![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

weather |
is the state of the atmosphere at a particular point in time. It is also known as the local measurement of temperature, wind speed, humidity, cloud cover, etc. |
|

climate |

the average of weather conditions over a long time (hundreds of years). |
|
|
air pressure |
the weight of air pressing down on Earth |
|
|
barometric pressure |
the pushing force of the atmosphere (measured with an instrument called a barometer) |
|
|
humidity |
The amount of water vapor in the air (measured with an instrument called a hygrometer) |
|
|
global warming |
The theory that increased concentrations of greenhouse gases are causing the Earth’s surface temperature to warm. |
|
|
troposphere |
It’s the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 75% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols. Day to day weather occurs in the troposphere. |
|
|
precipitation |
Rain, snow, sleet or hail that falls from clouds in the sky |
|
|
meteorologist |
A scientist who studies and predicts weather. |
|
|
climatologist |
someone who is expert in climatology (the scientific study of climate) |
|
|
forecast |
is a prediction of what the weather will be like in an hour, tomorrow, or next week. |
|
|
water cycle |
the changes to water when it evaporates into the air, condenses into clouds, and then precipitates back down to the earth's surface in different forms |
|
|
evaporation |
Physical change in matter from a liquid to a gas |
|
|
water vapor |
water in the form of an invisible gas |
|
|
condensation |
the process in which a gas turns into a liquid |
|
|
clouds |
a visible collection of particles of water or ice suspended in the air, usually at an elevation above the earth's surface |
|
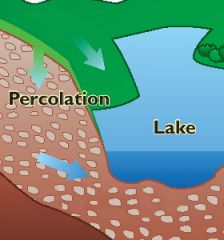
percolation (percolate) |
movement of water downward through openings in the soil to replenish aquifers under the ground. |
|
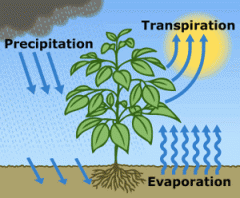
transpiration |
is the process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere. Transpiration is essentially evaporation of water from plant leaves. *tree sweat* |
|
|
run off |
water that runs along the soil and goes into lakes and rivers |
|
|
storage |
A lot of the Earth's water does not take part in the water cycle very often., Much of it is stored. The Earth stores water in a number of places. The ocean is the largest storage of water. Around 96 percent of the Earth's water is stored in the ocean. We can't drink the salty ocean water, so fortunately for us, freshwater is also stored in lakes, glaciers, snow caps, rivers, and below the ground in ground water storage. |
|
|
wind |
the movement of air caused by differences in air pressure |
|
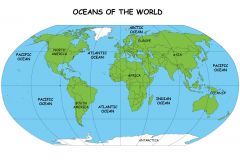
ocean |
One of 5 large bodies of salt water that cover 75% of Earth's surface |
|
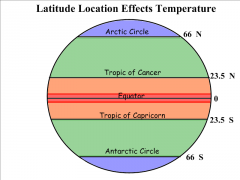
latitude |
a measure of how far a place is from the equator |
|
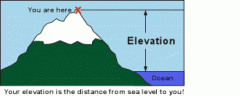
elevation |
height above sea level |

