![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
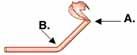
b. the tail allows vertical movement
|
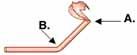
In this diagram of actin, which hinge allows for vertical movement necessary for actin binding and which hinge allows for the power stroke cycle?
|
|
|
c. it transfers energy to the myosin heads as ATPs hydrolyze in ADP & Pi.
|
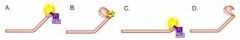
Which of these are high energy conformations of myosin? Why?
|
|
|
a. actin
b. ATP |
What binds at each of these sites on myosin?
|
|
|
a. actin subunit
b. tropomyosin c. troponin |
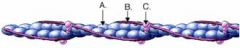
Identify the parts of the thin filament below.
|
|
|
a. tropomyosin
b. binding sites c. actin subunits d. troponin e. Ca+ ions |
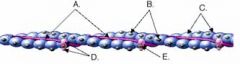
Identify the parts of the thin filament below.
|
|
|
According to the sliding filament theory, when a muscle cell contracts, the __________ filaments slide past the ___________ filaments and the ____________ shortens.
|
thin
thick muscle |
|
|
List the six most important chemicals involved in muscle contraction
|
1. ca++ ions
2. Myosin 3. actin 4. tropomyosin 5. ATP 6. troponin |
|
|
Where is myosin found in skeletal muscle cells?
a. in the thin filaments b. in the thick filaments c. in the sarcoplasmic reticulum d. in the terminal cisternae e. in the T tubules |
b. in the thick filaments
|
|
|
What are the two parts to a myosin molecule?
|
Cross bridges (heads) & tail
|
|
|
Which part moves providing the power stroke for muscle contraction?
|
The head
|
|
|
Which part of the myosin molecule has a hinge which allows vertical movement so that the cross-bridge can bind to actin?
|
tail
|
|
|
What two important binding sites are found on the cross bridges (heads) of myosin?
|
1. ATP binding sites
2. actin binding site |
|
|
What three protein molecules are the thin filaments made of?
|
1. actin
2. tropomyosin 3. troponin |
|
|
Each subunit on actin contains binding sites for _______________.
|
myosin cross bridges
|
|
|
Entwines around the actin
In unstimulated muscle it covers binding sites on actin subunits and prevents myosin cross bridge binding. |
tropomyosin function
|
|
|
to expose the binding sites w/ myosin.
First, tropomyosin must be moved aside though. |
troponin function
|
|
|
What causes the tropomyosin to move away from the myosin binding sites on the actin?
|
Ca++ ions from the terminal cisternae
|
|
|
a. Which of the following will attach to myosin?
actin tropomyosin troponin ATP calcium ions |
actin
ATP |
|
|
Which of the following will attach to actin?
actin tropomyosin troponin ATP calcium ions |
Actin
tropomyosin troponin ca++ ions |
|
|
Which of the following will attach to troponin?
myosin tropomyosin actin ATP calcium ions |
ca++ ions
|
|
|
What causes the release of calcium ions into the cytosol from the terminal cisternae?
|
action potential
|
|
|
What causes the myosin binding sites on actin to be exposed?
|
ca++ ions
|
|
|
What happens after the tropomyosin moves over, exposing the binding sites on the actin?
|
the energized cross bridge, and will bind to it.
|
|
|
What is it called when the cross bridge flexes, pulling the filament inward toward the center of the sarcomere?
|
"power stroke"
|
|
|
What happens to the myosin head (cross bridge when the power stroke occurs)?
|
it changes the conformation of the cross bridges, and releasing ADP & Pi
|
|
|
What causes the myosin heads (cross bridges) to disconnect from the actin?
|
ATP molecule
|
|
|
What causes the myosin cross bridges to go from their tilted state to their upright, high energy state?
|
hydrolysis
|
|
|
What causes the tropomyosin to cover back over the actin binding sites?
|
removal of ca++ ions
|
|
|
What is required to move the calcium ions from the cytosol back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
|
ion pumps that are energized by ATP.
|
|
|
List the following steps in the order they would occur in a single cross bridge cycle.
_____ a. ATP binds to the cross bridge and the cross bridge disconnecting from actin. _____ b. Myosin bind to actin. _____ c. Calcium ions are transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. _____ d. Presence of calcium ions in the cytosol trigger the exposure of binding sites on actin. _____ e. The power stroke occurs. _____ f. ATP is hydrolyzed, leading to the re-energizing and repositioning of the cross bridge. |
d, b, e, a, f, c
|
|
|
What would happen all the myosin cross bridges were synchronized (doing the same thing at the same time)?
|
it would contract
|
|
|
During the contraction of a muscle cell, what is happening to
a. the length of the sarcomere? b. the position of the Z lines with respect to one another? c. the length of the thin filament? d. the length of the thick filament? e. the width of the H zone? |
a. shortens
b. contracts (gets closer together c & d. DO NOT SHORTEN, they slide by each other e. it shortens |
|
|
After a sarcomere has contracted fully and the calcium ion concentration within the cytosol decreases, what happens within the sarcomere?
|
The sarcomere goes back to original shape.
|
|
|
Which of these is not a role of ATP in muscle contraction?
a. Allows the tropomyosin to move over, exposing the myosin binding sites on actin. b. Actively transports calcium ions into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. c. Energizes the power stroke of the myosin cross bridge. d. Disconnects the myosin cross bridge from the binding site on actin at the conclusion of a power stroke. |
a. Allows the tropomyosin to move over, exposing the myosin binding sites on actin.
|

