![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Boyle's Law?
|
Pressure and volume are inversely proportional. As volume increases, pressure decreases; as volume decreases, pressure increases.
|
|
|
What are the four basic physiological process that make up respiration?
|
pulmonary ventilation - the physical movement of air into and out of the lungs
pulmonary gas exchange - the movement of gases across the respiratory membrane gas transport - the movement of gases through the blood tissue gas exchange - the exchange of gases between the blood and the tissues |
|
|
What is the main inspiratory muscle and what assists it?
|
the diaphragm, and it is assisted by the external intercostal muscles
|
|
|
What is tidal volume?
|
TV - air exhaled/inhaled in one respiratory cycle (avg. 500 mL)
the amount of air exchanged with each breath during normal, quiet breathing |
|
|
What is expiratory reserve volume?
|
ERV - air exhaled below TV
is the volume of air that may be expired after a tidal expiration |
|
|
What is inspiratory reserve volume?
|
IRV - amount that can be inhaled above TV (male 3000 mL, female 1900 mL)
the amount of air that may be inspired after tidal inspiration |
|
|
What is residual volume?
|
RV - amount of air that remains in the lung after ERV; keeps lungs from collapsing
cannot be measured with a spirometer - the amount of air that remains in the lungs after maximal expiration and is generally equal to about 1100 - 1200 mL of air |
|
|
What is inspiratory capacity?
|
the amount of air a person can maximally inspire after a tidal expiration (2400 - 3600 mL)
TV + IRV = IC |
|
|
What is functional residual capacity?
|
the amount of air normally left in the lungs after tidal expiration (1800 - 2400 mL)
not measurable with general spirometry ERV + RV = FRC |
|
|
What is vital capacity?
|
represents the total amount of exchangeable air that moves in and out of the lungs (3100 - 4800 mL)
TV + IRV + ERV = VC |
|
|
What is total lung capacity?
|
TLC - represents the total amount of exchangeable and non-exchangeable air in the lungs (4200 - 6000 mL)
it is the total of all four respiratory volumes and is not measurable with general spirometry - TV + IRV + ERV + RV = TLC |
|
|
In regards to pH and CO2 levels what does hyperventilation do?
|
more CO@ is expelled from the body, and the carbon dioxide concentration of the blood decreases which raises the pH of the blood (more alkaline)
|
|
|
In regards to pH and CO2 what does hypoventilation do?
|
CO@ is retained and its concentration in the blood increases which decreases the blood pH = more acidic
|
|
|
Air moves into the lungs when...
|
intrapulmonary pressure is less than atmospheric pressure
|
|
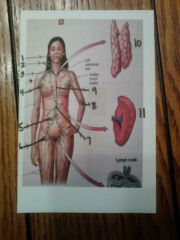
|
1. tonsil
2. cervical lymph nodes 3. R) lymphatic duct 4. axillary lymph nodes 5. intestinal lymph nodes 6. inguinal lymph nodes 7. cisterna chyli 8. cubital lymph nodes 9. thoracic duct 10. thymus 11. spleen |
|
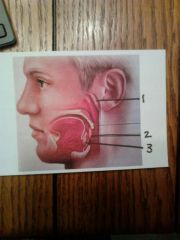
|
1. pharyngeal tonsil
2. palatine tonsil 3. lingual tonsil |
|

|
1. spleen
2. white pulp: contains phagocytes and lymphocytes that play a role in immune system 3. red pulp: involved in the destruction of old and worn-out RBCs |
|
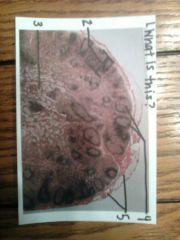
|
1. lymph node
2. cortex 3. medulla 4. lymphatic nodule 5. capsule |
|
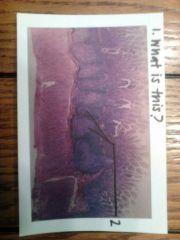
|
1. peyer's patches in the ileum
2. peyer's patches |
|
|
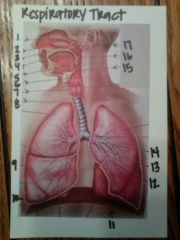
1. nasal cavity
2. nostril 3. hard palate 4. nasopharynx 5. oropharynx 6. laryngopharynx 7. larynx 8. trachea 9. visceral pleura 10. parietal pleura 11. diaphragm 12. tertiary bronchus 13. secondary bronchus 14. L) primary bronchus 15. epiglottis 16. soft palate (uvula) 17. conchae |
|
|
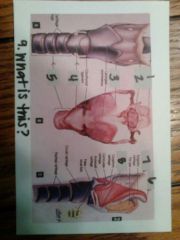
1. epiglottis
2. hyoid bone 3. thyroid cartilage 4. cricoid cartilage 5. trachea 6. epiglottis 7. hyoid bone 8. thyroid cartilage 9. larynx |
|
|
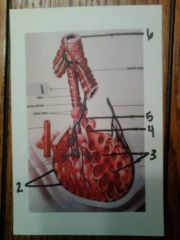
1. terminal bronchiole
2. alveoli 3. alveolar sac 4. alveolar duct 5. respiratory bronchiole 6. bronchiole |
|
|
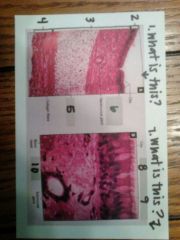
1. trachea
2. mucosa 3. submucosa 4. adventitia 5. hyaline cartilage 6. pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium 7. nasal mucosa with goblet cell 8. goblet cell 9. pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial cells |
|
|
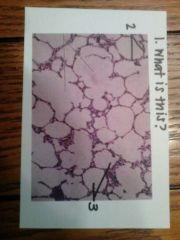
1. lung tissue
2. walls of alveoli (simple squamous epithelium) 3. alveoli |
|

|
1. tidal volume
2. expiratory reserve volume 3. inspiratory reserve volume 4. residual volume 5. inspiratory capacity 6. functional residual capacity 7. vital capacity 8. total lung capacity |
|
|
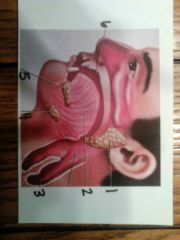
1. parotid gland
2. tongue 3. esophagus 4. submandibular gland 5. sublingual gland 6. oral cavity |
|
|
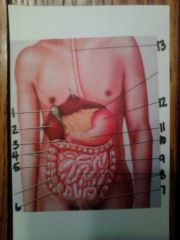
1. gallbladder
2. liver 3. duodenum 4. haustra 5. ascending colon of large intestine 6. cecum 7. sigmoid colon 8. small intestine 9. descending colon 10. transverse colon 11. pancreas 12. stomach 13. esophagus |
|
|
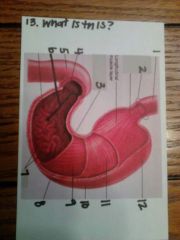
1. esophagus
2. gastroesophageal sphincter 3. lesser curvature 4. pyloric sphincter 5. duodenum 6. pylorus 7. rugae 8. greater curvature 9. oblique muscle layer 10. body 11. circular muscle layer 12. fundus |
|
|
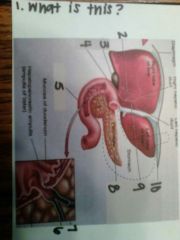
1. liver, gallbladder, duodenum
2. cystic duct 3. gallbladder 4. common bile duct 5. duodenum 6. pancreatic duct 7. common bile duct 8. pancreatic duct 9. common hepatic duct 10. falciform ligament |
|
|
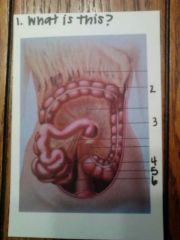
1. the mesentery and greater omentum
2. transverse colon 3. descending colon 4. jejunum 5. sigmoid colon 6. ileum |
|
|
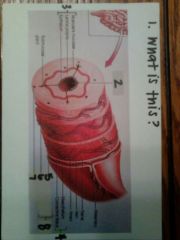
1. tissue layers of alimentary canal
2. lumen 3. mucosa 4. serosa 5. outer longitudinal layer 6. inner circular layer 7. submucosa 8. muscularis externa |
|
|
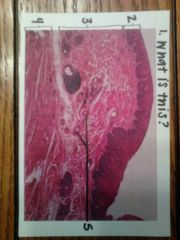
1. the esophagus
2. stratified squamous epithelium 3. submucosa 4. smooth muscle 5. seromucous glands |
|

|
1. gastric pit
2. surface epithelium 3. oblique layer 4. circular layer 5. longitudinal layer 6. mucosa 7. submucosa 8. muscularis externa 9. serosa 10. gastric pit 11. the stomach and gastric glands |
|
|
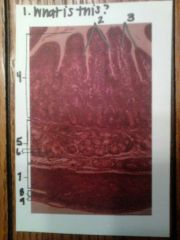
1. duodenum
2. goblet cells 3. villi 4. mucosa 5. submucosa 6. duodenal gland 7. muscularis externa, circular layer 8. muscularis externa, longitudinal layer 9. serosa |
|

|
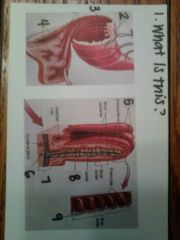
1. the pancreas
2. pancreatic islet 3. pancreatic duct 4. acinar cells |
|
|
1. folds of the small intestine
2. muscle layer 3. lumen 4. villi 5. villi 6. muscularis mucosae 7. submucosa 8. goblet cell 9. microvilli |
|

|
1. liver lobule
2. bile duct 3. hepatic triad/portal triad 4. bile duct 5. portal venule 6. hepatic arteriole 7. central vein |
|
|
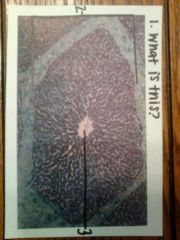
1. liver
2. liver lobule 3. central vein |

