment for Syphilis? - Tertiary/Late latent |
Benzathine penicillin G (2.4 mill units, 3x wk) Doxycycline (100mg b.d. for 28 days) Monitor serological response |
|
|
What is Chancroid? |
An STI characterised by painful sores on the genitalia |
|
|
What organism causes Chancroid? |
Haemophilus ducreyi |
|
|
How is the Chancroid ulcer different from the Syphilitic ulcer? |
Base is more necrotic with exudate Usually single lesions |
|
|
How is Chancroid diagnosed? |
Gram-ve organisms on swab PCR |
|
|
What is the treatment for Chancroid? |
Azithromycin/Ceftriaxone (single dose) |
|
|
What are possible causes of genital ulcers, other than Chancroid or Syphilis? |
Granuloma inguinale (Klebsiella granulomatis) Lymphogranuloma venereum (Chlamydia trachomatis) |
|
|
Define Urtheritis |
Inflammation of the urethra characterised by urethral discharge and dysuria |
|
|
What tests should be done upon seeing Urethritis? |
Gram stain (Gram-ve diplococci) M/C Urinary NAAT testing |
|
|
What pathogen most commonly causes Urethritis? |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
|
|
What are the non-gonococcal causes of Urethritis? |
C. trachomatis U. urealyticum T. vaginalis M. genitalium HSV |
|
|
What are the widespread complications of gonorrhoea? |
Conjunctivitis Septic arthritis Pharyngeal infection Peri-hepatitis |
|
|
What is the treatment for Gonorrhoea? |
Ceftriaxone (125mg i.m.) Azithromycin (2g o.d.) Quinolones |
|
|
To what antibiotic class is Gonorrhoea almost completely resistant? |
Beta-lactams (penicllins etc.) |
|
|
What is the treatment for NGU? |
Ceftriaxone Azithromycin Doxycycline |
|
|
What is the causative organism of Genital Warts? |
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) |
|
|
How do genital warts present? |
Usually asymptomatic Diffuse range of size/shape |
|
|
What are large/cauliflower like genital warts called? |
Condylomata acuminata |
|
|
What is the treatment for genital warts? |
Scraping, cryotherapy, keratolytics Podophyllin Imiquimod |

