![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ecosystem |

all the living and nonliving things in an area and their interactions |
|
|
biotic element |
something that grows changes, and makes other living things; Includes both, organisms that are currently alive, as well as organisms that were once alive (dead organisms); |
|
|
abiotic element |
an object/thing that is not alive; Examples: air, water, soil, sunlight; |
|
|
organism |
any living thing; (examples include: a plant, an animal, a bacteria, a virus) |
|
|
habitat |

a place that provides all the things an organism needs to live |
|
|
adaptation |
a structure or behavior that helps an organism survive in its environment |
|
|
producer |

organism that makes its own food for energy |
|
|
consumer |

organism that cannot make its own food |
|
|
carnivore |
an animal that eats other animals for food |
|
|
herbivore |
a consumer that eats only plants |
|
|
omnivore |
an organism that eats both plants and animals |
|
|
decomposer |

organism that gets its energy by breaking down wastes and dead organisms |
|
|
excrete |
to separate and eliminate from an organic body |
|
|
nitrogen cycle |

repeated movement of nitrogen through the environment in different forms |
|
|
niche |
a special role that a species fills in its habitat |
|
|
individual |
a single member of a population of organisms |
|
|
population |

a group of organisms of one species that live in an area at the same time |
|
|
community |

the group of all populations in an area |
|
|
food chain |

a series of steps by which energy moves from one type of living thing to another |
|
|
food web |

a diagram that combines many food chains into one picture |
|
|
predator |

a consumer that hunts and eats other animals |
|
|
prey |

an animal that is hunted by others for food |
|
|
nocturnal |
active at night |
|
|
competition |

the struggle among organisms for the same limited resources |
|
|
grazing animal (graze) |
herbivores that usually feed on grass |
|
|
symbiosis |
a long-term relationship between two different organisms where one organism is always helped. The other organism might be harmed, helped, or not affected. |
|
|
parasite |
an organism that lives in or on another organism (its host) and benefits by deriving nutrients at the host's expense. |
|
|
thrive |
to grow or develop well |
|
|
perish |
to die or be destroyed |
|
|
environment |

all of the conditions surrounding an organism |
|
|
impact |
direct effect or change on |
|
|
carrying capacity |
the population size an environment can feed and support |
|
|
oxygen (O2) |
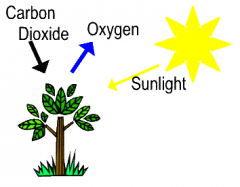
a gas produced by plants during photosynthesis that animals use for respiration |
|
|
carbon dioxide (CO2) |
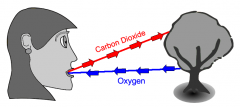
a gas produced by animals during respiration that plants use to make food, water and oxygen |
|
|
carbon cycle |

The movement of carbon on Earth by the processes of respiration and photosynthesis. (Oxygen is often involved in the processes in which carbon dioxide moves. This give-and-take of oxygen and carbon dioxide has many paths through an ecosystem.) |
|
|
respiration |
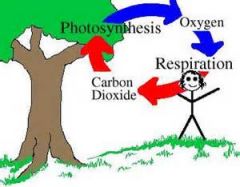
(breathing in and out) The process by which animals use oxygen and food to make energy and carbon dioxide |
|
|
photosynthesis |
The process where plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce food (sugar) and therefore release oxygen. |
|
|
Plants and Animals roles in the carbon and oxygen cycles |
Plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Animals take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. |

