![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bus topology is generally associated with
10Base__? and 10Base__? networks. |
Bus topology
is generally associated with 10Base2 and 10Base5 networks. |
|
|
10Base2 is also known as what?
|
"Thinnet"
|
|
|
10Base2 ("Thinnet") uses what cable?
|
10Base2 ("Thinnet") uses:
RG-58 coaxial cable. |
|
|
10Base5 is also known as what?
|
"Thicknet"
|
|
|
10Base5 ("Thicknet") uses what cable?
|
10Base5 ("Thicknet") uses:
RG-8 Cable |
|
|
10Base2 has a max
Max Segment length? and Max Speed?_____Mbps |
10Base2 has a max
Max Segment length: 185m and Max Speed?_10Mbps |
|
|
10Base5 has a max
Max Segment length? and Max Speed?_____Mbps |
10Base5 has a max
Max Segment length? 500m and Max Speed? 10Mbps |
|
|
List the 5 network topologies.
|
1. Bus
2. Star 3. Ring 4. Mesh 5. Hybrid |
|
|
Mesh topology description:
|
All Systems are interconnected with the other devices
|
|
|
Ring topology description:
|
All systems are connected through a bus with the ends joined. A token is passed around the ring and stops while a device passes data.
|
|
|
Usual speed of a Ring network?
|
16Mbps
|
|
|
Bus 10Base2 topology description:
|
All devices are tapped into a bus with a BNC 'T' the ends of the cable are terminated with a resistor.
|
|
|
What is the rating of a BNC Terminator for 10Base5 or 10Base2 network?
|
50 Ohm BNC Terminator
|
|
|
What is an advantage of Mesh topology?
|
Very robust. This network functions with redundant links and alternate pathways. Multiple devices could be "down" and the net would still function 24x7hour access.
|
|
|
Disadvantage of Mesh topology?
|
Expensive.
|
|
|
Mesh Topology is used in what situations, primarily?
|
Network Backbones... ties devices together that are mission critical.
WAN links primarily. |
|
|
Star Topology advantages?
|
Price! Speed!
|
|
|
Category 1 Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 1 Cable:
Speed: 1Mbps Max Segment length? 4 feet |
|
|
Category 1 Cable:
What is it used for? |
Category 1 Cable:
Standard phone line. |
|
|
Category 2 Cable:
What is it used for? |
Category 2 Cable:
ISDN and T1 Lines |
|
|
Category 2 Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 2 Cable:
Speed: upto 4Mbps Max Segment length: 100 meters |
|
|
Category 3 Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 3 Cable:
Speed: 16Mbps Max Segment length: 100 meters. |
|
|
Category 3 Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 3 Cable:
Speed: 16 Mbps Max Segment length: 100 Meters |
|
|
Category 4 Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 4 Cable:
Speed: 20 Mbps |
|
|
Category 5 Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 5 Cable:
Speed: 100Mbps |
|
|
Category 5e Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 5e Cable:
Speed: 1000Mbps (Gigabit) Max Segment length: 100 Meters |
|
|
Category 6 Cable:
Speed? Max Segment length? |
Category 6 Cable:
Speed: 10 Gps (10 Gigabit) Max Segment Length: 100 Meters |
|
|
Category 3 Cable:
What is it used for? |
Category 3 Cable:
What is it used for? 10BaseT networks Max |
|
|
10BaseT max speed?
|
10BastT max speed:
10 Mbps |
|
|
Category 5 Cable:
What is it used for? |
100BaseT / Category 5 Cable:
It is used for: 100BaseTX networks |
|
|
Category 5e Cable:
What is it used for? |
Category 5e Cable:
1000BaseT It is used for: Gigabit /1000Mbps networks |
|
|
Category 6 Cable:
What is it used for? |
Category 6 Cable:
It is used for? 10 Gigabit Networks |
|
|
UTP stands for?
|
UTP Stands for:
Unshielded Twisted Pair |
|
|
STP Stands for?
|
STP Stands for:
Shielded Twisted Pair |
|
|
100BaseT is also referred to as _?_ ethernet?
|
100BaseT is also referred to as
"FAST" ethernet. |
|
|
MAU is what?
|
MAU: Multistation Access Unit
Logical Token Ring in a Physical Star topology. |
|
|
EEProm on a NIC contains programmed info. Name 3.
|
1. MAC (Media Access Control)
2. IRQ 3. I/O Memory Address Preference |
|
|
Plenum cable and STP cable are used in what type of applications?
Why? |
Business/Commercial under floor or dropped ceilings.
Because of building code and EMI considerations. |
|
|
100BaseFX refers to what?
|
Fiber Optic cable.
|
|
|
100BaseFX segment length?
|
100BaseFX segment length:
412 meters |
|
|
Types of Fiber Optic connectors: (5)
|
1. FC
2. MT-RJ 3. LC 4. SC 5. ST |
|
|
FC fiber optic
Application: DATACOM |

What type of connector is this?
Used for what application? |
|
|
MT-RJ fiber optic
Application: High Density Interconnection |

What type of connector is this?
Used for what application? |
|
|
LC fiber optic
Application: High Density Interconnection |
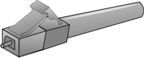
What type of connector is this?
Used for what application? |
|
|
SC fiber optic and
sc duplex Application: DATACOM |

What type of connector is this?
Used for what application? |
|
|
ST fiber optic
Used for what application: Inter-/Intra-Building, Security, Navy |

What type of connector is this?
Used for what application? |
|
|
ISDN?
ISDN (BRI) Speed? |
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
Speed: Basic Rate ISDN(BRI) = 128 Kbps (64K+64K=128) $75 - $125 per mo. |
|
|
DSL?
DSL Speeds? Cost? |
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
~5 Mbps on the average. $20-$40 per mo. |
|
|
DSL types (4)
|
DSL types (4)
4. VDSL 1. ADSL 2. SDSL 3. HDSL |
|
|
How close must one be to the phone company's central office or end loop?
|
20,000 feet. (less than 4 miles)
|
|
|
Digital cable disadvantage?
Price? |
Users share bandwidth.
Some days/times are faster than others. $20 - $40/mo. |
|
|
Satellite speed?
Satellite advantage? Price? |
1Mbps downstream / 200 Kbps up.
Can reach rural areas and faster than dialup. $100 per month. |
|
|
ATM?
What is it? Speeds/cable? |
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Fast LAN / WAN TECHNOLOGY USED IN ISDN, DSL AND OTHER BROADBAND. 25-2028Mbps w/ copper 10Gbps has been acheived. reserved for large corporations. |
|
|
Laplink
|
Serial and parallel networking two pcs peer to peer.
|

