![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Robert Hook 1663
|
Empty cells of cork
|
|
|
Schwann
|
All animals made of cells
|
|
|
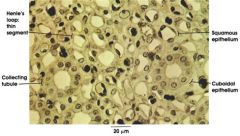
Cell Types
|
Cuboidal
Squamous Columnar |
|
|
Cuboidal
|
"dice shapped" w/ spherical nucleus
Glandular tissue Function to secrete |
|
|
Squamous
|
Flattened cells w/ oval nucleus
Epithelial tissue - skin and esophagus lining Function to protect |
|
|
Columnar
|
column shaped w/ ovoid nucleus
lines the intestine, trachea, bronchi function to absorb |
|
|
Descriptive terms for cells
|
simple
statified ciliated |
|
|
simple
|
one layer of cells
|
|
|
stratified
|
more than one layer of cells
|
|
|
ciliated
|
cell has hair-like projections to sweep or clean
|
|
|
squamous
|
|
|
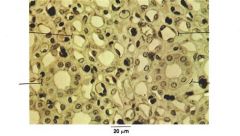
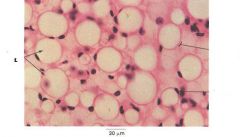
adipose
|
|
|
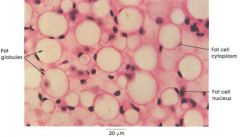
adipose labled
|
|
|
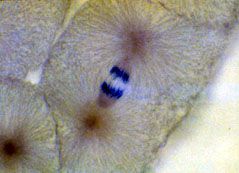
anaphase - chromosomes begin to separate
|
|
|
areolar connective tissue
|
|

|
areolar connective tissue labeled
|
|
|
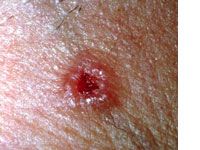
nodular basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
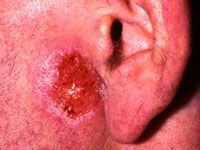
superficial basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
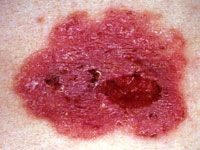
ulcerated basel cell carcinoma
|
|
|
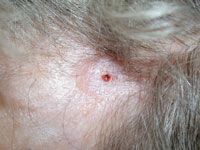
Morphoeic basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
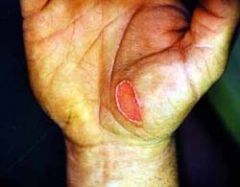
2nd degree burn partial thickness burn to palm of hand
|
|
|
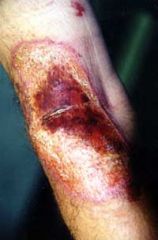
2nd degree burn "partial thickness", nylon jacket, no sign of infection
|
|
|
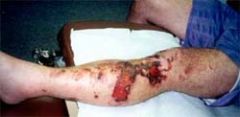
3rd degree, severe burn, 3 days before treatment was sought, burn w/ infection
|
|
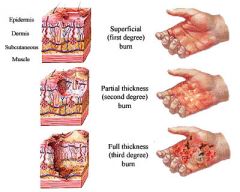
|
burn classifications
|
|
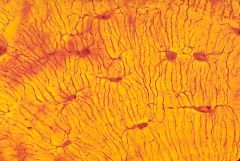
|
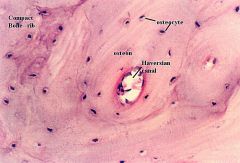
canalunli and lacunae
|
|
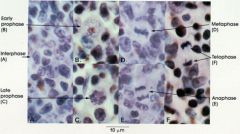
|
cell division
|
|
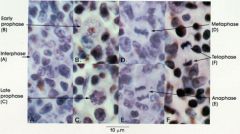
|
cell division 1
|
|
|
cell types labeled
|
|
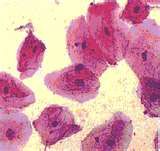
|
cheek cells
|
|
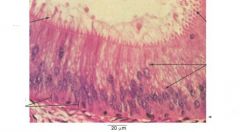
|
stereo ciliated columnar
|
|
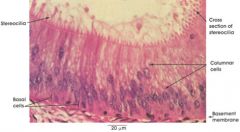
|
stereo ciliated columnar labeled
|
|
|
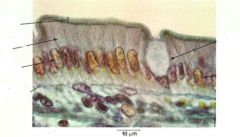
columnar cells w goblet cell (produces mucus)
|
|
|
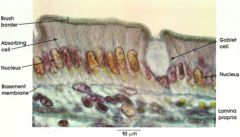
columnar cells labeled
|
|
|
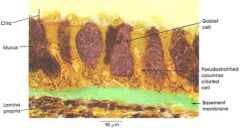
columnar epithoidal cilliated cells with globlet cells
|
|
|
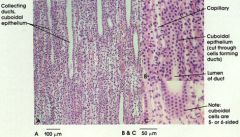
cuboidal cells
|
|
|
cuboidal cells labeled
|
|
|
dense irreg
|
|

|
dense reg
|
|
|
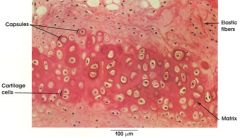
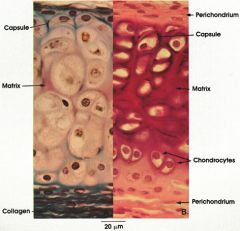
elastic cartilage
|
|
|
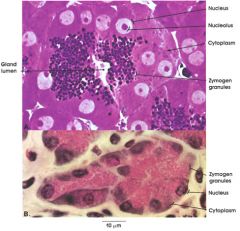
glandular acinar cells
|
|
|
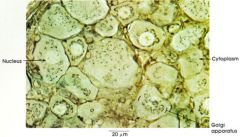
golgi apparatus
|
|
|
hyaline cartilage labeled
|
|
|
labeled osteon
|
|
|
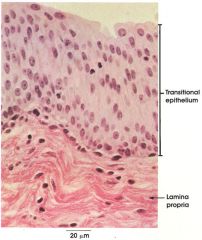
lamina propria transitional epitheleum
|
|
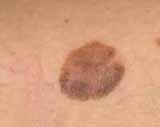
|
early superficial spreading melanoma
|
|
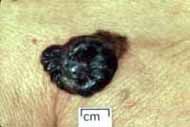
|
nodular melanoma
|
|
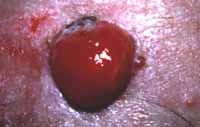
|
nodule melanoma
|
|
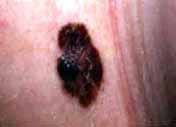
|
nodule in spreading melanoma
|
|
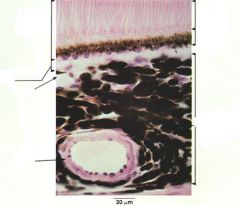
|
melanocytes labeled
|
|
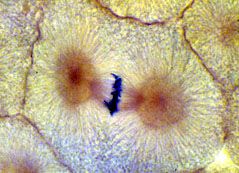
|
metaphase -
chromosomes line up on equatorial plate of dividing cell |
|
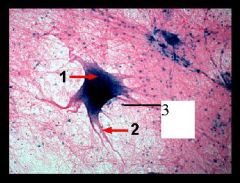
|
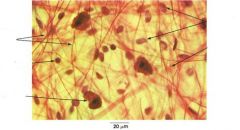
nerve cell labeled
|
|
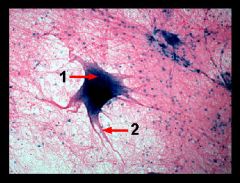
|
nerve cell smear
|
|
|
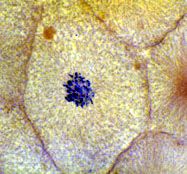
prophase -
chromosome condense nuclear envelope disapears centrioles divide and migrate to opposite poles of cell spindle fibers form and attach to chromosomes |
|
|
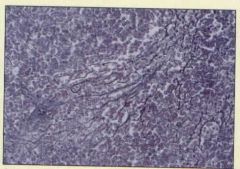
reticular
|
|
|
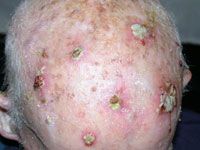
squamous cell carcinoma's that's yet to matasticize
|
|
|
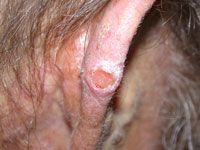
squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
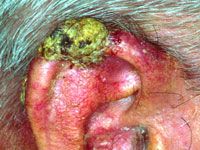
matasticized squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
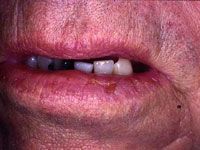
metastasized squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
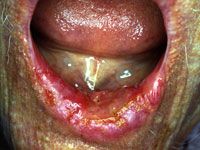
matasticized squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
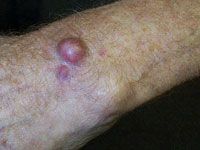
nodular systemic basal cell or melenoma
|
|
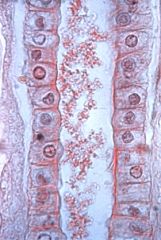
|
simple cuboidal
|
|
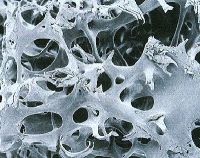
|
spongy bone
|
|
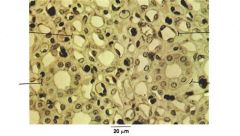
|
squamous and cuboidal
|
|
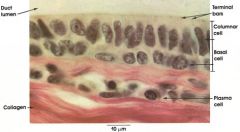
|
stratified columnar
|
|
|
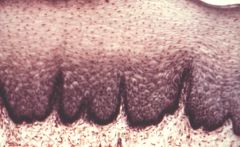
stratified squamous
|
|
|
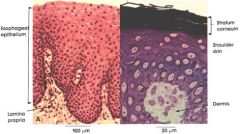
stratified squamous
|
|
|
telophase -
chromosomes migrate to opposite poles new nuclear envelope forms chromosomes uncoil |
|
|
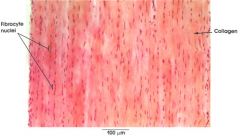
tendon
|
|
|
cell membrane
|
Semi-permeable outer covering of cell that defines boundaries.
Has a fluid structure made of phospholipids and proteins and has receptor sites for communication by chemical signals. |
|
|
microvilli
|
1-2micrometers
major job: increase surface area. Found on cells specialized for absorption. Brush border or fringe on some cells. |
|
|
Cilia (Stereo Cilia)
|
Hairlike processes about 7-10 micrometers.
Move mucus thru respiratory tract or move egg cells thru Fallopian tube |
|
|
Flagellum
|
Long whip-like structure like the tail of a sperm
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
contents of the cell between the plasm membrane and the nuclear envelope
|
|
|
Cytosol
|
Clear, gelatinous substance which holds the organelles, cytoskeleton and inclusions
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
Largest organelle
surrounded by nuclear envelope Houses DNA |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
|
system of interconnected channels called "cisternae"
Rough ER: covered w ribosomes, flattened sacs Smooth ER: lacks ribosomes, more tubular shaped |
|
|
Rough ER:
|
Covered w/ ribosomes, flattened sacs
Produce phospholipids & proteins of the plasma membrane Synthesizes proteins |
|
|
Smooth ER:
|
More tubular shaped & lacks ribosomes
Synthesises steroids, lipids Detoxifies alcohol & other drugs Manufactures all of the membranes of the cell |
|
|
Ribosomes
|
Reads genetic mesages from nucleus
Assembles acids into proteins |
|
|
Golgi Complex - Golgi Apparatus
|
Small sys of cisternae
Synthesize carbohydrates Finish protein and glycoprotein synthesis Resembles a stack of pita bread Sorts, cuts, splices proteins and adds carbohydrates to some Packages proteins |
|
|
Peroxisomes
|
neutralize free radicals
Detoxifies alcohol & other drugs Kills bacteria Breaks down fatty acids |
|
|
Mitochondria
|
Energy extracted from organic compounds and transferred to ATP
"Powerhouse of Cell" |
|
|
Centrioles
|
2 are located in centrosome
Assembly of microtubules Play roll in cell division |
|
|
Cytoskeleton
|
protein filaments
Determine shape of cell Structural shape of cell Structural support Move and organize contents of cell |
|
|
Inclusions (Vacules)
|
Stored cellular products: glycogen, pigments & fat droplets.
Foreign bodies: Dust, Viruses & bacteria |
|
|
Cell Cycle
|
sequence of events from one cellular division to another.
Interphase Mitosis prophase metaphase anaphase telophase |
|
|
Interphase
|
G1: RNA, protein & other molecules are synthesized
S: DNA is replicated, chromosomes become double stranded G2: mitochandria divide, precursors of spindle fibers are synthesized |
|
|
Mitosis
|
2nd part of cell cycle
4 parts: PMAT prophase metaphase anaphase telephase |
|
|
Cytokenesis
|
3rd part of cell cycle:
Cleavage furrow forms and deepens Cytoplasm divides (cellular division) |
|
|
Significance of cell cycle
|
essential in multicellular organisms
Some cells retain their capacity to divide: (ie: Bone marroe, epidermis,..) Some cells do not divide after adulthood (ie: most cells of nervous sys) |
|
|
Life span of cells (Hayflick limit)
|
Cells undergo a finite number of mitotic divisions
|
|
|
Aging disorders
|
Progeny- usually die by 14yrs
Werner Syndrom - usually die between 45-50 |

