![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does amplitude change in a soud?
|
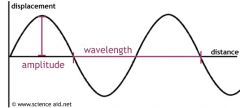
The volume. High amplitude = high volume Low amplitude = low volume |
|
|
What does wavelength change in a sound? |
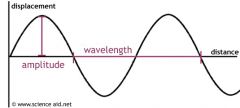
The pitch. long wavelength = low pitch short wavelength = high pitch |
|
|
What is the frequency of a sound? |
Frequency is the waves per second higher frequency = smaller wavelenght |
|
|
What is a convex lens? What does it do? |
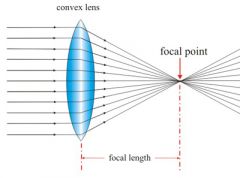
A convex lens is a converging lens. When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens the refracted rays converge at one point called the focal point. The distance between the focal point and the centre of the lens is called the focal length. |
|
|
What is a concave lens? What does it do? |
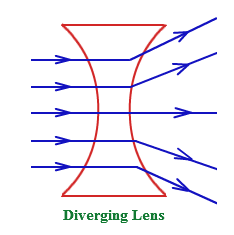
Concave lenses are thinner at the middle. Rays of light that pass through the lens are spread out (they diverge). When parallel rays of light pass through a concave lens the refracted rays diverge so that they appear to come from one point called the focal point. |
|
|
What is the 1st law of reflection?
|
The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Angles are measured from normal. |
|
|
What is the 2nd law of reflection?
|
the incident ray, the normal, at the point of incident and then reflected ray all lie at the same point.
|
|
|
Where is the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection measured from? |
The normal.
THE FLIPPING NORMAL. N O R M A L !!!!! |
|
|
What does amplitude change in light? |
The brightness. |
|
|
What does wavelength change in light? |
The colour. |
|
|
What is conduction? |
Heat directly transmitted through a solid when there is a difference of temperature between regions energy flowing through one particle to another. |
|
|
What is convection? |
Heat transfer of a fluid such as air or water, when the heated fluid is caused to move away from the source of heat, carrying energy with it. Convection above a hot surface occurs because hot air expands, becomes less dense, and rises |
|
|
What is radiation? |
Radiation is energy that comes from a source and travels through some material or through space. |

