![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Leydig and ____ Cell Tumors are usually [benign/malignant].
|
Leydig and Sertoli (supportive cells) tend to be benign; only make up 5% of testis ca
|
|
|
Most common type of tumor in testis.
|
Germ Cell (which is benign in women, but malignant in men!)
|
|
|
Types of Germ Cell Tumors in Men
|
Seminoma (45%), Embryonal Carcinoma (40%)
|
|
|
Subtypes of Embryonal Carcinomas.
|
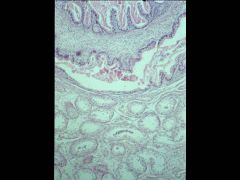
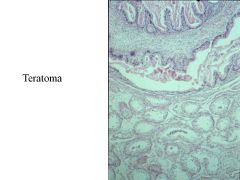
Somatic-->Teratoma
Extraembryonic-->Yolk Sac & Choriocarcinoma (placenta!!) |
|
|
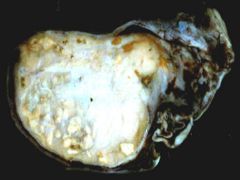
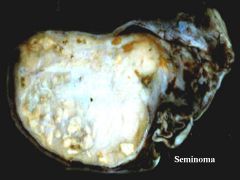
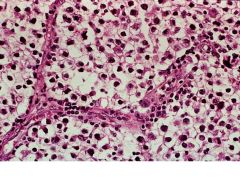
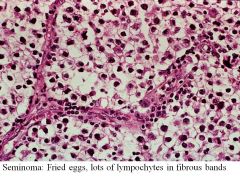
Presentation of Seminoma
Treatment |
Large, painless
Responsive to chemo Only mets during late in course |
|
|
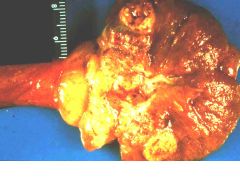
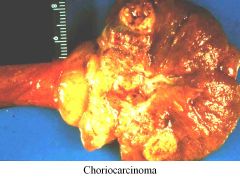
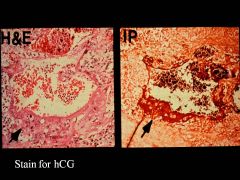
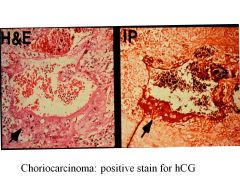
Choriocarcinoma:
Characteristics Presentation |
Wants to be a placenta, so tried invading blood vessels
Might present with mets in lungs Small primary lesion, spreads by blood vessel invasion MAKE HCG!!! |
|
|
This testicular tumor produces alpha-fetoprotein.
|
Yolk Sac Tumor
|
|
|
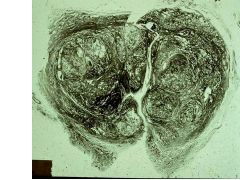
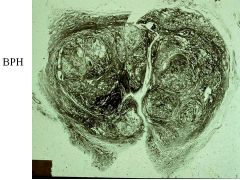
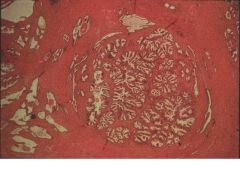
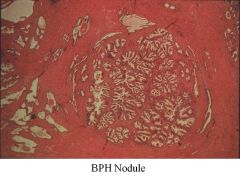
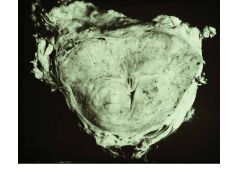
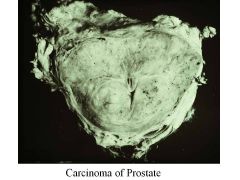
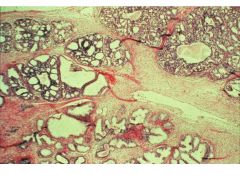
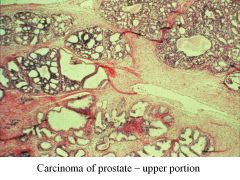
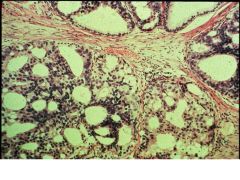
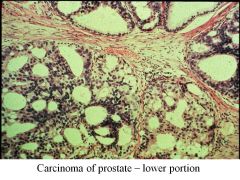
BPH vs Carcinoma of Prostate:
Locations affected |
BPH: periurethral area-->urinary syx, bladder infections, pyelonephritis
CaP: occurs away from urethra, so will not exhibit urinary syx early on in dz; posterior aspect (near rectum) |
|
|
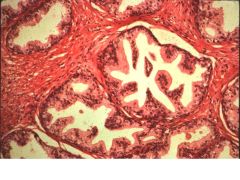
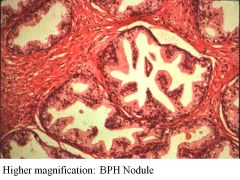
Glandular vs Smooth Muscle Nodules:
Treatment Example of each treatment (drug) |
Glandular Nodules: need nodules to proliferate, so need to remove them to tx them. Dec DHT via 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor (finasteride)
Smooth Muscle: relax SM mass via alpha-antagonist (terazosin) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

