![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
... |
Hi..... supercalifragilisticexpialidocious. |
|
|
What is a watershed? |
Land area that drains into a body of water. |
|
|
What is a tributary? |
Stream or river that flows into a larger stream, river, or lake. |
|
|
What lake does the St. Louis river start in? |
Seven Beavers Lake |
|
|
How long is the St. Louis River? |
192 miles |
|
|
What are the rivers that drain the St. Louis River watershed? |
St. Louis river, Cloquet river, Whiteface river |
|
|
What is an estuary? |
Where two chemically different bodies of water mix together in a shallow wetland area. |
|
|
What are the two main types of estuaries? |
Freshwater/saltwater. Freshwater/freshwater |
|
|
How many acres is the St. Louis river estuary? |
12,000 acres. |
|
|
How many miles long is the St. Louis river estuary? |
21 miles long |
|
|
What was the name of the last ice age? |
Wisconsin ice age. |
|
|
What is the name of the ice sheet that covered the northern half of North America? |
Laurentide ice sheet |
|
|
How long ago did the ice cover the northern part of North America? |
2.6 million to about 11,000 years ago. |
|
|
How thick was the ice of the last ice age? |
8-10 thousand feet thick. |
|
|
How long did it take for the ice of the last ice age to retreat completely? |
Over 10,000 years |
|
|
Explain how the glacier move across the ground. |
Weight of the thicker ice pushes down causing the thinner ice in front of it to move. |
|
|
Explain how a glacier carves out the Earth's surface. |
Weight of the extremely thick ice digs out the soft soil as the glacier moves. Pushes the soft materials along with the glacier as it moves. |
|
|
What is the soft material that glaciers carve out called? |
Till |
|
|
Describe a glacial valley. |
Trough - shaped, steep, near vertical cliffs. |
|
|
What is a glacial fjord and explain what happens. |
It is a glacial valley that forms near the ocean. Ice melts and retreats exposing valley to sea water. Creates a long, narrow inlet filled with sea water. |
|
|
How is a glacial lake formed? |
Glacier carves out a hole. Glacier melts, filling the hole or space that it has created with water. |
|
|
How many years ago did ice cover the Great Lakes area? |
About 15,000 years ago |
|
|
What river did the glacier start draining towards? |
Mississippi River |
|
|
How many years ago did the ice melt and retreat exposing all of the Great Lakes area? |
9,000 years ago |
|
|
Explain post glacial rebound. |
Weight of the glacier pushed ground down. Ground on edges of glacier was forced upward. |
|
|
What is matter? |
Anything with mass and volume. |
|
|
What is an atom? |
The smallest particle of Matter that can exist on its own. |
|
|
What is mass? |
Amount of stuff in an object. |
|
|
What is density? |
Amount of stuff in a given amount of space. |
|
|
What is atomic mass? |
Average number of protons and neutrons in atoms nucleus. |
|
|
Are most elements metals or non-metals? |
Metals. |
|
|
What are the properties of metals? |
Malleable, magnetic, good conductor of heat, good conductor of electricity, makes a "ting" sound when hit. |
|
|
What are the properties of matter? |
Measurable and observable characteristics that allow us to identify matter and tell it apart from other matter. |
|
|
What are the two types of properties of matter? |
Physical properties and chemical properties. |
|
|
What is a physical property? |
Characteristics of matter that can be observed without changing the matter. |
|
|
What are the two types of physical properties? |
Intensive and extensive. |
|
|
What is intensive physical properties? |
Properties of matter that do not depend on how much matter there is. |
|
|
Name thirteen intensive physical properties. |
•color •taste •melting point •freezing point •boiling point •density •luster •hardness •texture •odor •state of matter •malubility •solubility |
|
|
What is extensive physical properties? |
Properties of matter that do depend on how much matter there is. |
|
|
Name six extensive physical properties of matter. |
•mass •volume •weight •length •size •shape |
|
|
What is a physical change? |
Change in matter that does not change the identity of the matter. |
|
|
Name five examples of a physical change. |
•melting •freezing •molding clay •sanding wood •sugar dissolving in water |
|
|
What is a chemical property of matter? |
Describes matters ability to change into something new or combine with another substance. |
|
|
Name five examples of a chemical property. |
•flammability •reactivity •radioactivity •toxicity •oxidation |
|
|
What is a chemical change? |
When one or more new substances are formed that have different properties. |
|
|
Name three examples of a chemical change. |
•wood burning •baking a cake •rust |
|
|
What are the seven signs of a chemical change? |
•color change •production of heat •production of light •production of sound •production of odor •formation of a solid •formation of a gas |
|
|
What is the law of conservation of mass? |
The amount of mass in a closed system cannot increase or decrease through chemical or physical change. |
|
|
What does the law of conservation of mass actually mean? |
The appearance of substance may change but the total amount of mass will remain the same. |
|
|
What is an open system? |
When substance is exposed to outside environmental factors. |
|
|
What is a closed system? |
When substance is not exposed to outside environmental factors. |
|
|
What is a mixture? |
Made when two or more substances are combined but they are not combined chemically. |
|
|
What are the general properties of a mixture? |
-the components of a mixture can be easily separated. -the components each keep their original properties. -the proportion of the components are not always equal. |
|
|
What is a pure substance? |
-all the particles within a pure substance are the same. -cannot separate the particles by physical means. |
|
|
What are some examples of a pure substance? |
Water, carbon dioxide, and all the elements on the periodic table. |
|
|
What are the three types of rocks? |
Igneous, sedimentary and, metamorphic. |
|
|
How is igneous rock formed? |
From the cooling of molten rock. |
|
|
What is lava? |
Molten rock on Earth's surface. |
|
|
What is magma? |
Molten rock trapped within the Earth. |
|
|
Describe the crystal sizes that make up extrusive Igneous rock. |
Small crystals. |
|
|
Describe the crystal sizes that make up intrusive Igneous rock. |
Large crystals. |
|
|
What steps are in the formation of sedimentary rock? |
Weathering -process of breaking rock into small pieces called sediment. Erosion -wind, water, and ice move sediment Deposition -sediment laid down in layers. Compaction -layers of sediment pile up. apply pressure to the layers below packing the material into rock. Cementation -minerals dissolve into spaces between sediment and glue the particles together. |
|
|
What are the three types of sedimentary rock? |
Clastic, organic, chemical. |
|
|
What is clastic rock? |
Rock formed from other pieces of rock. |
|
|
What is organic rock? |
Rock formed from the remains of plants and animals deposited in thick layers. |
|
|
What is chemical rock? |
Rocks formed from minerals that are dissolved in water when the water evaporates. |
|
|
How is metamorphic rock formed? |
By heating and/or applying pressure to already existing other kinds of rock. |
|
|
Draw the rock cycle. |
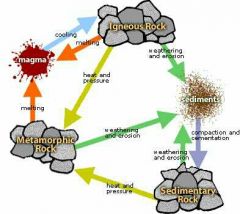
|
|
|
Explain the law of original horizontality. |
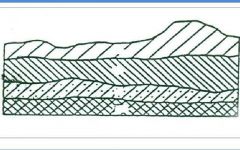
Sedimentary layers and lava flows are deposited in horizontal or flat sheets. |
|
|
Explain the law of superposition. |
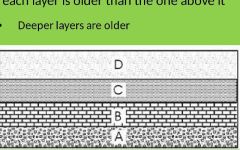
-In an undisturbed sequence layers or lava flows each layer is older than the one above it •Deeper layers are older |
|
|
Explain the law of inclusions. |
-Inclusions are rocks, crystals, or fossils contained in another type of rock. -Any inclusion is older than the rock layer it is in. |
|
|
Explain the law cross-cutting. |
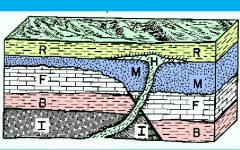
-Any feature that cuts across a rock or sediment layer must be younger than the rock or sediment layer it cuts through. -Fracture, faults, igneous intrusions. |
|
|
Explain the law of unconformities. |
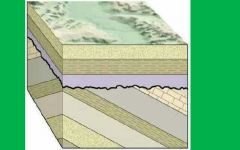
-Unconformities represent gaps in geologic time when erosion removed layers of rock. •Requires some type of uplifting or tilting of the rock layers. |
|
|
Name the four layers of the Earth's Interior. |
Inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. |
|
|
Draw a picture of the four layers of the earth. |
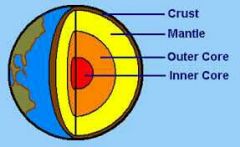
|
|
|
Explain oceanic crust. |
•Mostly made of extrusive Igneous rock. •Very dense (heavy) |
|
|
Explain continental crust. |
•Consists of all three main types of rock (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic) •Much less dense than oceanic crust. •Sits higher on the mantle than oceanic crust. |
|
|
What are the two parts of the mantle? Explain them. |
Lithosphere- Consists of the crust and upper most solid part of the mantle. Asthenosphere- Hot, soft layer of the mantle below the Lithosphere. -Bends and flexes like tar -Flows slowly |
|
|
Describe the outer core. |
•Magma like liquid surrounding the inner core -Iron and some nickel •Constantly moving around the inner core -Creates the Earth's Magnetic Field •Heated by the inner core |
|
|
Describe the inner core. |
•Solid inner most layer of the Earth -Iron and nickel |
|
|
What are the three types of thermal energy movement and describe them. |
•Radiation - transfer of thermal energy through empty space. •Conduction - transfer of thermal energy by direct particle contact. •Convection - transfer of thermal energy through moving fluids. |
|
|
What is lava? |
Molten rock on Earth's surface. |
|
|
What is magma? |
Molten rock trapped within the Earth. |
|
|
What is a convection current? |
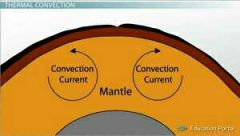
Rising and falling mantle resulting from heating and cooling of the mantle. |
|
|
Explain the theory of continental drift. |
•Theory that all the continents had once been joined together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart. -Supercontinent -PANGAEA |
|
|
What are some examples of evidence that continental drift happened? |
•Mountain ranges on different continents match up. •Shapes of different continents match up, like a puzzle. •Same fossils found on different continents. •Fossils of tropical animals found on Antarctica. •Tropical plant seeds found in artic regions. |
|
|
Why did Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift fail? |
He could not explain what caused the continents to move. |
|
|
Explain seafloor spreading. |
•Earth's crust under the ocean is cracked and lava is pushing up through it onto the ocean floor. -Rising lava pushes the two sides away from each other. -New crust is created -Ridges and mountains form. |
|
|
Explain subduction. |
•Oceanic crust collides with continental crust. •Oceanic crust gets pushed under continental crust. •Crust melts as it is pushed down into mantle. |
|
|
How do trenches and volcanoes form? |
Form where oceanic crust sinks back down under continental crust. |
|
|
Explain the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench. |
-It is the deepest point in the Mariana Trench. -The pressure there is over 8 tons per square inch. |
|
|
Explain plate tectonics. |
•Theory that pieces of the Earth's crust are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. -Explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth's plates. |
|
|
What is a fault? |
Breaks in Earth's crust. |
|
|
Describe a Transform Boundary. |
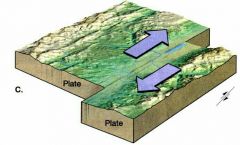
•Plates are moving past each other in opposite directions. -Earth's crust is not created or destroyed. |
|
|
Describe a Divergent Boundary. |
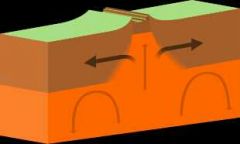
Place where two plates move away from each other. |
|
|
Describe a Convergent Boundary. |
•Two plates coming together or colliding. -The density of the plates determines which plate goes up and which goes down. •More dense plate goes down into the mantle. •Same density, crust piles up into mountains. -Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust. |
|
|
What is sediment? |
Small particles of other substances. |

