![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
128 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The urinary system consists of 2 kidneys ___ ureters, and ___ urinary bladder, and one urethra.
|
2, 1
|
|
|
The kidneys lie at the posterior abdominal wall at T-- to L___
|
T12 to L3
|
|
|
The lateral surface of the kidney is ____ and the medial surface Is _____. The slit is the ____ with nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics.
|
convex, concave
hilum |
|
|
Kidney has 3 layers of protective connective tissue: 1. renal fascia - ____ most covering deep to parietal peritoneum. 2 Andipose Capsule or Perirenal Fat Capsule- a layer of andipose tissue for ______. 3The renal capsule of fibrous tissue . These layers: 1, 2, and 3 are outter to ____ with renal capsule most innner.
|
outter
cushioning inner |
|
|
Kidney functions include: regulation of blood volume and ______, regulation of osmoraity of body fluids. Osmolarity is measure of molar concentration of particles.
|
Pressure
|
|
|
The kidney is the size of a bar of ___ and retroperitoneal.
|
soap
|
|
|
The outer 1cm of the kidney is the ______
|
cortex
|
|
|
The outer part of the kidney lobe contains the renal cortex, renal capsule, and _____
|
nephron
|
|
|
The renal medulla is the _____ part of the kidney lobe.
|
middle
|
|
|
The minor calyx is in the ____ papilla.
|
renal
|
|
|
Functions of the kidney: secretes _____ which activates _______ which activates aldosterone. Aldosterone controls BP by sodium retention. Raises BP.
|
resin
angiotensin II |
|
|
The medial cavity occupied by blood and lymphatic vessels, urine collecting structures, and _____ tissue is called the renal ____
|
andipose
sinus |
|
|
Extensions of the cortex called renal columns project toward the sinus and divide the medulla into 6 to 10 _____ pyramids.
|
renal
|
|
|
Each renal pyramid is shaped like a ____ or conical. The broad base faces the ____. The blunt point facing the sinus or the lower part of the renal pyramid is the renal ____
|
cone
cortex papilla |
|
|
Kidney functions: filters blood plasma, eliminates waste, and returns useful substances to the _____
|
blood
|
|
|
Kidney functions: the kidney secretes ______ for RBC formation.
|
ethrropoietin
|
|
|
Kidney functions: regulates the ___ / ___ balance.
|
acid/base
|
|
|
The papilla of each renal pyramid is nestled in a cup called a minor calyx which collects _____. Two or three minor calyxes converge to form a ____ calyx.
|
urine
major |
|
|
Functions of the kidney: deotxifies free radicals and _____
|
drugs
|
|
|
Functions of the kidney: gluconeogenesis or the formation of _____ from other sources.
|
glucose
|
|
|
Functions of the urinary system: Urine formation which includes: glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular ______.
|
secretion
|
|
|
Functions of the urinary system: urine and renal function and tests and Urine _____ and eliminaiton.
|
storage
|
|
|
There are 3 openings at the renal pelvis: the renal artery, a branch of the _____ ____, the renal vein which drans the blood and transports to the inferior _____ _____and the ureter which transports urine from kidney to urinary bladder.
|
abdominal aorta
IVC |
|
|
The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids which contain the renal _____, minor ____, and ____ calyx, and renal columns.
|
papillae,
calyx, major |
|
|
The nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the ____ and it is located in the renal _____
|
kidney
cortex |
|
|
The collecting duct is not a part of the ______
|
nephron
|
|
|
Excretion is separation from body fluids and ++++++ them.
|
eliminating
|
|
|
Excretion In the respiratory system, ____ is excreted.
|
CO2
|
|
|
Excretion In the integumentary system, water, salts, _____ acid, and urea are eliminated.
|
lactic
|
|
|
Excretion: In the digestive system: water, salts, CO2, ____ bile pigments, and cholesterol are eliminated
|
lipids
|
|
|
Excretion: In the urinary system, many metabolic wastes, toxins, drugs, ____, salts, H+, and water.
|
hormones
|
|
|
_____ wastes are the main waste products.
|
nitrogenous
|
|
|
Nitrogenous waste products include: urea, proteins or amino acids with NH2 removed which forms ammonia and the liver converts to ____
|
urea
|
|
|
Nitrogenous wastes: uric acid comes from nucleic acid metabolism. Gout comes from too much _____ ____
|
uric acid
|
|
|
Nitrogenous Wastes:
Creatinine is created by _____ phosphate catabolism. |
creatine
|
|
|
Nitrogenous Wastes:
Renal Failure: Azotemia Increased BUN or Increased ______ wastes in the blood. Uremia comes from the toxic wastes that accumulate. |
nitrogenous
|
|
|
Angiotensin II is changed from Angiotensin I by angiotensin converting _____ secreted by the lung. Renin, which comes from the ____, activates Angiotensin I.
|
enzyme
|
|
|
Angiotensin II and Aldosterone increase _____ ____
|
blood pressure
|
|
|
Agiotensin II causes constriction of the ____ arteriole. Angiotensin II also causes increase in glomerular filtration and ____ pressure.
|
efferent
blood |
|
|
Angiotensin II also reduces resistance to tubular _______
|
reabsorption
|
|
|
Angiotensin II reduces urine volume but ______ is high.
|
concentration
|
|
|
The kidney renal fascia binds it to ______ wall.
|
abodimnal
|
|
|
The PCT or promimal convoluted tubule is the longest most coiled simple ____ with brush border.
|
cuboidal
|
|
|
The Neprhon loop is u shaped with _____ and descending loops.
|
ascending
|
|
|
Renal Tubule: the thick part is simple cuboidal and intial part of _____ limb and part or all of ascending limb. Active transport of _____
|
salts
|
|
|
The thin segment is simple sqaumous and very water _____
|
permeable
|
|
|
The collecting duct is not a part of the _____, but several DCT's join.
|
nephron
|
|
|
The renal medulla includes the renal pyramids and the space between the pyramids is the renal ______
|
columns
|
|
|
Path of Blood thru the kidney
Renal Artery: Interlobar arteries first up renal columns between lobes. Next, ____ arteries over pyramids. Next, interlobular arteries up into the cortex. Next, _____ arterioles. Next, glomerulus, a cluster of capillaries. Next, ____ arterioles near medulla and vasa recta. Next peritubular capillaries. Next interlobular veins to arcuate veins to interlobar veins to renal vein. |
arcuate
afferent efferent |
|
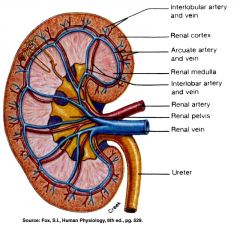
what arteries are up in the renal columns between the lobes?
|
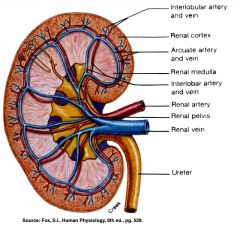
The Interlobar Arteries
|
|
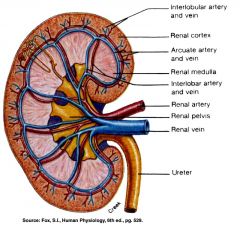
What arteries are over the pyramids but not interlobar?
|
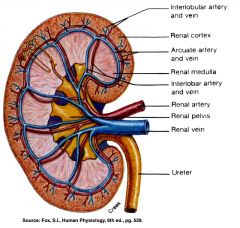
The arcuate arteries
|
|
|
The main function of the loop of Henle is to maintain osmolarity Na and _____ balance.
|
water
|
|
|
The renal medulla includes the renal pyramids, renal papillae, minor calyx, major calyx, and _____ ______
|
renal columns
|
|
|
The renal corpuscle includes the glomerulus and _____ capsule.
|
bowman's
|
|
|
The function of the PCT is _____
|
reabsorption
|
|
|
Tubular rebsorption is the process of reclaiming water and solutes from the _____ fluid and returning them to the _____. PCT functions in reabsorption.
|
tubular
blood |
|
|
ADH and And Aldosterone are hormones that regulate the ____
|
DCT
|
|
|
A drop in BP induces aldosterone secretion.Aldosterone also increases when Na falls or K rises. It stimulates the kidney to secrete _____. Renin produces angiotension I which angiotensin II converting enzyme converts to angiotensin II
|
renin
|
|
|
The filtration Membrane
The fenestrated endothelium or 70-90 mm pores exclude _____ cells. |
blood
|
|
|
The filtration Membrane
Basement Membrane: Made of proeoglycan gel of _____charge that excludes molecules > than 8mm |
negative
|
|
|
The Glomerular Filtration Rate
Filtrate formed per minute GFR= NFP X Kf= 125ml/min or 180L/day for ____. For females, 105ml/min or 150L/day. The filtration coefficient kf depends on permeability and surface area of the ______ barrier. |
males
filtration |
|
|
Glomerular Filtration Rate or GFR
99% of the filtrate is reabsorbed and 1to 2 liters of urine _____ |
excreted.
|
|
|
Effects of GFR abnormalities
Increased GFR, urine output increases which lead to dehydration or ______ depletion. |
electrolyte
|
|
|
Effects of GFR abnormalities
Decreased GFR leads to wastes reabsorbed which makes ______ possible |
azotemia
|
|
|
GFR is controlled by adjusting glomerular blood pressure thru autoregulation, _____ control, and hormonal mechanism: renin and angiotensin.
|
sympathetic
|
|
|
Renal Autoregulation of GFR
Increased BP constricts afferent arteriole which dilates efferent _____ |
arteriole
|
|
|
Renal Autoregulation of GFR
Decreased BP leads to dilate afferent arteriole which ______ efferent arteriole. |
constricts
|
|
|
Renal Autoregulation of GFR
Increased BP constricts afferent arteriole which ______efferent arteriole |
dilates
|
|
|
Renal Autoregulation of GFR Stable for BP range of 80 to 170 mm Hg which is systolic. Cannot _____ for extreme BP
|
compensate
|
|
|
Negative Feedback control of GFR
High GFR leads to rapid flow of ____ in renal tubules, which is sensed by macula densa receptors which cause an unidentified _____ secretion which leads to _____ constriction of the afferent arterioles which reduces GFR |
filtrate
paracrine constriction |
|
|
Sympathetic Control of GFR
Strenuous exercise or acute condtions like circulatory shock stimulate afferent arterioles to ______ |
constrict
|
|
|
Sympathetic Control of GFR
Decreased GFR and ____production redirect blood flow to heart, brain, and skeletal muscles in exercise. |
urine
|
|
|
Hormonal Control of GFR
A drop in BP signals the kidney to produce Renin which produces Angiotensin I in the ____ |
liver
|
|
|
Hormonal Control of GFR
Angiotensin I and angiotensin-converting _____ produces Angiotensin II, which produces______ of the efferent arterioles elevates blood pressure. |
enzyme
vasocontriction |
|
|
Hormonal Control of GFR
Alodosterone is secreted from the andrenal cortex. Aldosterone increases the reabsorption of Na and water. Increases Blood vol and _____ |
pressure
|
|
|
Effects of Angiotensin II- Causes _____ of the efferent arteriole, which increases glomerular blood _____ and filtration and reduces blood pressure in the ______ capillary. Reduced BP in the peritubular capillary reduces resistance to tubular _____ . As tubular reabsorption increases, urine volume is less but concentration is high.
|
constriction
pressure peritubular reabsorption |
|
|
The kidneys collaborate with the lungs to regulate _____and acid-base balance of the body fluids.
|
pCO2
|
|
|
The kidneys regulate blood volume and pressure by eliminating or conserving ____ as necessary.
|
water
|
|
|
The kidneys carry out the final step in synthesizing the hormone calcitrol and thereby contribute calcium ______
|
homeostasis
|
|
|
An elevated BUN, or blood area nitrogen is called _______and may indicate renal insufficiency. May progress to uremia.
|
azotemia
|
|
|
Blood circulation in the kidney
Aorta to _____to segmental artery to interlobar artery to _____ artery to interlobular artery to afferent arteriole to glomerulus |
renal artery
arcuate artery |
|
|
Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion: 1_____ filtration creates a plasma like filtrate of the blood.2 Tubular reabsorption: Removes useful useful solutes from the filtrate and returns them to the ____
3. Tubular Secretion: Removes additonal ____ from the blood and adds them to the filtrate. 4. Removes water from the urine and returns it to the blood concentration wastes. |
glomerular
blood wastes |
|
|
PCT rebsorbs 65% of GF to peritubular ______
|
capillaries
|
|
|
The PCT has great length, prominent microvilli, and many ______ for active transport. Reabsorbs greater variety of chemicals than other parts of nephron.
|
mito
|
|
|
Tubular Secretion of PCT and Nephron Loop:
Waste removal includes urea, uric acid, bile salts, _______ and many drugs. |
catecholamines
|
|
|
Tubular Secretion of PCT and Nephron Loop
Acid Base Balance Secretion of hydrogen and ______ ions regulates the ____ of body fluids. |
bicarbonate
ph |
|
|
Tubular Secretion of PCT and Nephron Loop
Primary function of Nephron Loop: Water ++++++ and generates ______ gradient, allows collecting duct to concentrate urine. Also involved in electrolyte reabsorption. |
conservation
salinity |
|
|
Peritubular Capillaries
Blood has unsually high COP or colloid osmotic ++++++ and BHP or blood hydrostatic ++++++ is only 8mm Hg or lower. Even lower when constricted by angiotensin II. Favors reabsorption. |
pressure
pressure |
|
|
Peritubular Capillaries
Water absorbed by ++++++ and carries other solutes with it called solvent _____ |
osmosis
drag |
|
|
DCT and Collecting Duct
The principal cells are receptors for ______ Intercalated cells are involved in _______ balance. |
hormones
acid/base |
|
|
DCT and Collecting Duct
Function: Decreases ____by renin release and angiotensin II formation. |
BP
|
|
|
DCT and Collecting Duct 2
Adrenal Cortex secretes _______. It promotes Na reabsorption which promotes _______ reabsorption which maintains BP. |
aldosterone
water |
|
|
DCT and Collecting Duct
Effects of ADH- dehydration stimulates _______. The hypothalamus stimulates the posterior ______. The posterior pituitary secretes ADH and ADH increases +++++ reabsorption. |
hypothalamus
pituitary water |
|
|
DCT and Collecting Duct 2
Effects of PTH or parathyoid _____. Increases blood Ca2+ ande increases ______ reabsorption. PTH decreases phosphate _______ and decreases bone formation. Stimulates kidney production of _______ |
hormone
calcium reabsorption calcitrol |
|
|
DCT and Collecting Duct 2
Opposing effect of atrial natriuretic peptide or ANP Increases ____ by stimulating the right atrium to secrete ANP. Promotes -------- and water excretion and blood volume. It inhibits the renin/ alodosterone pathway and BP drops. |
BP
Na |
|
|
Control of Water Loss
Producing ---------- Urine NaCl reabsorbed by cortical CD. Water remains in the urine. |
Hypotonic
|
|
|
Control of Water Loss
Producing hypertonic urine. Dehydration leads to increased ____ which increases apuaporin channels which increase CD's water ______ |
ADH
permeability |
|
|
The efferent arteriole must connect with the ++++++ capillaries.
|
peritubular
|
|
|
The PCT must connect with Bowman's capsule and the DCT must connect with the ______ duct.
|
collecting
|
|
|
The male urethra has 3 regions: the prostatic urethra which during orgasm receives semen, the +++++ urethra which passes thru the pelvic cavity between corpus spongiosum and corpus ++++++. the 3rd part of the male urethra is the ______ urethra.
|
membraneous
cavernosum spongy |
|
|
The male urethra has 3 regions: the prostatic urethra which during orgasm receives semen, the +++++ urethra which passes thru the pelvic cavity between corpus spongiosum and corpus ++++++. the 3rd part of the male urethra is the ______ urethra.
|
membraneous
cavernosum spongy |
|
|
The male urethra has 3 regions: the prostatic urethra which during orgasm receives semen, the +++++ urethra which passes thru the pelvic cavity between corpus spongiosum and corpus ++++++. the 3rd part of the male urethra is the ______ urethra.
|
membraneous
cavernosum spongy |
|
|
The male urethra has 3 regions: the prostatic urethra which during orgasm receives semen, the +++++ urethra which passes thru the pelvic cavity between corpus spongiosum and corpus ++++++. the 3rd part of the male urethra is the ______ urethra.
|
membraneous
cavernosum spongy |
|
|
Osmolarity is 4x as concentrated deep in the ____
Medullary portion of collecting duct is more permeable to water than to ++++ |
medulla
NaCl |
|
|
Countercurrent Multiplier= multiplies the +++++ in medulla. Recaptures +++++ and returns it to the renal medulla.
|
salinity
NaCl |
|
|
Countercurrent Multiplier multiplies the salinity in the medulla. Descending limb reabsorbs _____ but not salt. Concentrates _____ fluid.
|
water
tubular |
|
|
Countercurrent Multiplier multiplies the _____ in the medulla. In the ascending limb, reabsorbs Na, ____, and ____
|
salinity
K Cl |
|
|
Countercurrent Multiplier The ascending limb maintains high osmolarity of ------- and is impermeable to _____. Tubular fluid becomes ______
|
medulla
water hypotonic |
|
|
Countercurrent Multiplier multiplies the salinity in the medulla. Recycling of ____: Collecting duct-medulla urea accounts for 40% of high _____ of medulla.
|
urea
osmolarity |
|
|
Countercurrent Multiplier of Nephron Loop diagram The ability of the conducting duct to concentrate ++++ depends on the ++=== gradient of the renal medulla.
|
urine
salinity |
|
|
The nephron loop acts as a countercurrent _____ which continually recaptures salt and returns it to the deep medullary tissue.
|
multiplier
|
|
|
The nephron loop is called a countercurrent multiplier because it is based upon fluid flowing in _____ directions in the ascending and descending limbs.
|
opposite
|
|
|
The Countercurrent Mulitiplier Nephron Loop
Step 1: More salt is continually added by the ____ |
PCT
|
|
|
The Countercurrent Mulitiplier Nephron Loop
Step 2 through 5 forms a positive feedback loop. The higher the ______ of the ECF, the more water leaves the descending limb by _____ Step 3 The more water that leaves the _____ limb, the saltier the fluid is that remains in the tubule. Step 4 The saltier the fluid in the +++++ limb, the more salt the tubule pumps into the ECF. Step 5: The more salt that is pumped out of the ascending limb, the saltier the ECF is in the renal medulla. |
osmolarity
osmosis descending ascending |
|
|
The nephron loop, collecting duct, and ____ ____ work together to maintain a gradient of osmolarity in the renal medulla.
|
vasa recta
|
|
|
The renal medulla must have a blood supply to meet its metabolic needs, and this could be problematic because capillaries of the medulla could carry away the urea and salt that produce the high +++++
|
osmolarity
|
|
|
Countercurrent Exchange System
The vasa recta that supply the medulla forms a countercurrent that prevents the carrying away of urea and salt that produce ______ |
osmolarity
|
|
|
Countercurrent Exchange System
Blood flows in opposite directions to adjacent parallel capillaries. Vasa Recta supplies blood to medulla and does not remove salt from medulla. Blood flowing downward in the _____ ____ exhanges water for _____ water diffuses out of the capillaries and salt diffuses in. |
vasa recta
salt |
|
|
Countercurrent Exchange System of Vasa Recta
In the ascending capillaries, water diffuses into the blood and ____ diffuses out of the blood. |
salt
|
|
|
Hormones Affecting Renal Function: Nephron Loop, DCT, and CD- Aldosterone promotes Na ______ and K secretion. Water reabsorption. Maintains blood _____ and reduces _____ volume.
|
reabsorption
volume urine |
|
|
Hormones Affecting Renal Function
Angiotensin II Afferent and Efferent arterioles and PCT. Reduces ____ loss encourages water intake, and constricts blood vessels. Acts as a generalized ______ raises GFR and stimulates PCT to reabsorb water and salt. Stimulates ADH and aldosterone secretion and stimulates _____ |
water
vasoconstrictor thirst |
|
|
Hormones Affecting Renal Function
ADH affects the collecting duct. Promotes water ______ reduces urine volume and increases ______ |
volume
concentration |
|
|
Hormones Affecting Renal Function:
Natriuretic peptides affect afferent and efferent arterioles and collecting duct. ____ afferent arteriole and constrict efferent arteriole. Increase ____ and inhibit secretion of renin, ADH, and aldosterone, inhibits NaCl reabsorption by collecting duct. Increases urine volume and lowers ____ |
dilate
GFR BP |
|
|
Hormones Affecting Renal Function
Calcitonin affects DCT. Weak effects similar to those of ____ |
PTH
|
|
|
Hormones Affecting Renal Function
Calcitrol affects DCT. Weak effects similar to those of ____ |
PTH
|
|
|
Epinephrine and Norepinenphrine affects juxtaglomerular apparatus and afferent arteriole. Induce renin secretion, _____ afferent arteriole, reduces GFR and urine +++++
|
constricts
volume |
|
|
Hormones Affecting Renal Function
PTH or parathyroid hormone affects PCT, DCT, and nephron loop. Promotes ____ reabsorption by loop and DCT, increases phosphate secretion by PCT promotes calcitrol synthesis. |
Ca2+
|
|
|
Tubular Reabsorption by the PCT: Glucose, amino acids, protein, vitamens, lactate, urea, and ++++ acid.
|
uric
|

