![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as _______
|
heat
|
|
|
Photosynthesis generates ____________, which are used in cellular respiration
|
O2 and organic molecules
|
|
|
True or False: photosynthesis generates O2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
|
True
|
|
|
Cells use __________ energy stored in organic molecules to regenerate ATP, which powers work
|
chemical
|
|
|
True or False: Cells use chemical energy stored in organic molecules to regenerate ATP, which powers work
|
True
|
|
|
3 types of phosphorylation:
* substrate level * ____________ (mitochondria) * ____________ (chloroplasts) |
3 types of phosphorylation:
* substrate level * chemiosmotic (mitochondria) * photophosphorylation (chloroplasts) |
|
|
3 types of phosphorylation:
* ____________ * chemiosmotic ( ____________ ) * photophosphorylation ( _________ ) |
3 types of phosphorylation:
* substrate level * chemiosmotic (mitochondria) * photophosphorylation (chloroplasts) |
|
|
3 types of ____________ :
* substrate level, * chemiosmotic (mitochondria) * ______________ (chloroplasts) |
3 types of phosphorylation:
* substrate level * chemiosmotic (mitochondria) * photophosphorylation (chloroplasts) |
|
|
___________ is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2
|
Fermentation
|
|
|
_______________ consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP
|
Aerobic respiration
|
|
|
True or False: Aerobic respiration consumes ATP and O2 and yields CO2.
|
False. Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP
|
|
|
True or False: Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP
|
True
|
|
|
Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes ______________
|
compounds other than O2
|
|
|
Anaerobic respiration yields __________
|
ATP
|
|
|
Cellular respiration occurs mostly in the ____________ in eukaryotes
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
The electron donor is called the ________ agent
|
reducing
|
|
|
The electron receptor is called the ___________ agent
|
oxidizing
|
|

What is this equation?
|
Cellular Respiration
|
|

What is missing?
|
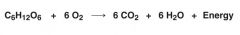
|
|
|
NAD + functions as the __________ agent in many of the redox
steps during the catabolism of glucose |
oxidizing
|
|
|
The Citric Acid Cycle generates ___ ATP, ___ NADH, and ___ FADH2 per turn.
|
The Citric Acid Cycle generates 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per turn.
|
|
|
True or False: The Citric Acid Cycle generates 1 ATP, 3 FADH2, and 1 NADH per turn.
|
False: The Citric Acid Cycle generates 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per turn.
|
|
|
Only ___ of 38 ATP ultimately produced by respiration of glucose are derived from substrate-level phosphorylation.
|
4
|
|
|
____________ in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space
|
Electron transfer
|
|
|
During cellular respiration, most energy flows in this sequence:
glucose -> _______ -> _________ -> proton-motive force -> ATP |
During cellular respiration, most energy flows in this sequence:
glucose -> NADH -> electron transport chain -> proton-motive force -> ATP |

