![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
167 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the production site of follicle stimulating hormone?
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
What is the production site of luteinizing hormone?
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
What is the production site of adrenocorticotropic hormone?
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
What is the production site of thyroid-stimulating hormone?
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
What is the production site of prolactin?
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
What is the production site of growth hormone?
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
What is the production site of oxytocin?
|
hypothalamus/posterior pituitary
|
|
|
What is the production site of antidiuretic hormone?
|
hypothalamus/posterior pituitary
|
|
|
FSH is
|
follicle stimulating hormone
|
|
|
LH is
|
luteinizing hormone
|
|
|
ACTH is
|
adrenocorticotropic hormone
|
|
|
TSH is
|
thyroid-stimulating hormone
|
|
|
PRL is
|
prolactin
|
|
|
hGH is
|
growth hormone
|
|
|
OT is
|
oxytocin
|
|
|
ADH is
|
antidiuretic hormone
|
|
|
What is the target site of follicle stimulating hormone?
|
ovaries/testes
|
|
|
What is the target site of luteinizing hormone?
|
ovaries/testes
|
|
|
What is the target site of adrenocorticotropic hormone?
|
adrenal cortex
|
|
|
What is the target site of thyroid-stimulating hormone?
|
thyroid
|
|
|
What is the target site of prolactin?
|
mammary glands
|
|
|
What is the target site of growth hormone?
|
skeletal muscle, bone, cartilage, liver
|
|
|
What is the target site of oxytocin?
|
uterus, breasts/mammary glands
|
|
|
What is the target site of antidiuretic hormone?
|
kidneys/arterioles
|
|
|
What hormone stimulates oocyte development and testosterone production?
|
follicle stimulating hormone
|
|
|
What hormone stimulates ovulation and testosterone production?
|
luteinizing hormone
|
|
|
What hormone stimulates glucorticoids (cortisol)?
|
adrenocorticotropic hormone
|
|
|
What hormone stimulates the synthesis/secretion of T3/T4?
|
thyroid-stimulating hormone
|
|
|
What hormone stimulates milk production?
|
prolactin
|
|
|
What hormone stimulates IGF synthesis that triggers protein anabolism, lipolysis, decreased glucose uptake?
|
growth hormone
|
|
|
What hormone stimulates smooth muscle contraction in wall of uterus, milk ejection?
|
oxytocin
|
|
|
What hormone increases water reabsorption and constriction of arterioles?
|
Antidiuretic hormone
|
|
|
When ACTH acts on its target site(?), what is the response?
|
adrenal cortex/increase cortisol reduce stress
|
|
|
When TSH acts on its target site (?) what is the response?
|
thyroid/increase T3/T4, increase basal metabolic rate
|
|
|
When hGH acts on its target site (?) what is the response?
|
skeletal muscle, bone, cartilage, liver/increased growth, increase blood sugar level
|
|
|
When ADH acts on its target site (?) what is the response?
|
kidneys, arterioles/increase blood volume, decrease urine production, decrease H2O loss in sweat, increase blood pressure
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for ACTH?
|
stress, decreased cortisol levels
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for TSH?
|
low T3/T4 – decreased basal metabolic rate
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for hGH?
|
hypoglycemia
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for antidiuretic hormone?
|
dehydration/low blood volume
|
|
|
What is the hormone produced in the thyroid from the follicular cells?
|
T3/T4
|
|
|
What is the target site for T3/T4?
|
general body
|
|
|
What does increased T3/T4 do (action)?
|
increased glycolysis and lipolysis
|
|
|
What is the response for T3/T4?
|
increased BMR
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for T3/T4?
|
low BMR, increased TSH
|
|
|
When BMR is low and there is increased TSH, which hormone is stimulated?
|
T3/T4
|
|
|
What hormone’s action is increased glycoloysis and lipolysis?
|
T3/T4
|
|
|
What hormone, when stimulated, increases BMR?
|
T3/T4
|
|
|
T3/T4 is produced where?
|
thyroid/follicular cells
|
|
|
What is the hormone produced in the thyroid from the parafollicular cells?
|
calcitonin
|
|
|
What is the target site for calcitonin?
|
osteoclasts
|
|
|
What does increased calcitonin do (action)?
|
inhibits osteoclasts
|
|
|
What is the response for calcitonin?
|
decreased blood calcium
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for calcitonin?
|
high blood calcium
|
|
|
When blood calcium is high, which hormone is stimulated?
|
calcitonin
|
|
|
What hormone’s action is inhibiting osteoclasts?
|
calcitonin
|
|
|
What hormone, when stimulated, decreases blood calcium?
|
calcitonin
|
|
|
Calcitonin is produced where?
|
thyroid/parafollicular cells
|
|
|
What is the hormone produced in the parathyroid gland?
|
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
|
|
|
What is the target site for PTH?
|
osteoclasts
|
|
|
What does increased PTH do (action)?
|
stimulates osteoclasts
|
|
|
What is the response for PTH?
|
increased blood calcium
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for PTH?
|
low blood calcium
|
|
|
When blood calcium is low, which hormone is stimulated?
|
PTH
|
|
|
What hormone’s action is stimulating osteoclasts?
|
PTH
|
|
|
What hormone, when stimulated, increases blood calcium?
|
PTH
|
|
|
PTH is produced where?
|
parathyroid gland
|
|
|
What is the hormone produced in adrenal medulla?
|
epinephrine/norepinephrine
|
|
|
What is the target site for EPI/NE?
|
heart, lungs, liver
|
|
|
What does increased EPI/NE do (action)?
|
stimulates all sympathetic responses: increased HR, glycolysis, lipolysis, glycogenolysis
|
|
|
What is the response for EPI/NE?
|
increased O2 and BSL
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for EPI/NE?
|
stress/fight or flight
|
|
|
When the bodies stress/fight or flight responses are stimulated, which hormone is being stimulated?
|
EPI/NE
|
|
|
What hormone’s action is stimulating the sympathetic NS responses ?
|
EPI/NE
|
|
|
What hormone, when stimulated, increases O2 and BSL?
|
EPI/NE
|
|
|
EPI/NE is produced where?
|
adrenal medulla
|
|
|
What is the hormone produced in the adrenal cortex?
|
cortisol
|
|
|
What is the target site for cortisol?
|
general body/liver
|
|
|
What does increased cortisol do (action)?
|
glucose homeostasis, increased gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, protein catabolism
|
|
|
What is the response for cortisol?
|
decreased stress, increased BSL
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for cortisol?
|
increased stress
|
|
|
When there is increased stress to the body, which hormone is stimulated?
|
cortisol
|
|
|
What hormone’s action is glucose homeostasis?
|
cortisol
|
|
|
What hormone, when stimulated, decreases stress and increases BSL?
|
cortisol
|
|
|
cortisol is produced where?
|
adrenal cortex
|
|
|
What is the hormone produced from the alpha cells in the pancreas?
|
glucagon
|
|
|
What is the target site for glucagon?
|
liver, general body
|
|
|
What does increased glucagon do (action)?
|
raises BSL, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, lipolysis
|
|
|
What is the response for glucagon?
|
increased BSL
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for glucagon?
|
hypoglycemia
|
|
|
When blood sugar is low, (hypoglycemia), which hormone is stimulated?
|
glucagon
|
|
|
What hormone’s action raising BSL by glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and lypolysis?
|
glucagon
|
|
|
What hormone, when stimulated, increases BSL?
|
glucagon
|
|
|
glucagon is produced where?
|
alpha cells of the pancreas
|
|
|
What is the hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancrease?
|
insulin
|
|
|
What is the target site for insulin?
|
liver, general body
|
|
|
What does increased insulin do (action)?
|
lowers BSL through glycogenesis, lypogenesis, glycolysis
|
|
|
What is the response for insulin?
|
decreased BSL/hyperglycemia
|
|
|
What is the stimulus for insulin?
|
high BSL
|
|
|
When BSL is high, which hormone is stimulated?
|
insulin
|
|
|
What hormone’s action is lowering BSL through glycogenesis, lipyogenesis, glycologysis?
|
insulin
|
|
|
What hormone, when stimulated, decreases BSL?
|
insulin
|
|
|
Insulin is produced where?
|
beta cells of the pancrease
|
|
|
Name four sympathetic responses that are triggered with EPI/NE is stimulated?
|
increased HR, glycolysis, lipolysis, glycogenolysis
|
|
|
Name three ways cortisol maintains glucose homeostasis
|
through increased gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, protein catabolism
|
|
|
Name three ways glucagon raises BSL
|
glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, lipolysis
|
|
|
Name three ways insulin lowers BSL
|
glycogenesis, lipogenesis, glycolysis
|
|
|
What turns adrenocorticotropic hormone off?
|
corticotropin
|
|
|
what turns thyroid stimulating hormone off?
|
thyrotropin
|
|
|
what turns growth hormone off?
|
somatostatin
|
|
|
What do the ovaries produce?
|
estrogen, progesterone, inhibin
|
|
|
What produces estrogen, progesterone, inhibin?
|
ovaries
|
|
|
What do the testes produce?
|
testosterone, inhibin
|
|
|
What produces testosterone and inhibin?
|
testes
|
|
|
What does the pineal gland produce?
|
melatonin
|
|
|
What produces melatonin?
|
the pineal gland
|
|
|
What does the thymus produce?
|
thymosin
|
|
|
What produces thymosin?
|
the thymus
|
|
|
What does Diabetes Mellitus stem from?
|
an inability of glucose to be taken into the cell
|
|
|
What is diabetic neuropathy?
|
nerve damage that leads to foot ulcers, and lower extremity aputations
|
|
|
What is diabetic retinopathy?
|
damage to the retina
|
|
|
What is diabetic nephropathy
|
kidney failure
|
|
|
diabetes mellitus is known as what?
|
sugar diabetes
|
|
|
diabetes insipidus is also known as what?
|
water diabetes
|
|
|
There are three types of diabetes mellitus, what are they?
|
Type 1, Type 2, gestational diabetes
|
|
|
Which type of diabetes mellitus is insulin dependent?
|
type 1
|
|
|
Hypersecretion of hGH in adults will result in?
|
acromegaly
|
|
|
Hyposecretion of ADH will result in ?
|
diabetes insipidus
|
|
|
Hypersecretion of hGH in children will result in?
|
pituitary gigantism
|
|
|
Hyposecretion of cortisol and aldosterone results in?
|
addison’s disease
|
|
|
Hypersecretion of cortisol results in?
|
cushing’s syndrome
|
|
|
Hyposecretion of insulin results in?
|
diabetes mellitus
|
|
|
Hyposecretion of T3/T4 in infancy results in?
|
cretenism
|
|
|
Hyposecretion of T3/T4 after infancy results in?
|
hashimoto’s disease
|
|
|
Hypersecretion of T3/T4 results in?
|
Grave’s disease
|
|
|
Glucose is what type of saccharide?
|
monosaccharide
|
|
|
What is glycogen?
|
the storage form of glucose
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in glycogenolysis
|
glucagon,EPI/NE,hGH
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in glycogenesis
|
insulin
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in glycolysis
|
T3/T4, EPI/NE, hGH, insulin
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in gluconeogenesis
|
glucagon, cortisol
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in lipolysis
|
T3/T4, cortisol, hGH, EPI/NE, glucagon
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in lipogenesis
|
insulin
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in protein synthesis
|
insulin, T3/T4, hGH
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in protein breakdown
|
cortisol
|
|
|
What is another name for the anterior pituitary?
|
adenohypophysis
|
|
|
What is another name for the posterior pituitary?
|
neurohypophysis
|
|
|
The “Flat Peg” hormones are found in the anterior or posterior pituitary?
|
anterior
|
|
|
The medulla of the adrenal gland is stimulated by what?
|
the sympathetic NS
|
|
|
99% of cells in the pancrease are….
|
acini cells
|
|
|
1% of cells in the pancrease are….
|
islets of langerhans
|
|
|
The acini cells in the pancrease produce enzymes/hormones?
|
enzymes
|
|
|
The islets of langerhans produce enzymes/hormones?
|
hormones
|
|
|
What is the action of thymosin?
|
matures T cells making them immunocompetent
|
|
|
Endocrine has/has no ducts?
|
has none
|
|
|
Exocrine has/has no ducts?
|
has ducts
|
|
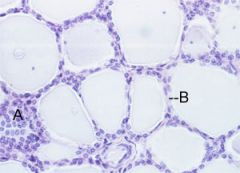
What tissue is this? Cells can be seen? What hormones are made here? What disorders are associated with this?
|
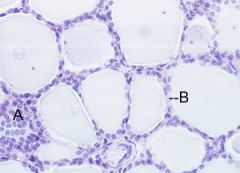
Thyroid
Follicular, parafollicular, follicles T/3-T4, calcitonin Grave's disease, Hashimoto's disease |
|
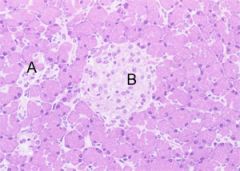
what is this? What cells can be seen? What hormones are made here? Where? What disorders are associated with this tissue?
|
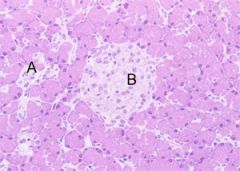
Pancreas, acini cells/islets of langerhans, glucagon/insulin, alpha cells/beta cells, diabetes mellitus
|
|
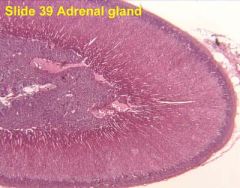
What is this? What hormones are produced here? Where? What disorders are associated with it?
|
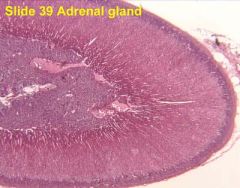
Adrenal, cortisol/aldosterone - EPI/NE - cortex/medulla, Cushing's syndrome/Addison's disease
|
|
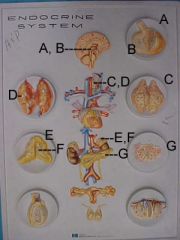
Name A, B, C, D, E and F
|
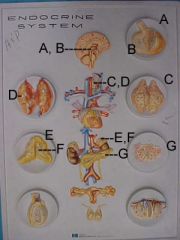
A - Anterior Pituitary
B - posterior pituitary C - thyroid D - parathyroid E - adrenal cortex F - adrenal medulla |
|
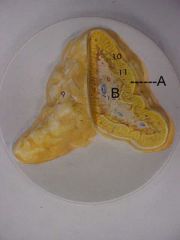
Name A and B
|
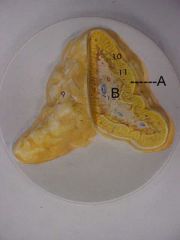
A - adrenal cortex
B - adrenal medulla |
|
|
Name A and B
|
A - posterior pituitary
B - anterior pituitary |
|
|
What is the stimulus for aldosterone?
|
decrease in BP/blood volume
|
|
|
A decrease in BP/blood volume stimulates the secretion of what hormone?
|
aldosterone
|
|
|
what is the target site of aldosterone?
|
kidneys
|
|
|
what is the action that occurs when aldosterone reaches the kidneys?
|
increases Na+/H20 absorption, K+ secretion
|
|
|
what is the response for aldosterone?
|
increase in BP/blood volume
|

