![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
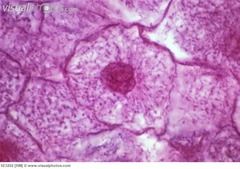
|
Interphase not dividing nucleus with membrane |
|
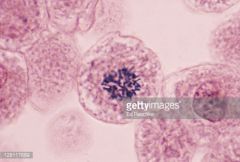
|
Prophase Dense, star like Nuclearenvelope dissipates |
|
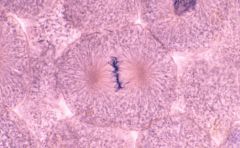
|
Metaphase Metaphysicalplate |
|
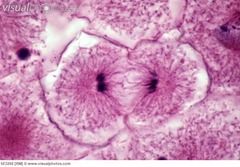
|
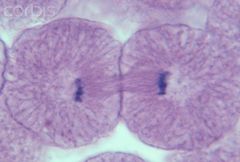
Anaphase separation begins |
|
|
Telophase |
|
|
4“primary” tissues |
Epithelial Connective- biggest Muscle Nervous |
|
|
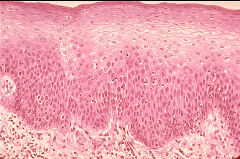
Squamous Thin, lots of cytoplasm, small nucleus. Lookslike a fried egg. Lines the ureters, lungs, blood vessels, skin |
|
|
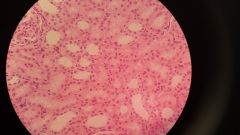
Cuboidal Smaller cells, less cytoplasm In urogenital system: kidneys |
|
|
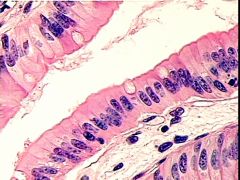
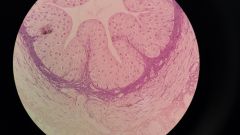
Columnar Elongated, cylindrical Goblet cells can be present Stomach |
|
|
Transitional in urinarybladder and ureter Small look cuboidal Half the size of squamous cells They can stretch |
|
|
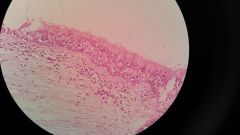
PseudostratifiedColumnar- not stratified but look stratified · columnar · All cells couch the bottom layer · In the respiratory system- trachea· May have cilia, microvilli, and/or brush border |
|
|
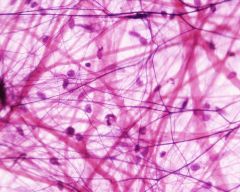
Areolar Connective Tissue disorganized, fibers in all directions In the skin, hypodermis, strong, flexible |
|
|
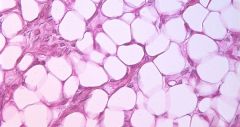
Adipose- fat Connective Tissue |
|
|
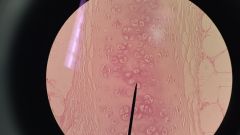
Hyaline cartilage- Connective Tissue smooth, often coveringsomething, at the ends of long bones, ribs, layrnx |
|
|
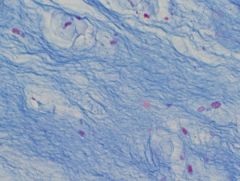
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue very strong, acts as acushion to buffer the space between 2 bones Ex.Disk in between vertebra |
|
|
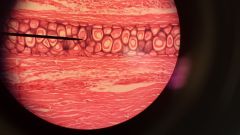
3. Elastic Cartilage Connective Tissue - flexible, strong, bendy Ear pinna, epiglottis, retinoids |
|
|
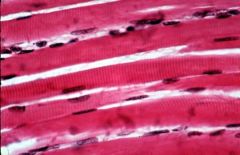
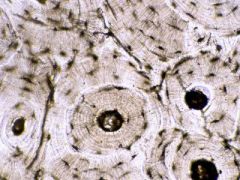
Skeletal muscle many long cells in parallel Multinucleatedin each muscle cell Hasstriations, best visible at the end |
|
|
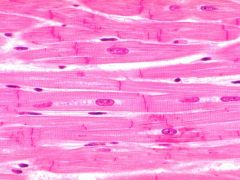
Cardiac muscle striated Single nucleus Intercalateddisk (a dark line) |
|
|
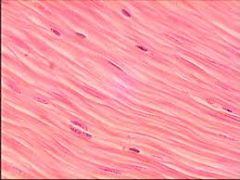
Smooth muscle (insphincter) - do not have striations Thin closely packed together Single nucleus |
|
|
Osseous tissue Connective Tissue |
|

|
Nervous tissue |
|
|
Basophil Granular- lots of granules! Connective Tissue |
|
|
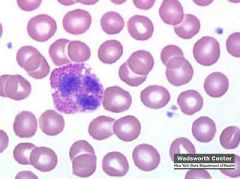
Eosinophil bi-lobed nucleus Granular Connective Tissue |
|
|
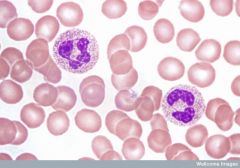
Neutrophil Granular Multi-lobes nucleus Cheeto Connective Tissue |
|
|
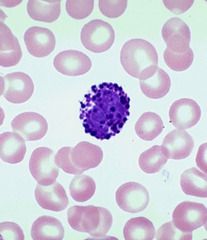
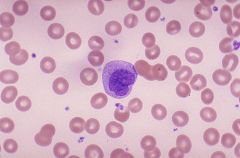
Lymphocyte Agranular large nucleus, small cytoplasm Connective Tissue |
|
|
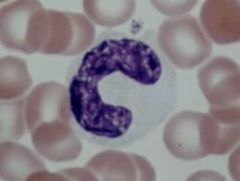
Monocyte Agranular cheeto puff Connective Tissue |
|
|
Bronchial Tree |
1. Primary/Mainstem 2. Secondary/lobar 3. Tertiary 4. Terminal 5. Aveolar ducts 6. Aveoli |
|
|
5 passageways of the Pharynx |
Eustachian tubes oral cavity Trachea Nasal cavity Esophagus |
|
|
The five layers of the epidermis |
1 Stratum corneum 2 Stratum lucidum 3 Stratum granulosum 4 Stratum spinosum 5 Stratum basale |
|
|
Position of esophagus and trachea |
esophagus is dorsal to the trachea trachea is ventral to esophagus |
|
|
Gastric Mucosal layers |
1 Serosa - top layer 2 Muclaris a longitudinal b circular c oblique 3 submucosa 4 Mucosoa- bottom layer |
|
|
Peyers patches |
patches of lympatic tiseu built into the wall of the ileum |
|
|
Falciform ligament |
anchors the liver to the wall of the abdomen |
|
|
Coronary ligament |
anchors the bloes of the liver together |
|
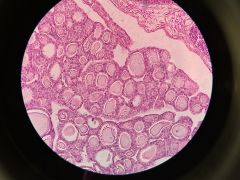
|
Thyroid |
|
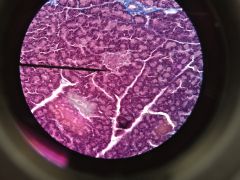
|
Pancreas Acini cells Islet of Langerhans |
|
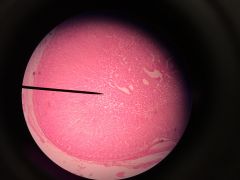
|
Adrenal gland Glomerulosa- darker, most dense Fasciulata- lighter reticularis- darker, more nuclei Medulla- lighter and has more open spaces |
|
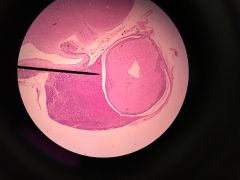
|
Pituitary Gland Anterior- darker, heavily nucleated Pars intermedia- around the Posterior |
|
|
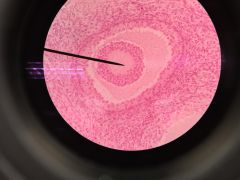
Ovary Oocyte zona pellucida- around Oocyte Corona radiata- around that grandulosa cells |
|
|
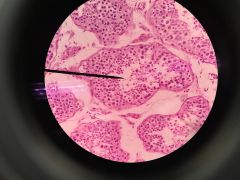
Testes sertoli cells & spermatogenic cells seminiferous tubule |
|
|
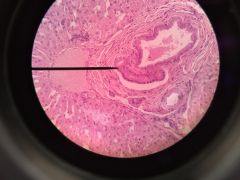
Liver Portal hepatic Artery- Portal Vein- biggest? bile duct- smaller Kupffer cells, hepatacytes Sinusoid |
|
|
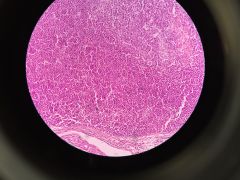
Parathyroid made up of Chief cells |

