![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
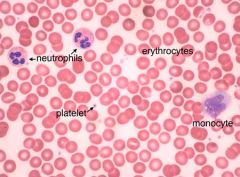
|
Blood Smear: erythrocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, platelets |
|
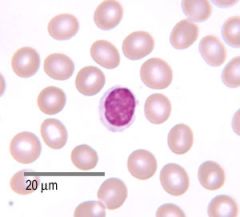
|
Lymphocyte w/ erythrocytes |
|
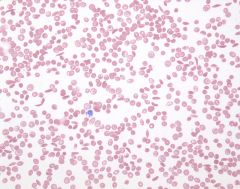
|
Blood Smear: Sickle Cell Anemia |
|
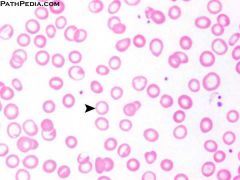
|
Iron Deficient Anemia: Low RBC Volume |
|

A B C D E |
A. neutrophil: granulocyte B. eosinophil: granulocyte C. basophil: granulocyte D. monocyte: agranulocyte E. lymphocyte: agranulocyte |
|
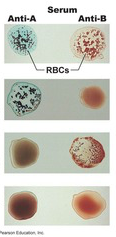
1.
2.
3.
4.
|

1.
2.
3.
4. |
|
|
Functions of Neutrophils |
- Most numerous (50-70% of WBCs) - Cytosol contains bactericidal granules and lysosomal enzymes - Attack and digest (phagocytosis) bacteria "marked" with antibodies or complement proteins |
|
|
Functions of Eosinophils |
- (2-4% WBCs) - aka "acidophils" - bi-lobed nucleus - Attack via phagocytosis but primary mode of attack is exocytosis of toxic compounds to kill parasites - Can release enzymes to reduce inflammation at injury sites |
|
|
Functions of Basophils |
- Least numerous granulocyte (<1% WBCs) - release heparin at sites of injury to reduce clotting - attract eosinophils and other basophils to area of injury -discharge granules that contain histamine |
|
|
Functions of Monocytes |
- least numerous granulocytes (2-8% WBCs) - large with kidney shaped nucleus - In blood stream < 24 hrs before becoming tissue macrophage - |
|
|
Functions of Lymphocytes |
- (20-30% WBCs) - Continuously migrate from bloodstream to tissues and back - Three Functional Classes: 1) T cells: cell-mediated immunity 2) B cells: humoral immunity 3) NK Cells: immune surveillance |
|
|
Hematocrit |
Measure of packed cell volume (RBCs, WBCs, and platelets) |
|
|
Differential Count of WBCs |
Count of each type of cell in sample of 100 WBCs to obtain percentage of each type of WBC |
|
|
Universal Blood Donor for ABO system |
Type O |
|
|
Plasma |
- (46-63% of total blood) - 92% water - 1% solutes - 7% plasma proteins |
|
|
What is the Tallquist Method? |
Test for hemoglobin (anemia) |
|
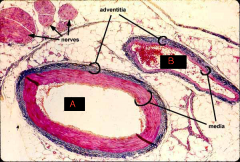
|
Vessels
A: artery lumen B: vein lumen |
|
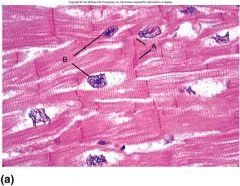
|
Cardiac Muscle Cells
A: Intercollated Discs B: Nuclei |
|
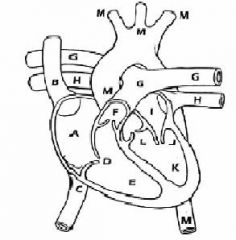
|
Anatomy of the Heart A: right atrium B: superior vena cava C: inferior vena cava D: tricuspid valve (rt. AV) E: right ventricle F: pulmonary valve G: pulmonary artery H: pulmonary vein I: right atrium J: mitral valve (aka bicuspid/lt. AV) K: left ventricle L: aortic valve M: aorta |
|
|
Study Wigger's Diagram |
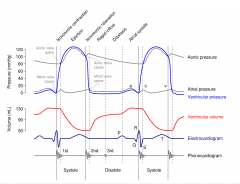
|
|
|
Organs/ tissues of the lymphatic system |
Tonsils, Thymus, Spleen, MALT (mucosa-associated lymph tissue found in digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems), nodes, and appendix |
|
|
The right lymphatic duct drains __________. |
right side of head and thorax, right upper extremity |
|
|
Most lymph returns to the venous circulation by way of the _____________. |
thoracic duct |
|
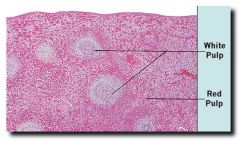
|
Spleen Slide
White pulp- resembles lymphoid tissues, responsible for spleen's immune functions
Red Pulp- high red blood cell count |
|
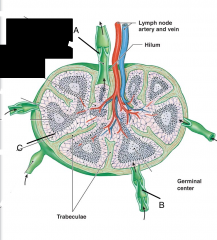
|
Lymph Node Diagram
A: efferent vessel B: afferent vessel C: subcapsular space
|
|
|
Order of Circulation |
Systems -> Right Atrium (via sup/inf vena cava) -> Right Ventricle (through RT AV valve) -> Pulmonary Artery (through pulmonary valve) -> Lungs -> Pulmonary Veins -> Left Atrium -> Left Ventricle-(through Mitral Valve)
|
|
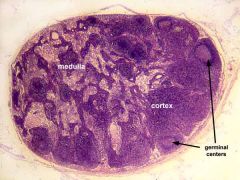
|
Lymph Node I |
|
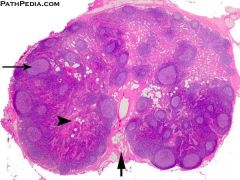
|
Lymph Node II |
|
|
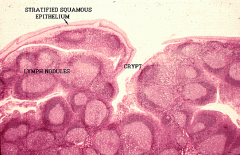
Human Palatine Tonsil |
|
|
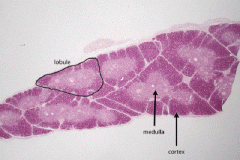
Thymus |
|
|
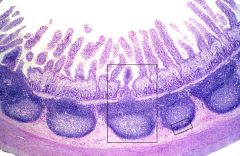
Peyer's Patches Ileum. |
|
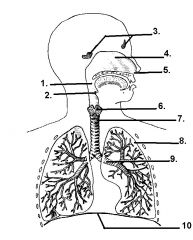
|
1. pharynx 2. epiglottis 3. frontal and sphenoidal sinus 4. nasal cavity 5. external nares (nostrils) 6. larynx 7. trachea 8. Left Lung 9. bronchus 10. diaphragm |
|
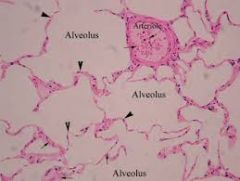
|
Lung Tissue: Alveoli, Arteriole, and Capillaries |
|
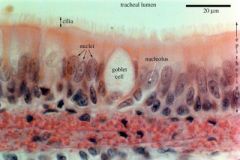
|
Trachea, including lumen, cillliated cells and goblet cells |
|
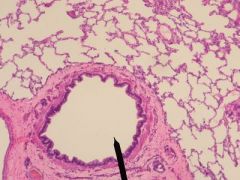
|
Bronchiole |
|
|
Fates of Germ Layers |
Endoderm- Gut, Liver, Lungs Mesoderm- skeleton, Muscle, Kidney, Heart, Blood Ectoderm- Skin and CNS |
|
|
Early Embryonic Stages |
Ovulation--> Oocyte--> Fertilization --> (A) Zygote --> (B) 4-cell stage (2 days) --> (C) Morula (3 days) --> (D) early blastocyst (4 days)-->(E) implanting blastocyst |
|
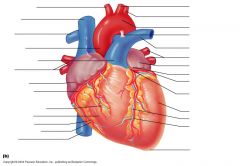
Coronary Circulation Anterior View |
Circumflex Artery (top left vent.), Left Coronary Artery (medial left vent.), Anterior Interventricular Artery (down septum), Great Cardiac Vein (down septum), Right, Anterior, ad small Cardiac Veins (Along right atrium/vent) |
|
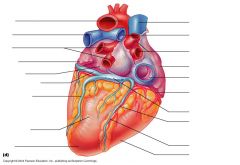
Coronary Circulation Posterior |
coronary sinus (vein pocket in middle), great cardiac vein (travels around left vent), Posterior vein of left ventricle, Right coronary artery (around right ventricle) |
|
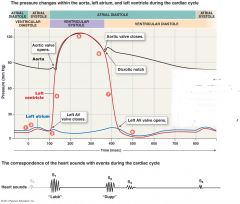
Lubb- AV valves close Dupp- semilunar valves close |
1. Atrial Contraction Begins 2. Atria eject blood into ventricles 3. Atrial systole ends, AV valves close 4. isovolumetric contraction 5. ventricular ejection occurs 6. semilunar (aorta/pul) valves close 7. isovolumetric relaxation occurs 8. AV valves open, passive filling begins
|
|
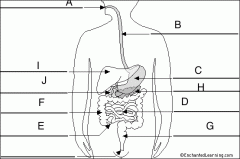
|
A. Mouth B. esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) E. Appendix F. Large Intestine (Ascending, Transverse, Descending, Sigmoid) G. Anal Canal H. Pancreas I. Liver J. Gallbladder |
|
|
Functions of Ovaries |
Secretion of hormones, inhibin formation of immature gametes production of oocytes |
|
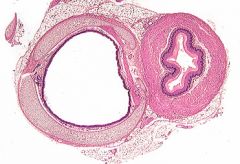
|
Trachea and Esophagus |
|
|
Maltase, Lactase, Sucrase |
Source: small intestine Target: carbohydrates (maltose, sucrose, lactose) Products: monosaccharides |
|
|
Pancreatic alpha-amylase |
Source: pancreas Target: complex carbohydrates Products: di/trisacchardes |
|
|
Salivary Amylase |
Source: salivary glands Target: complex carbohydrates Products: di/trisaccharides |
|
|
Carboxypeptidase, Chymotrypsin |
Source: Pancreas Target: Proteins and polypeptides Products: Short-chain polypeptides Notes: released as proenzymes ( procarboxypeptidase and chymotrypsinogen)
|
|
|
dipeptidase, peptidases |
Source: small intestine Target: di/tripeptides Products: amino acids |
|
|
Elastase (Proelastase) |
Source: Pancreas Target: Elastin Products: short-chain peptides Notes: activated by trypsin |
|
|
Enteropeptidase |
Source: small intestine Target:Trypsinogen Products: Trypsin |
|
|
Pepsin (pepsinogen) |
Source: stomach Target: proteins Products: short-chain polypeptides |
|
|
Rennin |
Source: stomach Target: milk proteins Notes: Infants only |
|
|
Trypsin (Trypsinogen) |
Source: Pancreas Target: Proteins Products: short-chain peptides
|
|
|
Lingual Lipase |
Source: tongue Target: triglycerides Products: fatty acids
|
|
|
Pancreatic lipase |
Source: pancreas Target: triglycerides Products: fatty acids |
|
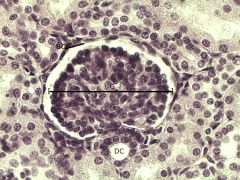
|
Bowman's Capsule |
|
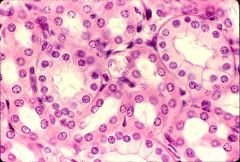
|
Kidney Tubules |
|
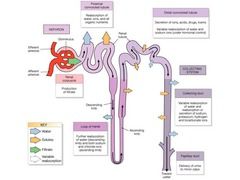
|
Nephron- Removal of Waste Products From Blood
Renal corpuscle --> Proximal Convoluted Tubule (water/solute reabsorption) --> Nephron Loop (descending-water loss, ascending-solute loss) --> Distal Convoluted Tubule (secretion of ions, toxins, drugs; variable water reabsorption) --> Collecting Duct --> Papillary Duct (drain to minor calyx) --> Renal Pelvis --> Ureter |
|
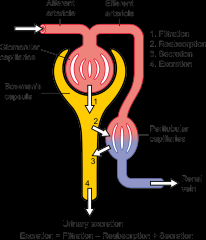
|
Renal Circulation- Blood through Kidneys Gets Filtered
Renal Artery --> Segmental Arteries--> Interlobar arteries--> Arcuate arteries--> Cortical Radiate arteries--> Afferent arterioles --> glomerulus--> efferent arteriole --> Peritubular Capillaries --> Venules --> cortical radiate veins --> arcuate veins --> interlobar veins--> renal veins
|
|
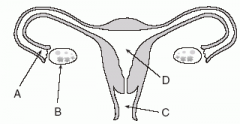
|
Female Reproductive Anatomy
A: Fallopian Tube (Fimbrae, Infundibulum, Ampulla, Isthmus) B: Ovary C: Vagina (Lined with rugae) D: Uterus |
|
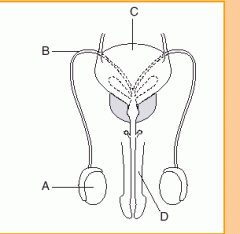
|
Male Reproductive Anatomy
A: Testicles B: Ductus Deferens C: Bladder D: Penis |
|
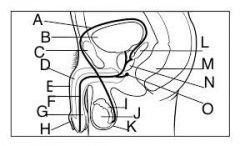
|
Male Anatomy
A: Ductus Deferens B: Bladder C: Pubic Symphysis D: Corpus Cavernosum E: Penis F: Urethra G: Corpus spongiosum H: Foreskin I: Epididymis J: Testis K: Scrotum L: Seminal Gland M: Rectum N: Prostate O: Bulbo-urethral Gland |
|
|
Path of sperm |
Epididymis --> Ductus Deferens --> Ejaculatory Duct --> Urethra |
|
|
Actions of Estrogen |
Stimulation of bone growth Maintaining accessory reproductive organs Maintain secondary sex characteristics Initiating repair of endometrium |
|
|
Spermatic cord |
Bundle of tissue that contains the ductus deferens, blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics that serve the testis |
|
|
Site of sperm maturation |
epididymis |
|
|
Secretes testosterone |
interstitial cells of testes |
|
|
Spermatogenesis |
1. spermatogonium --> 1 spermatocyte, 1 spermatogonium 2. spermatocyte--> meiosis, secondary spermatocytes 3. Secondary spermatocytes-->meiosis 2, 4 haploid spermatids 4. spermatids--> spermiogenesis (maturation)--> spermatozoa |
|
|
Oogenesis |
1. oogonium--> 1 oogonium, 1 diploid primary oocyte 2. primary oocyte --> meiosis 1, 1 polar body, diploid secondary oocyte 3. polar body--> 2 polar bodies/ secondary oocyte --> 3rd polar body, mature ovum (haploid) |

