![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Is a teratogen always a drug?
|
No, can be drug, chemical, infectious or physical agent, maternal dz, altered metabolic state (DM, fever)
|
|
|
What stage of pregnancy is most susceptible to teratogens?
Caveats? |
First trimester
Caveats: first two weeks generally unaffected by drug use as this is a period of pre-dx/dy and implantation (any major teratogens would cause loss of embryo at this time) |
|
|
Which organ system is susceptible to teratogens through the first 16 weeks of pregnancy?
|
CNS; it is the most susceptible organ system!
|
|
|
What is the placental mode of drug transfer?
What factors contribute to this transfer? |
Simple diffusion
Rate of diffusion determined by diffusion constant (determined by lipid solubility, MW, pH, binding) of drug, surface area, concentration gradient, thickness of epithelium |
|
|
What fetal factors affect drug transfer and effect?
|
Fetal placenta blood flow
Fetal circulatory distribution Drug clearance mechanisms (reduced hepatic metabolism, reduced enzymatic activity) |
|
|
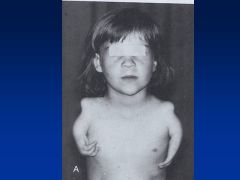
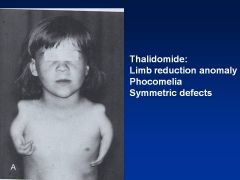
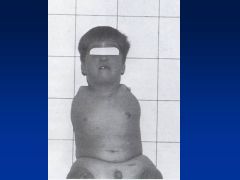
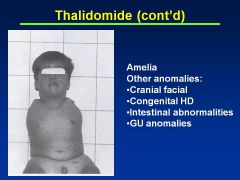
Thalidomide
|
Limb reduction anomaly
Symmetric defects Phocomelia (hands attached closed to trunk) Can also have absence of limbs (other anomalies: cranial facial, congenital HD, intestinal abnlts) |
|
|
ACE Inhibitors
|
1st trimester use: CV and CNS system defects
2nd, 3rd trimester: oligohydramnios w/pulm hyperplasia, joint contractures, hypocalvaria, renal failure, hypotn and death |
|
|
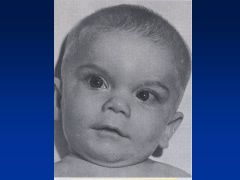
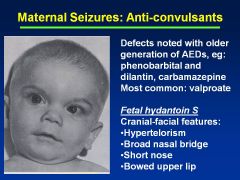
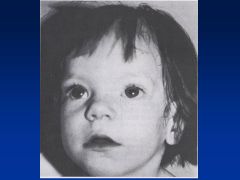
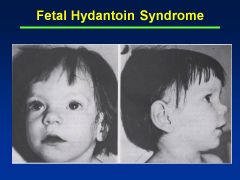
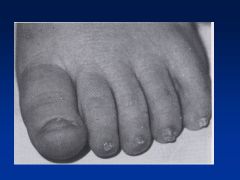
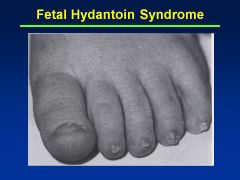
Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome:
Definition Causes |
Fetal hydantoin S:
Cranial-facial features--hypertelorism (inc'd dist b/t eyes), broad nasal bridge, bowed upper lip Cause = anti-convulsants; valproate, carbamazepine, phenobarbital |
|
|
Valproate
|
Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome
Reduced IQ (6-9 points) |
|
|
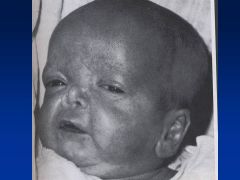
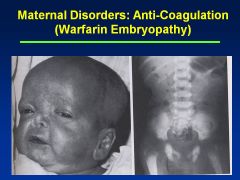
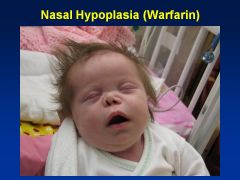
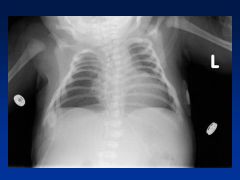
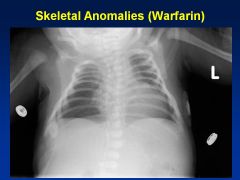
Warfarin
|
Embryopathy
Nasal/Facial hypoplasia Skeletal abnlts; calcifications of axial skeleton Prenatal growth deficiency Cognitive defects |
|
|
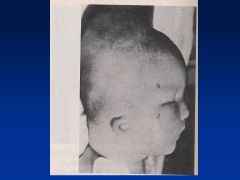
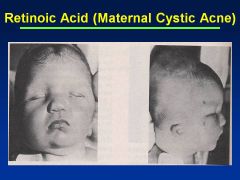
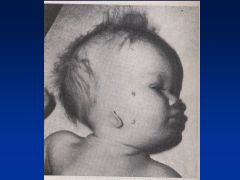
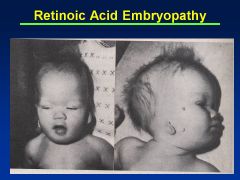
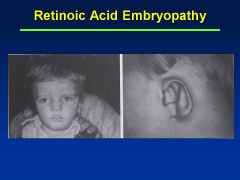
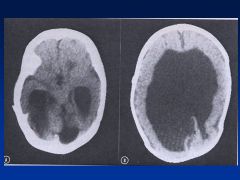
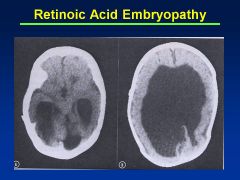
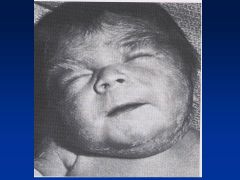
Accutane
|
Asymmetry to cranial vault
Uneven distribution of brain Huge ventricles In addition to facies (see images) |
|
|
What is the grace period for teratogenic effects of retinoic acid?
|
15 days
|
|
|
SSRI:
Effects Examples |
Paxil>Prozac, Celexa, Zoloft
No effects in 1st trimester Neonatal adaptation syndrome (3rd trimester use); respiratory distress, jitteriness, irritability (more common with Paxil) |
|
|
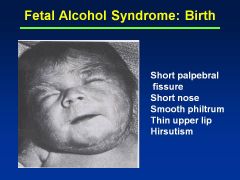
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
|
Growth restriction: pre- and postnatal growth deficiency
CNS dysfn |
|
|
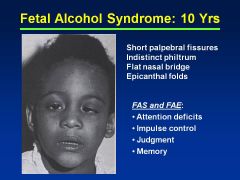
Fetal Alcohol Effects
|
Probably due to lower quantities of EtOH consumed during pregnancy
Attention deficits Impulse control Judgment issues Memory issues |
|
|
Cocaine
|
No embryopathy!
Placental abruptions Intrauterine growth restriction Prematurity CNS (infarct, schizencephaly, porencephaly) GI: atresias: gastrochisis (infant intestine sticks out through umbilical cord defect) INTENSE VASOCONSTRICTION |
|
|
Heroin
|
Absence of embryopathy!
Accelerates lung maturation Prenatal onset growth def Prematurity Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: Wakefullness Irritability Tremulousness, temp instab, tachyp Diaphoresis, diarrhea Rub marks, rhinorrhea Autonomic dysfn Weight loss Alkalosis Lacrimation |
|
|
Prevention of premature lung syndrome
|
Ante-natal steroids
|
|
|
Treatment of fetal arrhythmias
|
Digoxin, Procainamide (given to mother)
|
|
|
Prevention of neural tube defects
|
Folic acid
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

