![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
190 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood is a type of... |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Formed elements of the blood include... |
Leukocytes Erythrocytes Platelets |
|
|
The liquid portion of blood is... |
Plasma |
|
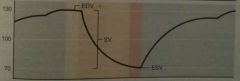
Does this graph depict volume or pressure during the cardiac cycle? |
Volume |
|
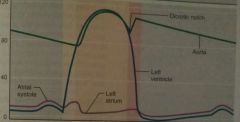
Does this graph depict volume or pressure during the cardiac cycle? |
Pressure |
|
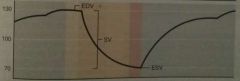
What is happening during the first phase of this cycle? |
Ventricular filling Atrial contraction |
|
|
Erythrocytes normally constitute about _____ of the total volume of a blood sample. |
45% |
|
|
Plasma constitutes _____ of whole blood. |
55% |
|
|
The buffy coat makes up _____ of whole blood. It consists of _________. |
<1% Leukocytes and Platelets |
|
|
Blood volume in adult males... |
5-6L |
|
|
Blood volume in adult females... |
4-5L |
|
|
3 basic components of the circulatory system that work to maintain homeostasis... |
Heart Blood vessels Blood |
|
|
Normal RBC hematocrit for males... |
42-56% |
|
|
Normal RBC hematocrit for females... |
38-46% |
|
|
Blood is _____ more viscous than water. |
5x |
|
|
The pH of blood is... which makes it ________. |
7.35-7.45 Slightly alkaline |
|
|
The temperature of blood is... |
100°F |
|
|
Blood transports |
Oxygen Wastes Hormones |
|
|
Blood regulates... |
Body temperature Body fluid pH Body fluid volume |
|
|
Blood protects the body by... |
Preventing blood loss Preventing infection |
|
|
Dissolved solutes in blood plasma... |
Plasma proteins Nutrients Electrolytes Respiratory gases Hormones Wastes |
|
|
Types of plasma proteins... |
Albumin Globulins Clotting proteins |
|
|
What is the most abundant plasma protein? |
Albumin |
|
|
Name two clotting proteins. Where are they produced? |
Prothrombin and Fibrinogen The Liver |
|
|
Albumin function in the blood... |
Maintains plasma osmotic pressure Buffer Transport of steroids and bilirubin |
|
|
Albumin is produced by... |
The Liver |
|
|
These globulins transport lipids, metal ions and fat-soluble vitamins... |
Alpha and Beta globulins |
|
|
These globulins are antibodies produced during the immune response... |
Gamma globulins |
|
|
Globulins are produced in... |
The liver |
|
|
Examples of nutrients in the blood... |
Amino acids Fatty acids Triglycerides Vitamins Cholesterol |
|
|
Where does blood get its nutrients? |
Absorbed from the GI tract or body reserves |
|
|
Examples of electrolytes found in blood... |
Calcium Potassium Sodium |
|
|
Respiratory gases dissolved in blood... |
Carbon dioxide Oxygen Nitrogen |
|
|
Types of wastes found in blood... |
(by products of cell metabolism) Urea, Uric acid, Ammonia, Creatinine, and Lactic acid |
|
|
What is the function of buffers in the blood? |
They are chemicals that prevent fluctuations in plasma pH. |
|
|
Hemoglobin _______ binds oxygen for quick pick up and easy release. |
Weakly |
|
|
What gives blood its color? |
Red heme pigments |
|
|
Globin consists of ___ polypeptide chains. Each chain has its own _____. |
Four Heme |
|
|
Each heme contains one... |
Iron (Fe) atom |
|
|
Each hemoglobin can transport _____ oxygen molecules. |
Four |
|
|
When hemoglobin binds oxygen, it's called... |
Oxyhemoglobin |
|
|
Once hemoglobin releases oxygen, it becomes... |
Deoxyhemoglobin |
|
|
20% of blood's carbon dioxide is transported by combining with amino acids called ________. |
Carbaminohemoglobin |
|
|
What is blood cell formation called? |
Hemopoiesis or hematopoiesis |
|
|
Hemopoiesis occurs in _____ bone marrow. |
Red |
|
|
Adult red bone marrow is found in... |
Skull Ribs Vertebrae Sternum Pelvis Humerus Femur |
|
|
All blood cells arise from... |
Hemocytoblasts |
|
|
Red blood cell formation is called... |
Erythropoiesis |
|
|
How many blood cells are produced per second? |
3 million |
|
|
How long does erythropoiesis take? It requires ____ and ____. |
5 days Iron (Fe) and Vitamin B12 |
|
|
The # of RBCs in blood is constant and maintained via ________. |
Negative feedback |
|
|
The ______ releases the hormone _______ which controls the rate of erythropoiesis. |
Kidneys Erythropoietin |
|
|
If blood oxygen levels ⬇️, the kidneys ___ erythropoietin release. |
Increase |
|
|
What factors can cause kidney oxygen levels to change? |
Increase RBC # Increased altitude Increase aerobic activity Lung disease Cardiovascular disease |
|
|
____ of circulating RBCs are removed daily. |
1% |
|
|
________ phagocytize old and damaged RBCs in the ______ and _______. |
Macrophages Spleen and Liver |
|
|
Lifespan of a RBC... |
120 days |
|
|
During RBC removal, hemoglobin is broken down into its ______ and ______ portions. |
Globin Heme |
|
|
During RBC ♻️/removal, the remainder of heme turns into ________, which is transported to the ________ by ________. |
Bilirubin Liver Albumin |
|
|
Low WBC count= |
Leukopenia |
|
|
High WBC count= |
Leukocytosis |
|
|
Most WBCs are found in ________. |
Lymphatic organs |
|
|
In an immune response, ______ perform _______ when they leave the bloodstream. |
WBCs Diapedesis |
|
|
Attraction to/movement to chemicals released by pathogens, damaged cells, or WBCs is called... |
Positive chemotaxis |
|
|
Low neutrophil count= |
Neutropenia |
|
|
Attacks parasitic worms and lessens body's response to allergic reaction... |
Eosinophils |
|
|
Count increases during acute bacterial infection... |
Neutrophils |
|
|
Granules turn dark purple... |
Basophils |
|
|
Release histamine and heparin; released during inflammation... |
Basophils |
|
|
Count increases in viral infections... |
Lymphocytes |
|
|
3 main types of Lymphocytes... |
T Lymphocytes B Lymphocytes Natural Killer Cells |
|
|
Attacks virus-infected and tumor cells, also controls the immune system... |
T Lymphocytes |
|
|
Differentiates into plasma cells, which produce antibodies... |
B Lymphocytes |
|
|
Function of Natural Killer cells... |
Kill virus- infected and tumor cells |
|
|
Leaves the bloodstream to become macrophages... |
Monocytes |
|
|
WBC formation... |
Leukopoiesis |
|
|
Leukopoiesis occurs... |
Within red bone marrow and lymphatic tissues |
|
|
Contain granules filled with chemicals involved in blood clotting... |
Platelets |
|
|
Platelet formation is called... |
Thrombopoiesis |
|
|
Platelet formation occurs in the ________, begins with _______ and is stimulated by a hormone called ________. |
Red bone marrow Hemocytoblasts Thrombopoietin |
|
|
About 30% of platelets are stored in the _______. |
Spleen |
|
|
3 events in hemostasis... |
Vascular Spasm Platelet plug formation Coagulation
|
|
|
Aggregation of platelets is a... |
Platelet plug |
|
|
A platelet plug is restricted to the injury site because intact endothelial cells release... |
Prostacyclin (inhibits platelet aggregation) |
|
|
Procoagulants... |
Initiate and stimulate the formation of a blood clot |
|
|
Anticoagulants... |
Inhibit and impede the formation of a blood clot |
|
|
A blood clot is... |
A fibrin mesh of RBCs, WBCs, and plasma |
|
|
Fibrin is formed from the inactive plasma protein _________. This is catalyzed by ________. |
Fibrinogen Thrombin |
|
|
Thrombin is formed from the inactive plasma protein _______. This is catalyzed by _______. |
Prothrombin Prothrombin Activator
|
|
|
Two pathways in which prothrombin activator is formed.... |
Intrinsic Extrinsic |
|
|
Extrinsic path= |
Starts with exposure of blood to chemicals released by damaged tissue. Has few steps and can form quickly |
|
|
Intrinsic path= |
Starts with the release of chemicals by platelets in response to vessel damage. Has many steps, slower, yields tremendous amounts of PTA |
|
|
Breakdown of the clot is called... |
Fibrinolysis |
|
|
_______ digests fibrin following vessel repair. |
Plasmin |
|
|
Following vessel repair, the inactive plasma protein _______ is converted into plasmin. |
Plasminogen |
|
|
Fibrinolysis= After blood vessel repair➡️_______🔀_______ by ______ and plasmin digests _______. |
Plasminogen Plasmin Plasminogen Activator Fibrin
|
|
|
Clots are restricted from growing too large by the removal of ________and the presence of normal _______. |
Clotting factors Anticoagulants |
|
|
Coagulation can be promoted by a roughened vessel lining and by a ________ within vessels. |
Pooling of blood |
|
|
Response to blood loss >10% of blood volume... |
Activates the SNS= vasoconstriction ⬆️heart rate ⬆️force of cardiac contraction ⬆️blood pressure (All maintains blood flow to the brain) |
|
|
Arteries= |
Carry blood away from the heart |
|
|
Veins= |
Carry blood towards the heart |
|
|
Capillaries= |
Link arteries and veins Sites of exchange between blood and tissues |
|
|
Positioned within the mediastinum, the medial cavity of the thorax |
The heart |
|
|
_____ of the heart points towards the right shoulder |
The base |
|
|
______ of the heart points towards the left hip. |
The apex |
|
|
The ______ encloses the heart. |
Pericardium |
|
|
Which cavity around the heart contains serous fluid? |
Pericardial cavity |
|
|
Layers that enclose the heart from outermost to innermost... |
Fibrous pericardium Parietal serous pericardium Visceral serous pericardium (aka epicardium) |
|
|
Which outer layer of the heart is continuous with the great vessels? |
Parietal and visceral layers |
|
|
Pericardial cavity is the space between the ______ & ______ layers. |
Parietal Visceral |
|
|
Two types of cardiac muscle cells... |
Contractile (99%) and Autorhythmic cells (1%) |
|
|
Contractile cells function and structure... |
Generate the pumping force Striated, short and branched |
|
|
Autorhythmic cells function... |
Spontaneously depolarize to set the rate of contraction |
|
|
Intercalated discs link cardiac muscle cells together ______ and ______. |
Mechanically and electrically |
|
|
Intercalated discs contain... |
Gap junctions Desmosomes |
|
|
Desmosomes= |
Protein filaments that physically connect adjacent cardiac muscle cells...prevents cells from separating during contraction |
|
|
Intrinsic control of heart rate is performed by the _______ cardiac muscle cells |
Autorhythmic |
|
|
5 main groups of autorhythmic cells... |
Sinoatrial node AV node AV bundle Right and Left bundle branches Purkinje fibers |
|
|
List the pathway of electrical conduction within the heart. |
Sinoatrial node AV node AV bundle Right and Left bundle branches Purkinje fibers
|
|
|
A group of autorhythmic cells near the opening of the superior vena cava... |
Sinoatrial node |
|
|
Group of autorhythmic cells in the inferior interatrial septum near the tricuspid orifice... |
AV node |
|
|
Group of autorhythmic cells in the superior interventricular septum... |
AV bundle |
|
|
Group of autorhythmic cells in the middle & inferior interventricular septum... |
Right and Left bundle branches |
|
|
Separate autorhythmic cells that wind through the ventricles... |
Purkinje fibers |
|
|
All autorhythmic cells have the ability to rhythmically and spontaneously_______. |
Depolarize |
|
|
SA node cells have the fastest rate of _______ and are the _______ of the heart. |
Depolarization Pacemaker |
|
|
Extrinsic control of heart rate is conducted by the _____ and_____ systems. |
Nervous Endocrine |
|
|
The medulla oblongata contains 2 cardiac centers that can alter the heart's activity, they are... |
Cardioacceleratory center Cardioinhibitory center |
|
|
The cardioacceleratory center projects to the heart via cardiac ________. |
Sympathetic nerves |
|
|
Cardioinhibitory center projects to the heart via ______ neurons in the CNS. |
Parasympathetic |
|
|
Releases NE upon the SA node, AV node, and ventricular myocardium. Increases contraction rate and force. |
Cardioacceleratory center |
|
|
Releases Ach upon the SA node and AV nodes. Decreases heart rate, but causes no change in the heart's contractile strength. |
Cardioinhibitory center |
|
|
At rest, both parasympathetic & sympathetic neurons are releasing neurotransmitters onto the heart, but the _________ branch releases more. |
Parasympathetic |
|
|
During stress, exercise, and excessive heat, the ______ branch dominates. |
Sympathetic |
|
|
"LUB" sound = |
Shutting of AV valves Occurs at onset of ventricular contraction |
|
|
"DUP" sound = |
Shutting of the semi-lunar valves Occurs at the end of ventricular contraction |
|
|
Cardiac cycle = |
Ventricular filling Isovolumetric contraction Ventricular ejection Isovolumetric relaxation |
|
|
Ventricular Filling |
-LA bp is lower -LV bp is lower -so blood tries to backflow from Aorta & closes semi-lunar valve -Atrium & Ventricle are in diastole -80% of ventricular bl. volume enter in this passive manner -LA depolarizes + contracts, pushing the remaining 20% into the LV -LV now has max volume of blood for this cycle =EDV -For the rest of the cycle LA will be in diastole |
|
|
Isovolumetric contraction |
-LV depolarizes & contracts, LV bp>LA bp -Mitral Valve closes - "LUB" -AV & semi-lunar valves are shut, blood volume is unchanging
|
|
|
Ventricular ejection |
LV bp finally >Aortic bp Semi-lunar valve is forced open, 🅱️ LV➡️AA Not all of the 🅱️ LV is ejected, remaining amt is ESV (Amt 🅱️ ejected is Stroke Volume) |
|
|
Isovolumetric relaxation |
-LV stops contracting, bp⬇️<Aortic bp & shuts semi-lunar valve... DUP -Takes time for LV bp⬇️<LA bp (AV & semi-lunar valves are closed, volume unchanging) -LV bp⬇️<LA bp and mitral valve opens ...cycle begins again |
|
|
Is LV pressure greater than RV pressure? |
Yes |
|
|
Is RV pressure greater than LV pressure? |
No |
|
|
Do the RV and LV of the heart contract together? |
Yes |
|
|
Do the RV and LV have identical stroke volumes? |
Yes |
|
|
Cardiac output= |
Amount of 🅱️ pumped by each ventricle in one minute |
|
|
CO = ____ x ____ |
HR x SV |
|
|
During exercise, cardiac output ______ dramatically. |
Increases |
|
|
Norepinephrine _____ heart rate. |
Increases |
|
|
Increase in cardioacceleratory center activity _____ heart rate. |
Increases |
|
|
Decrease in cardioinhibitory center activity _____ heart rate. |
Increases |
|
|
Decrease in CAC _____ the heart rate. |
Decrease |
|
|
Increase in Cardioinhibitory center activity ______ heart rate. |
Decreases |
|
|
Epinephrine is released by the _______. |
Adrenal gland |
|
|
Thyroxine _____ heart rate and released by the _______. |
Increases Thyroid Gland |
|
|
Epinephrine ____ heart rate. |
Increases |
|
|
Other factors that raise heart rate... |
⬆️body temp Caffeine Nicotine Ephedrine |
|
|
Other factors decrease heart rate... |
⬇️body temp Beta blockers (drugs) |
|
|
Regulation of SV depends on 3 variables... |
Preload Contractility Afterload |
|
|
Effects of cardiovascular training... |
Increased LV contractility Increased size of LV chamber Increased branching of coronary blood vessels |
|
|
Frank-Starling Law |
"What returns to the heart will get pumped out of the heart" |
|
|
Contractility= |
Strength of the heart's contraction independent of its degree of stretch |
|
|
Afterload= |
Pressure that must be overcome to open semi-lunar valve and eject blood |
|
|
The fibrous skeleton is composed of... |
Dense Irregular CT within the heart |
|
|
Supports heart valves and separates atria from ventricles physically and electrically... |
Fibrous skeleton of the heart |
|
|
Provides origins and insertion points for cardiac contractile cells... |
Fibrous skeleton of the heart |
|
|
During an infection, the size of the buffy coat will... |
Increase |
|
|
During leukopenia, the body's ability to prevent bacterial infection will... |
Decrease |
|
|
As the rate of RBC destruction increases, plasma (bilirubin) will... |
Increase |
|
|
Ferritin function... |
Storage of iron in the liver |
|
|
Erythropoiesis, Leukopoiesis, and Thrombopoiesis all occur in the... |
Red bone marrow |
|
|
Smallest formed element... |
Platelet |
|
|
Inability to secrete bile would cause a rise in plasma _________. |
Bilirubin levels |
|
|
A deficiency in _____ could cause clotting problems. |
Calcium |
|
|
A deficiency in _____ could cause anemia. |
Iron |
|
|
PTA is produced quickly by the _____ clotting mechanism. |
Extrinsic |
|
|
PTA is produced more slowly by the _____ clotting mechanism. |
Intrinsic |
|
|
Which event associated with coagulation occurs last? |
Fibrinolysis |
|
|
Which Leukocyte exerts the most control over the immune system? |
Lymphocytes |
|
|
Shuttles iron to the liver... |
Transferrin |
|
|
Bilirubin is formed from... |
Heme |
|
|
In the liver, iron can be stored as... |
Hemosiderin |
|
|
Erythropoiesis involves cells called... |
Hemocytoblasts |
|
|
Coagulation in order... |
-Collagen is exposed -PTA formed -Thrombin from Prothrombin -Fibrin from Fibrinogen -Fibrinolysis |
|
|
Fragments of cells known as megakaryocytes...in circulation for 10-12 days |
Platelets |
|
|
Metal ion essential in virtually all stages of coagulation... |
Calcium |
|
|
Platelet plug formation is a _____ feedback mechanism |
Positive |
|
|
Bilirubin is transported to the blood by______. |
Albumin |
|
|
Majority of RBC destruction occurs in the ______. |
Spleen |
|
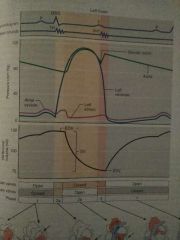
Interpret |
Volume and pressure |

