![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
You manage a computer that runs Windows 7.
While working with a new application, the application stops responding. You would like to analyze the application and its associated processes to identify which processes the application is waiting on. What should you do? - In resource Monitor, analyze the wait chain for the process. - In Task Manager, end the process tree for the process. - In Task manager, go to the service associated with the process. Open the Services console and view the dependencies for that service. - In Event viewer, create a filtered view for events related to the process. Examine the details of each event. |
- In resource Monitor, analyze the wait chain for the process.
Explanation You can use Resource Monitor to identify processes that a process is waiting for. a process wait chain includes all of the applications which are waiting for other processes to finish. To view the process wait chain, right-click the name of the process, then click 'Analyze Wait Chain. A process tree is the list of all processes and dependent processes used by an application. Ending the process tree terminates the selected process and all dependent processes, but does not show you processes that cause the process to wait. Dependencies int he Services console show services that rely on the selected service. The selected service must be started before dependent services can start. Section 7.4 |
|
|
You have a stand-alone computer running windows 7 Professional.
You need to determine if the computer has any administrative vulnerabilities. What should you do? - Use windows Server Update Services (WSUS) - Use System Center Essentials. - Use System Center configuration Manager (SCCM) - Use Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) |
- Use Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA)
Explanation Because the computer is a stand-alone machine, use Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA). MBSA is a tool you can use to scan local and remote computers for security compliance. The MBSA tool looks for operating system vulnerabilities, including: * Security updates * Administrative vulnerabilities, such as the guest account status, file-system type, file shares, and members of the Administrators group. * Weak passwords (blank or weak, non-expiring) The other options are available in a domain network and run as client-server applications: * Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) allows you to use a server on your intranet as a centralized point for updating software. * System Center essentials is an application that includes the ability to retrieve updates released through Microsoft Update and distribute them to servers and client computers in your private network. * The System center configuration Manager (SCCM) is an application that includes the ability to deploy operating systems, applications, and software updates. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You are troubleshooting a problem that keeps occurring. When the problem happens, there are several Warning and Error events logged to the Application and System logs in Event Viewer. You would like to be able to see only the Warning and Error events from both logs displayed at the same time. You want to save this configuration so that you can check back each day to see any new errors. What should you do? - On both logs, filter the log to show only Warning and Error events. Save both logs. - On both logs, create a Custom View. - On both logs, filter the log to show only Warning and Error events. On both logs, save the filter to a Custom View. - On the Application log, filter the log to show only Warning and Error events. Save the filter to a Custom View, adding the System log as an additional filter. |
- On the Application log, filter the log to show only Warning and Error events. Save the filter to a Custom View, adding the System log as an additional filter.
Explanation To view events from multiple logs at the same time, create a single Custom View that includes both logs. You can create a view from an existing filtered log and then modify the filter criteria, or you can just create a single new view with the necessary settings. Creating a Custom View from both logs leaves you with two Custom Views instead of one. Saving the logs saves the messages in the log. You can also save the filtered log file to save only messages currently showing. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a windows 7 computer shared by multiple users.
The computer has a single hard disk with a single partition. You want to make sure that each user can only save up to 4 GB of files on the existing hard disk. Files stored to USB devices should not count towards the limit. What should you do? - Configure removable storage access policies int he local security policy. - Configure disk quotas. - Configure NTFS permissions on the volume. - Configure user rights assignments in the local security policy. |
- Configure disk quotas.
Explanation Use disk quotas to restrict the amount of disk space that users' files can occupy. Quotas are configured on a per-disk and per user basis. NTFS permissions control the actions that users can take on files and folders on the volume, but do not restrict disk use. Use removable storage access policies to control read and write access to removable storage such as DVD, floppy, and USB drives. Configure user rights to control actions users can perform such as logging on or shutting down the computer. Section 3.3 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
The computer has a single hard disk configured as a basic disk with a single partition formatted with NTFS. The disk has run out of space. You need to add space to the disk. you install a new hard drive and start disk Management. You need to add space to the existing volume using only necessary actions. What should you do? (Select two.) - On the C:\ drive, create an empty folder. - Extend the C:\ volume. - Upgrade both disks to dynamic. - Initialize the new disk using GPT. - On the new hard disk, create a new partition without a drive letter. |
- On the C:\ drive, create an empty folder.
- On the new hard disk, create a new partition without a drive letter. Explanation Because this is the system volume, the only way to add space to the volume using space on the new disk is to create a mount point. A mount point is an empty folder on the existing volume that points to another partition. Data saved to the folder is physically saved on the referenced partition. To create a mount point: 1. The existing volume must be formatted with NTFS. 2. Create an empty folder on the existing volume. 3. Create a partition on the new disk without a drive letter. Mount the partition to the empty folder on the existing volume. you cannot extend the volume to another disk because the volume is the system volume. You cannot extend the system volume even if it is on a dynamic disk. You can create mount points on basic or dynamic volumes. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Professional.
While managing the available memory for applications, you need to increase the paging file to the recommended size for normal circumstances. What should you do? - Configure the paging file as large as possible. - Configure the paging file to 3 times the amount of physical RAM. - Configure the paging file to 1.5 times the amount of physical RAM. - Configure the paging file equal to the amount of physical RAM. |
- Configure the paging file to 1.5 times the amount of physical RAM.
Explanation Unless you are running applications that require large amounts of paging file space, the optimal setting for virtual memory swap file size is about 1.5 to 2 times larger than the physical RAM in the computer. As the size of the paging file exceeds this threshold, the system will spend more time swapping memory data in to and out of the paging file than is made available to the user to accomplish tasks, a condition known as thrashing, where system performance (particularly usability) becomes very poor, but hard drive activity is almost constant. Section 7.6 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You have just installed a custom application. The application generates Event Viewer events and logs those events to the default Application and the Security logs in Event Viewer. You are concerned about system performance while running the application. You would like to be able to view the current statistics for processor, memory, and disk reads and writes. You only want to see these statistics and no others, and you want to be able to easily save the configuration so that the same statistics are shown each time. What should you do? - Configure event subscriptions. - Create a data collector set in Performance Monitor. - Add objects and counters in Performance Monitor. - Create a Custom View in Event Viewer. |
- Add objects and counters in Performance Monitor.
Explanation Use Performance Monitor to view current system statistics. Add objects and counters to customize the statistics that are shown. Use data collector sets to define statistics to gather over time. These statistics are saved to a file. You open the file to analyze the statistics. You cannot view current statistics from a defined data collector set. A custom view is a saved filter in Event Viewer. Use Event Subscriptions to view a set of events stored in multiple logs on multiple computers. Events that occur on one computer are sent to another computer where they are saved and can be viewed. Event Viewer shows events, such as error messages, and not data about system statistics. Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Home Premium.
You need to customize which utilities and programs are processed at startup for the computer. What should you do? - Run the Services MMC snap-in - Run Startup Repair - Run Msconfig - Run Startup and Recovery options. |
- Run Msconfig
Explanation Use the System Configuration Utility (Msconfig.exe) to boot the system excluding specific files or file entries. In addition, you can use Msconfig to: * Configure startup preferences. * View and customize Windows setup components. * Customize the boot configuration, including the default operating system and Safe Mode boot selection. * Disable or enable services. * Access available tools and view the file and file path for the application that runs each tool. If your system detects a startup failure, it will automatically start the Startup Repair tool. Use the Startup and Recovery options in the 'Advanced' tab of the System Properties to manage and maintain startup and recovery settings, including the Default operating system for startup, the number of seconds a list of operating systems is displayed before the default operating system is booted, and the actions to take when the system stops unexpectedly. Use the Services snap-in to view and mange running services. A service is a program that processes requests from other applications or users. Section 7.1 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You are troubleshooting a problem that keeps occurring. When the problem happens, there are several Warning and error events logged to the Application log in Event Viewer. You create a custom View that shows only Warning and Error events. During troubleshooting, you filter the Custom View to show only the Error messages. You would like to create a new custom View using the current filter settings. What should you do? - Copy the Custom view using a new name. - Save the events in the Custom View. - Export the Custom View, then import it using a different name. - Save the filter to a Custom View. |
- Save the filter to a Custom View.
Explanation To create a new custom View based on a filter that has been applied to the Custom View, right-click the Custom View and choose 'Save Filter to Custom View....' Exporting the view or copying the view can be used to create a view based on the properties of the existing view. however, filters applied to the view are not applied to the view settings. Saving the events int he view saves the log entries in the view to log file, but does not create a new Custom View Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You need to free up disk space and would like to delete all but the most recent restore point. What should you do? (Select two. Each selection is a complete answer) - From the command prompt, run 'Defrag /M' - In Explorer, edit the properties for the drive. On the 'Tools' tab, click 'Check now....' - In Explorer, edit the properties for the drive. On the 'Tools' tab, click 'Check Now...' - Run 'Cleanmgr' as an administrator, then use the 'More Options' tab to clean up the restore points. - In Disk Cleanup, select 'Clean up system files', then use the 'More Options' tab to clean up the restore points. - From an elevated command prompt, run 'Chkdsk /r' |
- Run 'Cleanmgr' as an administrator, then use the 'More Options' tab to clean up the restore points.
- In Disk Cleanup, select 'Clean up system files', then use the 'More Options' tab to clean up the restore points. Explanation Run 'Cleanmgr' as an administrator or select 'Clean up system files' from within Disk cleanup to expose the 'More Options' tab where you can remove programs and features or delete all but the most recent system restore point. Use the 'Defrag' command or 'Defragment Now...' to manually run disk defragmentation. use the 'Chkdsk' command or 'Check Now...' to verify the file system integrity of a hard disk. Section 3.3 |
|
|
You have a laptop running Windows 7 Ultimate.
You are on an airplane and are being instructed to turn off your laptop completely and immediately. you have several open windows with critical data that you cannot lose. What should you do? - Enable hibernation. - Enable hybrid sleep. - Enable sleep. - Enable hybrid sleep and switch batteries. |
- Enable hibernation.
Explanation Hibernation copies contents of RAM to a file on the hard disk, then shuts down completely. Hibernation uses no battery power because the device is off. Sleep, by itself, maintains power to the RAM which allows quick resume, but could drain the battery. hybrid sleep combines both sleep and hibernation features - battery power is still used to maintain RAM for fast resume, but the contents of RAM are also copied to the hard drive in case of battery failure. Neither sleep nor hybrid sleep turns the device off completely as long as the battery has some power left. |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7 Professional.
The computer has a standard SVGA graphics adapter. You upgrade the graphic card with a new adapter that should support Aero, but you are still unable to use Aero. You need to enable Aero with the minimum amount of effort. What should you do? - Upgrade to Windows 7 Ultimate Edition. - In Performance Information and Tools, click Re-run the assessment. - Upgrade to Windows 7 Enterprise Edition. - Re-install Windows 7 |
- In Performance Information and Tools, click Re-run the assessment.
Explanation Windows 7 needs to be updated with the latest score before you can use Aero. To do this, click 'Re-run the assessment' from the Performance Information and Tools. This will raise your base score so that Aero can be enabled. Reinstalling windows 7 would require more work. Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise, and Ultimate all support Windows Aero. Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You have just read about a new security patch for Windows 7. You install the patch as a Windows Update, but after you reboot and log back on your computer is unstable. What action should you take? - Reboot and use the Last Known good configuration. - Use the Software Explorer in Windows Defender. - Use Add or Remove Programs to remove the update. - Use Windows Update in the Control Panel to uninstall the update. |
- Use Windows Update in the Control Panel to uninstall the update.
Use windows Update in the Control Panel to uninstall the update. Use Software Explorer in Windows Defender to see and remove running software applications, not updates. The Last Known Good option is best used when experiencing hardware-related programs and can only be used if you have not yet logged on since making the change. Use Add or Remove Programs to repair or uninstall applications on the computer. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a laptop running windows 7 Ultimate.
You are about to give a presentation and have connected your laptop to a multimedia projector. You are concerned about interruptions to your presentation such as notification balloons and the screen turning black. What should you do? - In the Windows Mobility Center, enable the 'Presentation Settings' option. - In the Windows Mobility Center, configure the 'External Display' option. - In the Windows Security Center, disable notifications. - Configure Desktop properties to disable the screen saver. |
- In the Windows Mobility Center, enable the 'Presentation Settings' option.
Explanation Enable the 'Presentation Settings' option in Windows Mobility Center. When the 'Presentation Settings' option is turned on, your laptop stays awake and system notifications are turned off. Use the 'External Display' option to customize the display settings for the internal monitor and the external monitor or projector. Disabling the screen saver would not take care of disabling of notifications. Disabling notification from Security Center is poor security practice and would not disable all notification balloons. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
The computer has an extra disk that has three primary partitions and an extended partition with two logical drives. All volumes are formatted with FAT32. You want to convert the partitions to simple volumes, preferably without losing any data. What should you do? - Run the 'Fixboot' command to convert the partition type to GPT. - Delete the partitions and re-create them as simple volumes. - Upgrade the disk to a dynamic disk. - Run the 'Convert' command. |
- Upgrade the disk to a dynamic disk.
Explanation When you upgrade a basic disk to a dynamic disk, existing partitions are converted to simple volumes. You can convert the disk without deleting partitions or losing any data. Use the 'Convert' command to change the file system from FAT32 to NTFS. The partition table type (either MBR or GPT) does not affect the partition or volume type. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
As part of the regular system maintenance, you are checking Performance Monitor statistics and event log events. You notice that there are several error events listed with the same ID number and description that sounds as if the error is related to system hardware. you check your Performance Monitor logs but don't notice anything unusual around the time that the events were generated. You would like to get an e-mail every time the event is logged so you can check the system statistics at the moment. What should you do? - Attach a task to the event. - Configure event subscriptions. - Configure a performance counter alert. - Configure an event trace data collector. |
- Attach a task to the event.
Explanation Attach a task to an event or a log to receive notification or take other actions when an event is logged. Tasks attached to an event execute the action whenever an event with that ID, source, and log occurs. Use a performance counter alert to configure triggers that take an action when a counter reaches a threshold value. Alerts monitor a system performance statistic, such as processor time or disk space; they do not monitor Event log events. use an event trace data collector in Performance Monitor to capture events logged by software processes. Use Event Subscriptions to view a set of events stored in multiple logs on multiple computers. Events that occur on one computer are sent to another computer where they are saved and can be viewed. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
Your computer has a single hard disk with a single volume used by the C:\ drive. You have previously upgraded the disk to a dynamic disk. The disk has run out of disk space. You need to add more space to the C:\ volume. You add a new hard disk to the computer. You need to add space to the C: volume as quickly as possible. What should you do? - Create a mount point using space on the second disk. - Stripe the C:\ volume to the second disk. - Extend the C;\ volume to the second disk. - Span the C:\ volume to the second disk. |
- Create a mount point using space on the second disk.
Explanation A 'mount point' is an empty folder on the existing volume that points to another partition. Data saved to the folder is physically saved on the referenced partition. Extending a volume adds space to the volume. Extending a volume using space on a different disk creates a spanned volume. You cannot extend the system volume using space on a second disk. A striped volume uses two equal portions on two disks. You can create a new striped volume, but you cannot stripe an existing volume. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Ultimate. The computer meets the minimum hardware requirements.
When running multiple applications, the computer is slow to respond. You need to improve performance, especially for the application that you are actively working in. What should you do? - Adjust processor scheduling for best performance of background services. - Enable ReadyBoost on a USB flash drive. - Turn on DEP for all programs. - Enable UAC visualization for the application. |
- Enable ReadyBoost on a USB flash drive.
Explanation Use a USB drive to enable ReadyBoost. ReadyBoost treats the USB drive as extra RAM. It has slower access speeds than physical RAM, but is still much faster than accessing the page file (virtual memory) on the hard drive. Processor scheduling determines the response times of interactive applications or background applications running as services. Configuring scheduling for best performance of background services could decrease performance of active applications. Data Execution protection (DEP) helps to prevent damage to your computer from viruses and other security threats. UAC virtualization protects your computer by creating a protected area where a running program can run without modifying the registry or using full administrative privileges. Section 7.6 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
Your computer is configured to download and automatically install important (critical) patches using Windows Update. You notice that updates that Microsoft suggests, but does not mark as important, are not being downloaded. You would like these other updates to download and install automatically with the least amount of effort. What should you do? - Configure Windows Update to included recommended updates. - Configure Windows Update to install hidden updates. - Install a WSUS server. Point your client to WSUS for updates. - Use Internet Explorer to access the Windows Update website. |
- Configure Windows Update to included recommended updates.
Explanation To automatically download non-important updates, select the 'Give me recommended updates the same way I receive important updates' option. A Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server on your intranet could include important and non-important updates for all computers in the organization, but in this scenario, it requires more administrative effort than including the recommended updates on the individual computer. Using Internet Explorer works only if you manually visit the Windows Update site. Hidden updates are updates for which you no longer wish to be notified. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
the computer has a removable disk drive that has been formatted with NTFS. You want the drive to use FAT32 to be compatible with more operating systems. The drive is currently configured using drive letter D:. What should you do? - Back up the data on the D: drive. Run 'Format /c' - Back up the data on the D: drive. Run 'Convert.exe' - Back up the data on the D: drive. Reformat the D: drive using FAT32. Restore the data. - Upgrade the disk to a dynamic disk |
- Back up the data on the D: drive. Reformat the D: drive using FAT32. Restore the data.
Explanation The only way to go from NTFS to FAT32 is to reformat the drive. Because reformatting destroys all data, you should back up the drive before formatting, then restore the data after formatting the drive. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You manage a computer that runs Windows 7.
You would like to generate a report that runs several basic tests of the operating system, Security Center, hard disk, services, and hardware devices and drivers. The report should include suggestions for how to improve system performance. What should you do? - In Performance Monitor, run the System Diagnostics data collector set. - In Performance Monitor, runt he System Performance data collector set. - From Performance Information and Tools in the Control Panel, view advanced system details in System Information. - From Performance Information and Tools int he Control Panel, re-run the assessment for the Windows Experience Index, then view the detailed performance and system information associated with the index. |
- In Performance Monitor, run the System Diagnostics data collector set.
Explanation To view a report that shows the required information, go to Performance Monitor and run the System Diagnostics data collector set. You can also go to Performance Information and Tools in the Control panel and generate a system health report to create the same report. The System Diagnostics report runs several basic tests of the operating system, Secuirty Center, hard disk, services, and hardware devices and drivers. The System Diagnostics report also reports on warnings such as missing security tools (anti-virus software) and system components that might need to be upgraded to improve performance. The system Performance data collector set in Performance Monitor shows CPU, network, disk, and memory statistics, along with a brief report on performance issues. This information is a subset of the information available through the System Diagnostics report. System Information shows detailed information about the system and configuration, but does not report performance information or suggest ways for improving performance. The detailed report associated with the Windows Experience Index only shows details about the processor, memory, disk storage, network adapter, and video graphic capabilities. Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7.
you need to install an updated driver for a hardware device on the computer. You need a driver file which has been tested by Microsoft and comes from a legitimate source. What should you do? - Install an updated driver from the device manufacturer's Web site. - Install an updated driver from the Device's installation media. - Install an updated driver with a self-generated certificate. - Install an updated driver with a digital signature. |
- Install an updated driver with a digital signature.
Explanation Install an updated driver with a digital signature. A digital signature indicates that a particular driver or file has met a certain level of testing and is stable and reliable, and verifies that the publisher of the driver is a legitimate source (i.e. that the driver came from the company who claims to have produced the driver). The device's installation media would not contain an updated driver for the device. You could install an updated driver from the device manufacturer's Web site, but you would not know if it met a certain level of testing and is stable and reliable. In cases where drivers are not signed, but still necessary, the administrator can obtain and generate a self-signed certificate that is valid within the organization and use it to sign the driver. Section 3.1 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You are troubleshooting a problem that keeps occuriring. When the problem happens, there are several Warning and Error events logged to the Application and System logs in Event Viewer, which you are using a Custom View to examine. After several days, there are several events int he Custom View. You would like to clear the messgaes from the view sot hat you only see mesages starting from right now. You need to make sure that any messages in the corresponding logs still exist. What should you do? - Edit the Custom View properties and create a custom range for logged events, starting with today's date. - Clear the Custom View. - Export the Custom View, then import it with a new name. - Clear the Application and System logs. - Save the events in the Custom View. |
- Edit the Custom View properties and create a custom range for logged events, starting with today's date.
Explanation A Custom View shows all messages that exist in the corresponding log. To remove older messages from the Custom View without deleting the messages, edit the Custom View properties to change the logged parameters. You cannot clear a Custom View, you can only edit the filter properties that determine which events are shown. Clearing the logs specified by the Custom View filter properties will clear the Custom View, but also deletes the events from the log. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have two computers that run Windows 7: computer1 and Computer2.
Over the next few days, you want to monitor Computer1. You would like to automatically save the contents of the Application and System logs on Computer 1 to Computer2. You will then use Event Viewer on Computer2 to view the contents of the logs generated on Computer1. What should you do? - On Computer1, attach a task to the Application and System logs. Configure the task to run a script that copies the logs to Computer2. - On both computers, enable and configure Event Subscriptions. Configure Computer1 as a source, and Computer2 as a collector. - On Computer2, open the Reliability and Performance Monitor and connect to Computer1. Create a data collector set with event trace data. - On Computer1, create a Scheduled Task that saves the Application and System logs to a network share. configure the schedule to run every 15 minutes. |
- On both computers, enable and configure Event Subscriptions. Configure Computer1 as a source, and Computer2 as a collector.
Explanation To save events from one server to another, use Event Subscriptions. When an event occurs on the source server, those events are recorded on the local system and sent to the collector server. You can use Event Subscriptions to collect and view events from multiple servers. Events are saved on the collector server where they can be viewed and managed from Event Viewer. The default location for these events is the ForwardedEvents log. Use Reliability and Performance Monitor to monitor to monitor system statistics, such as processor percentage or disk space. Attach a task to an event log or an event to send e-mail, display a message, or run a program when an event occurs. Section 7.2 |
|
|
you have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You need to manually check for updates form Windows Update. What should you do? (Select two. Both answers are complete solutions.) - Use 'wusa.exe' - Run 'wuauclt.exe /detectnow' - Configure Windows Update to turn off automatic update checking. - Click the 'Check for updates' button in Windows Update. |
- Run 'wuauclt.exe /detectnow'
- Click the 'Check for updates' button in Windows Update. Explanation In this case, you can do the following to manually check for updates but not isntall them: * click the 'Check for updates' button in Windows Update * Run 'wuauclt.exe /detectnow' Run 'wusa.exe' to install Microsoft Update (MSU) files manually. Running Windows Update as an administrator will not enable the grayed out and unchangeable settings. Turning off automatic update checking is a configured option for Windows Update, and choosing this option does not contribute to you manually checking for updates. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
The computer is a member of a domain. Windows Update settings are controlled through Group Policy. You find that your computer has not been installing recent updates. You want to see information about how the computer is configured to get updates including the name of the server it tires to contact when checking for and downloading updates. What should you do? - Run 'Wuauclt.exe' - Check Event Viewer for Windows Update events. - Check the settings in the local security policy. - Look through the WindowsUpdate.log file. - Go to Windows Update in the Control Panel. |
- Look through the WindowsUpdate.log file.
Explanation Information about Windows Update is recorded in the %WinDir%\WindowsUpdate.log file. To find the server name, look for an entry starting with 'Using server URL' or 'WSUS server' followed by the server name. A URL of https://www.update.microsoft.com identifies that the computer gets updates from the Microsoft update server. If you check windows Update in the Control Panel, you will see that Windows Update is managed by the administrator (settings configured through Group Policy), but you will not be able to see the name of the server used for updates. Checking the local security policy won't give you the information you need because settings are applied through a Group Policy object (GPO) configured in the domain. 'Wuauclt.exe' is the client component for Windows Update. One of the few functions of this program is to check for updates using settings configured locally or through Group Policy. you can run 'wuauclt /detectnow' to force the computer to check for updates immediately, but there is no option for seeing the current Windows Update configuration. Event Viewer records that updates are performed, but does not include the source of the updates. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a Windows 7 computer.
You would like to configure Event Subscriptions for that computer to forward events to a network server. You need to configure your computer as a source computer for a collector initiated subscription. Which of the following will be part of your configuration? (Select two.) - Configure the local security policy to identify the FQDN of the collector computer. - Make the source computer a member of the SubscribedComputers group. - Run 'winrm qc' - Add the collector computer to the Event Log Readers group. - Run 'wecutil qc' |
- Run 'winrm qc'
- Add the collector computer to the Event Log Readers group. Explanation Use a collector initiated subscription to explicitly identify source computers that can forward events to the collector computer. To configure a source computer for collector initiated subscriptions: * Run the 'winrm qc' command to run WinRM. * Add the collector computer account to the local Event Log Readers group or the local Administrators group. Run 'wecutil qc' on the collector computer for collector initiated subscriptions. The other tasks are performed when configuring source computer initiated subscriptions. You would edit the local security policy or Group Policy to identify the collector computer when configuring a source computer for source computer initiated subscriptions. Adding the source computer to a computer group is a task performed in Active Directory or on the collector computer. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You mange a computer that runs Windows 7.
You would like to generate a report that shows the status of hardware resources, processes, and system and configuration information on the computer. The report should include suggestions for ways to maximize performance and streamline system operation. What should you do? - In Performance Monitor, run the System Performance data collector set. - From Performance Information and Tools int he Control Panel, view advanced system details in System Information. - From Performance Information and Tools int he control Panel, re-run the assessment for the Windows Experience Index, then view the detailed performance and system information associated with the index. - From Performance Information and Tools in the Control Panel, generate a system health report. |
- From Performance Information and Tools in the Control Panel, generate a system health report.
Explanation To view a report that shows the required information, generate a system health report from Performance Information and Tools in the Control Panel. You can also go to Performance Monitor and run the system Diagnostics data collector set to get the same report. The system Performance data collector set in Performance Monitor shows CPU, network, disk, and memory statistics, along with a brief report on performance issues. This information is a subset of information available through the System Diagnostics report. The system Diagnostics report also reports on warning such as missing security tools (anti-virus software) and system components that might need to be upgraded to improve performance. The system Diagnostics report runs several basic tests of the operating system, Security Center, hard disk, services, and hardware devices and drivers that are not performed by the System Performance data collector set. System Information shows detailed information about the system and configuration, but does not report performance information or suggest ways for improving performance. The detailed report associated with the Windows Experience Index only shows details about the processor, memory, disk storage, network adapter, and video graphic capabilities. Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a laptop running Windows 7 Ultimate.
You need to configure your laptop to save as much battery power as possible. What should you do? - Use the High Performance power plan. - Use the Power Saver power plan - Use the Balanced power plan. - Use the default power plan. |
- Use the Power Saver power plan
Explanation Use the Power Saver power plan to save as much battery power as possible. The default power plan is the Balanced power plan; that plan and the High Performance power plan do not save as much battery power as the Power Saver plan. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Enterprise.
After connecting to your company's network, you are able to access all of your personal files. Later in the day, you are having problems accessing the same files, as well as other files on the network. What should you do? - Run the Services snap-in - Run Windows Network Diagnostics - Run the Performance Monitor - Run the System Configuration Utility. |
- Run Windows Network Diagnostics
Explanation Run the Windows Network Diagnostics tool. The Windows Network Diagnostics Tool analyzes the computer's network connection, verifying connectivity. The Windows Network Diagnostics tool troubleshoots issues related to the following: * Internet connection * Shared folders * HomeGroup connection * Network printers Use the Services snap-in to view and manage running services. Performance Monitor displays statistics that tell you about the operation of your computer. Use Event Viewer to view logs about programs, system events, and security. Use the System Configuration Utility to configure startup preferences and enable/disable startup utilities and programs. Section 7.1 |
|
|
You have a Windows 7 computer with a new hard drive.
You want to create and format volumes on the hard drive. What should you do? - Run 'Diskpart' from the command prompt. - Run 'Fdisk' from the command prompt. - Run 'Chkdsk' from the command prompt. - Run 'Format' from the command prompt. |
- Run 'Diskpart' from the command prompt.
Explanation Use 'Diskpart to view and create partitions and volumes, format volumes, extend or shrink volumes, and perform many other disk storage tasks. Use 'Format' to format an existing volume. use 'Chkdsk' to check the integrity of the file system on a disk. 'Fdisk' is not a utility included with Windows 7. Section 3.2 |
|
|
What is the name of the Windows Update service?
|
Windows Update or wuauserv
|
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Professional.
To increase the available memory for applications, you need to increase the size of the paging file. What should you do? - Modify the Processor Scheduling settings. - Modify the System Protection settings. - Modify the Advanced system settings. - Enable ReadyBoost on a USB flash drive. |
- Modify the Advanced system settings.
Explanation Edit Advanced system settings to increase the size of a paging file. The paging file is an area on the hard disk that Windows uses as if it were RAM. The paging file is used to move unused data in RAM to the hard disk. Thereby making more space available in memory for other running applications or data. ReadyBoost is a feature that treats a USB drive as extra RAM in the machine. It has slower access speeds than physical RAM, but is still much faster than accessing the page file on the hard drive. While this would increase memory for applications (and is a better solution than the one you are asked to provide), using ReadyBoost does not increase the paging file size. Processor scheduling determines the response times of interactive applications or background applications running as services. System Protection settings enable backups of system files and user data files. Section 7.6 |
|
|
You have a windows 7 computer with a single hard disk.
You notice that the disk defragmentation schedule has been turned off on your computer. The disk is badly fragmented. You want to run disk defragmentation manually. What should you do? - Run 'Defrag' - Run 'Cleanmgr' - Run 'Diskpart compact' - Run 'Diskpart clean' |
- Run 'Defrag'
Explanation Run 'Defrag' at a command prompt to run Disk Defragmenter in text mode. 'Cleanmgr' runs Disk Cleanup which deletes temporary and other files from the hard disk to free up more disk space. 'Diskpart clean' removes all configuration information (all information) from the disk. 'Diskpart compact' attempts to reduce the physical size of a file. Section 3.3 |
|
|
You have a laptop running Windows 7 Ultimate.
You are starting a presentation Where would you minimize interruptions to your presentation? |
Enable the 'Presentation Settings' option in Windows Mobility Center. When the 'Presentation Settings' option is turned on, your laptop stays awake and system notifications are turned off.
Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You are troubleshooting a problem that keeps occurring. When the problem happens, there are several Warning and Error events logged to the Application log in Event Viewer. While troubleshooting the problem, you create a filter for the log that shows only the Warning and Error messages. You would like to save all messages in the application log (including Informational messages) so you can copy them to another computer and examine them there. What should you do? - Save the filtered log. - Save the filter to a Custom View. From the Custom View, save the events in the Custom View. - Save the filter to a Custom View. From the Custom View, export the Custom view. - Clear the filter, then save the log. |
- Clear the filter, then save the log.
Explanation To save all messages in the log, you can: * Clear (remove) the filter, then save the log. * Clear the log, choosing to save the log before clearing. Saving the filtered log saves only the messages that are currently showing (currently only Warning and Error messages). Messages that do not appear because of the filter are not saved. Form the scenario, you want to save all messages in the log, not just the filtered messages. Creating a custom view from the filter settings essentially creates a log that contains only the filtered messages. Saving the events in the Custom view is like saving the filtered log. Exporting the Custom View exports the filter settings so you can import them on another computer to create a Custom View on that system. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs windows 7.
You want to see the amount of disk activity that is generated by an application. What should you do? - Filter on the application in Resource Monitor. - On the Application tab in Task Manger, go to the process associated with the application. - On the Application tab in Task manager, create a dump file for the application. - In Performance Monitor, create a data collector set using the application as the object and disk use as the counter. |
- Filter on the application in Resource Monitor.
Explanation Resource Monitor displays additional information not found in Task Manager. By filtering on an application or process, you can view the CPU, memory, disk, and network activity generated by the application or process. You cannot use Task Manager to view disk activity for a specific application or process. You can view CPU percentage and the amount of memory used by a process. With Performance Monitor you can view individual statistics (counters), but you cannot separate those counters by application or process. Section 7.4 |
|
|
You want to monitor the processor utilization on your Windows 7 computer.
You want to get an e-mail notification every time the processor utilization exceeds 90%. You create a new Data collector Set in Performance Monitor. What type of Data collector should you create? - Configuration data collector - Performance counter data collector - Event trace data collector - Performance counter alert |
- Performance counter alert
Explanation Use a performance counter alert to be notified when a counter is above or below a threshold amount. Use a performance counter data collector to capture system statistics over time. Use an event trace collector to gather information reported by trace providers included with the operating system or some applications. Use a configuration data collector to collect registry key settings. Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a laptop running windows 7 Enterprise.
You connect an external USB hard drive to the laptop to access specific data files. After editing the files, you need to disconnect the external USB hard drive. You do not want to lose your work on the data files. With the least amount of effort, you want to remove the USB hard drive from the laptop. What should you do? - Check the drive's 'Policies' tab and ensure that the 'Quick Removal' option is selected, then remove the USB connector. - Check the drive's 'Policies' tab and ensure that the 'Turn off Windows write-cache buffer flushing on the device' option is selected, then remove the USB connector. - Check the drive's 'Policies' tab and ensure that the 'Better Performance' option is selected, then launch the Safely Remove Hardware utility. - Check the drive's 'Policies' tab and ensure that the 'Enable write caching on the device' option is selected, then remove the USB connector. |
- Check the drive's 'Policies' tab and ensure that the 'Quick Removal' option is selected, then remove the USB connector.
Explanation Check the drive's 'Policies' tab and ensure that the 'Quick Removal' option is selected. The 'Quick Removal' option disables write caching and sends the write commands to the device as if there were no cache. This could result in slower disk access, but allows you to remove the storage device from the system quickly without risking data loss. This option is the default for removable devices. The 'Better Performance' option enables write caching which is best for devices that you intended to remove from the system infrequently. Use the 'Safely Remove Hardware' feature before removing a device with the Better Performance option to avoid data loss or corruption caused by write caching. Use the 'Enable write caching on the device' option on fixed (internal) disks to enable write caching. This improves system performance, but a power outage or system failure might result in data loss. The 'Turn off Windows write-cache buffer flushing on the device' option disables the cache buffer and instructs the storage device to transfer all data waiting int he cache to the storage media. Section 7.6 |
|
|
You have a Windows 7 computer that you manage at work.
Because of security requirements for your company, you need to prevent all users from being able to save files to any removable storage device on the computer. users are allowed to copy files from these devices. You want to accomplish this with the least amount of effort as possible. What should you do? - For each removable drive, configure NTFS permissions to deny write permission. - In removable storage access in Group Policy, configure the policy for each device type to deny write access. - In removable storage access in Group Policy, deny access to all removable storage classes. - In device installation restrictions in Group Policy, prevent installation of removable devices using the GUID of each device class. - In device installation restrictions in Group Policy, prevent installation of removable devices. |
- In removable storage access in Group Policy, configure the policy for each device type to deny write access.
To prevent a specific type of access to removable devices (read, write, or execute), configure removable storage access policies in Group Policy. For example, you could allow read access but prevent write access. When allowing or denying a specific type of access, you must configure each policy for the device class you want to control (such as floppy, tape, or removable disks). For removable storage, you can deny all access to all classes through a single policy; however you cannot deny all write access to all classes denying all access to all devices not yet identified. Section 3.4 |
|
|
You manage three Windows 7 computers that are part of a workgroup.
You would like to configure event subscriptions so that you can view all events from those computers on your laptop (which also runs Windows 7). You need to configure the three source computers and one collector computer. The subscription will be a source initiated subscription. What should you do? (Select two. Each choice is a required part of the solution.) - On the collector computer, configure the subscription. - On all four computers, configure the subscription. - On all four computers, run 'winrm qc -q'. On the collector computer, run 'wecutil qc /q'. - On the source computers, run 'winrm qc -q'. On the collector computer, run 'wecutil qc /q'. - On all four computers, run 'winrm qc -q'. |
- On the collector computer, configure the subscription.
- On all four computers, run 'winrm qc -q'. On the collector computer, run 'wecutil qc /q'. Explanation To configure Event Subscriptions for a source initiated subscription: * Run 'winrm qc -q' on all computers. * In the local policy or Group Policy that applies to the source computers, identify the FQDN of the collector computer. * In the collector computer, run the 'wecutil qc /q' command. * On the collector computer, open Event Viewer and configure the subscriptions properties such as the location of the forwarded events. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a Windows 7 computer.
You would like to configure Event subscriptions for that computer to forward events to a network server. You need to configure your computer as a source computer for a source initiated subscription. Which of the following will be part of your configuration? (Select two.) - Configure the local security policy to identify the FQDN of the collector computer. - Add the collector computer to the Event Log Readers group. - Run 'winrm qc -q' - Run 'wecutil qc /q' |
- Configure the local security policy to identify the FQDN of the collector computer.
- Run 'winrm qc -q' Explanation use a source initiated subscription to configure a subscription when all the possible source computers are not known. To configure a source computer for source computer initiated subscriptions: * Run the 'winrm qc -q' command to run WinRM. * Configure and enable the Event Forwarding policy through Group Policy or the local security policy, and specify the collector computer's FQDN. Run 'wecutil qc /q' on the collector computer for collector initiated subscriptions. The other task is performed when configuring collector initiated computers. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You mange three computers that run windows 7 and a custom application.
The application generates Event viewer events and logs those events to a custom log for the application. You would like to send all events from the application to a fourth computer where you can save and view the logs. What should you do? - Create a custom view. - Configure a performance counter alert. - Attach a task to the application's log. - Configure event subscriptions. - Configure an event trace data collector. |
- Configure event subscriptions.
Explanation Use Event Subscriptions to view a set of events stored in multiple logs on multiple computers. Events that occur on one computers are sent to another computer where they are saved and can be viewed. Attach a task to an event or log to receive notification or take other actions when an event is logged. Tasks attached to a log or a custom view execute the action when any event is added to the log or the custom view. a custom view is a saved filter. Custom views are saved between Event Viewer sessions, and are available each time you use Event Viewer. Use a performance counter alert to configure triggers that take an action when a counter reaches a threshold value. Alerts monitor a system performance statistic, such as processor time or disk space. Use an event trace data collector in Performance Monitor to capture events logged by software processes. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
The computer has a single hard disk with a single partition. Windows is installed on this partition. You decide that you would like to modify the existing volume to make it a RAID-1 volume to add fault tolerance to the volume. You add a new hard disk to the computer. You want to convert the volume to a RAID-1 volume using the least amount of effort possible. What should you do? - Boot the computer from the installation disc. Create a new striped volume using both disks. Restore the computer from a system image backup. - Boot the computer from the installation disc. Create a new mirrored volume using both disks. Restore the computer from a system image backup. - Add a mirror to the existing Volume. - Extend the existing volume. |
- Add a mirror to the existing Volume.
Explanation A RAID-1 volume is a mirrored volume. With an existing volume, you can add fault tolerance by adding a mirror to the existing volume in Disk Management. The mirroring process duplicates data from one disk to the new disk without destroying the existing volume. Extending a volume adds space to the volume, but does not add fault tolerance. In addition, you cannot extend the system volume. A striped volume (Raid-0) uses two disks and provides increased performance but not fault tolerance. To stripe an existing volume, you must delete the volume and create it new as a striped volume. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
You want to modify the disk defragmentation schedule to run twice a week on Wednesdays and Saturdays at 11pm. What should you do? - From the command prompt, run 'Defrag /M' - In Scheduled Tasks, modify the default task to run on Wednesdays and Saturdays. - In Explorer, edit the properties for the drive. On the 'Tools' tab, click 'Defragment now...', then modify the defragmentation schedule. - Run 'Cleanmgr'. Select the drive letter, then use the 'More Options' tab to configure the defragmentation schedule. |
- In Scheduled Tasks, modify the default task to run on Wednesdays and Saturdays.
Explanation By default, disk defragmentation is set to run on a schedule. You can modify the schedule to run daily, weekly, or monthly. When accessing disk defragmentation through the properties of a drive, you can only run disk defragmentation once each day, week, or month. To run disk defragmentation more than once in a day, week, or month, use Scheduled Tasks in Computer Management to modify the schedule or to create additional scheduled tasks for each time you want the program to run. Use the 'Defrag' command to manually run disk defragmentation. You cannot use 'Defrag' to schedule or modify the schedule for disk defragmentation. Use 'Cleanmgr' to delete extra files from your hard drive. While this might improve performance, it does not defragment the drive. Section 3.3 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
Recently, a WSUS server was configured and enabled in your internal network. Now you need to configure Windows Update on your computer to search for and download updates from the WSUS server. What should you do? - Set the 'Specify intranet Microsoft update service location' setting in Group Policy. - Set the 'Configure Automatic Updates' setting in Group Policy. - Use the 'Check for updates' button in Windows Update. - Use the 'Change settings' in Windows Update. |
- Set the 'Specify intranet Microsoft update service location' setting in Group Policy.
Explanation Use the 'Specify intranet Microsoft update service location' setting in Group Policy to configure clients to connect to the specified intranet Microsoft update service, instead of Windows Update, to search for and download updates. Use the 'Configure Automatic Updates' setting in Group Policy to configure how automatic updates are applied on the system. The 'Change settings' options in Windows Updates will not determine where the client downloads updates. By default, each client contacts the Microsoft Web site for updates. Click the 'Check for updates' button in Windows Update to manually check for updates but not install them. Section 7.7 |
|
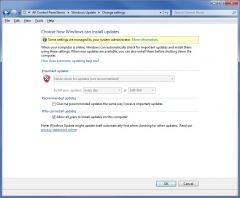
You have a computer that runs windows 7.
While manually configuring Windows Update, you notice that several settings are grayed out and unchangeable as shown in the image. You want to enable the settings so you can manually configure them. What should you do? - Use Group Policy to modify the Windows Update settings. - Run 'wuauclt.exe /detectnow' - Run Windows update in the Control Panel as a user with administrative privileges. - Use 'wusa.exe' |
- Use Group Policy to modify the Windows Update settings.
Explanation use Group Policy to modify the Windows Update settings. A user with administrative privileges can use Group Policy to disable settings or remove access to specific Windows features, including Windows Update. Run 'wuauclt.exe /detectnow' to manually check for updates but not install them. Run /wusa.exe/ to install Microsoft Update (MSU) files manually. Running Windows Update as an administrator will not enable the grayed out and unchangeable settings. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
The computer has a single hard disk with a single volume that takes up the entire hard disk. You need to create a new volume named 'Video' for storing digital video files that are used as you create music videos. You want the new volume to optimize performance; fault tolerance is not needed. What should you do? - Add three hard disks. Convert all disks to dynamic. Create a new RAID-5 volume using all disks. - Add two hard disks. Convert both disks to dynamic. Create a new striped volume using both disks. - Add two hard disks. Convert both disks to dynamic. Create a new spanned volume using both disks. - Add two hard disks. Convert both disks to dynamic. Create a new mirrored volume using both disks. |
- Add two hard disks. Convert both disks to dynamic. Create a new striped volume using both disks.
Explanation A striped volume provides an increase in performance. With a striped volume, a single file is divided into units and stored on both disks at the same time. Multiple disk controllers read and write the single file, improving performance. Striped volumes require two or more disks, but do not provide fault tolerance. A spanned volume uses multiple disks but does not improve performance. Data is saved to one disk until it is full, then it is saved to the other disk in the set. A mirrored volume uses two disks, but writes a single file to both disks. It provides fault tolerance because the data is written twice, once to each disk. A RAID-5 volume provides fault tolerance and improved performance. Striping provides performance increases, while parity information provides fault tolerance. RAID-5 volumes cannot be created in Disk Management on Windows 7. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a Windows 7 computer with a single hard drive.
You want to add fault tolerance to the existing hard drive. You install a new hard drive in the computer. What should you do? - From a command prompt, run 'Diskpart'. Use the 'Convert' command. - From a command prompt, run 'Diskpart'. Use the 'Expand' command. - From a command prompt, run 'Diskpart'. Use the 'Add' command. - From a command prompt, run 'Diskpart'. Use the 'Extend' command. |
- From a command prompt, run 'Diskpart'. Use the 'Add' command.
Explanation To add fault tolerance to an existing volume, use the 'Add' command within 'Diskpart' to add a mirror to the volume using the new disk. Use the 'Convert' command to convert from FAT32 to NTFS. Use the 'Extend' command to add space to an existing volume. Use the 'Expand' command to increase the maximum size of a virtual disk. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a laptop running windows 7 Ultimate.
You are about to give a presentation. You connect your laptop to an external display device. You want to make sure that your desktop icons and the Start Menu does not show up on the external display while you are presenting. What should you do? (Choose two. Each answer is a complete solution.) - In Display properties, select 'Duplicate these displays'. - Use the Mobility Center to extend your desktop on the external display. - In display properties, select 'Extend these displays'. - In Display properties, select the external monitor and click 'Make this my main display.' |
- Use the Mobility Center to extend your desktop on the external display.
- In display properties, select 'Extend these displays'. Explanation Extending the desktop extends the desktop background but not the Start Menu, the Taskbar, or any existing desktop icons. In this scenario, you can: * Use the Mobility Center to extend your desktop on the external display. * Select Extend these displays in the Display properties. Duplicating the display, and using the external monitor as the primary monitor, shows all contents of the desktop on the external display. Section 6.5 |
|
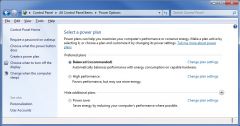
You have a laptop running windows 7 Ultimate.
You keep the laptop plugged in most of the time and would like to use the full CPU power for a video project you are working on. Select the power plan you would use to provide full CPU power? |
- High performance
Explanation The High Performance power plan is best for this project, since it will set the Processor power management setting to 100%. Use the Power Saver power plan to save as much battery power as possible. The default power plan is the Balanced power plan, which adjusts for optimum power based on usage. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs windows 7 and a custom application.
On a periodic basis, the application writes or modifies several registry entries. You want to monitor these registry keys so that you can create a report that shows their corresponding settings over the next 5 days. What should you do? - In Performance Monitor, configure a configuration data collector. - In Event Viewer, attach a task to the events that are logged when the registry values change. - Create a Scheduled Task that runs periodically. Int he task, create a script that backs up the necessary portions of the registry. - Use the reports generated in Reliability Monitor. Select each of the past 5 days and look for registry changes int he system Stability Report. |
- In Performance Monitor, configure a configuration data collector.
Explanation Use a configuration data collector in Performance Monitor to monitor registry keys and values. Configure an interval (such as every 10 minutes) for the data collector to report the setting of the registry keys at that time. Configure the Data Collector Set with a stop duration of 5 days to collect data only for those 5 days. By using the data collector, you can easily create a report from the log data. Changing a registry key does not automatically log an event int he Event Log, nor can you use Event Viewer to easily generate a report. Backing up the registry at selected intervals will capture the existing configuration, but the data is not in an easy-to-read format. The System Stability Report does not monitor registry changes, only software install/uninstall or failures (hardware, software, Windows, etc.). Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Ultimate.
After running the Backup and Restore console, you notice that backups are not created for open files. To troubleshoot the issue, you want to confirm that the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) is started and is configured to start automatically when the computer boots. What should you do? - Use Event Viewer. - Open the Services snap-in. - Open Reliability Monitor. - Open Performance Monitor. - Run Computer Management. |
- Open the Services snap-in.
Explanation Use the Services snap-in to view and manage running services. A service is a program that processes requests from other applications or users. Services can start automatically or they might be constantly running in the background, waiting for service requests. Performance Monitor displays statistics that tell you about the operation of your computer. use Event Viewer to view logs about programs, system events, and security. Reliability Monitor maintains historical data that describe the operating system's stability. Computer Management is a saved Microsoft Management Console (MMC) console that is used to manage your computer. Section 7.1 |
|
|
You have a laptop running windows 7 Ultimate.
You need to configure the following power options on your laptop when on battery power: * Put the computer to sleep after 15 minutes of idle time. * Have the wireless adapter enter a strict power saving mode. * Shut down the computer if you close the lid. What should you do? - Configure the laptop to use the default High Performance power plan. - Configure the laptop to use the default Power Saver power plan. - Configure the advanced settings of any power plan. - Configure the laptop to use the default balanced power plan. |
- Configure the advanced settings of any power plan.
Explanation The combination of the requirements force you to use the advanced settings of a power plan. Enabling a default power plan will not take care of all the requirements. Section 6.5 |
|
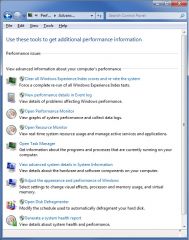
You suspect that a process on your windows 7 computer is causing a large amount of network activity. You would like to view the network activity on your computer filtered by specific processes.
Select the link that you would choose to view this information. |
- Open resource Monitor
Explanation Select the Open Resource Monitor link. resource Monitor displays additional information not found in Task Manager. by filtering on an application or process, you can view the CPU, memory, disk, and network activity generated by the application or process. You can view detailed statistics for each category, such as working set, shareable, and private memory for a process. Section 7.4 |
|
|
You have two computers that run Windows 7.
One computer has two hard disks. The second disk is a dynamic disk formatted with FAT32. You remove the second hard disk from this system and install it into the other system. After adding the disk, Disk Management reports it as foreign and you are unable to access data on the disk. What should you do? - Upgrade the disk to a dynamic disk. - Run the 'Convert' command. - Reactive the disk. - Initialize the disk. - Import the disk. |
- Import the disk.
Explanation Import a foreign disk to make it usable. A 'foreign' disk is a dynamic disk that was created in one system and moved to another system. When you first add the dynamic disk to a different system, import the disk so that the partition information on the system is updated. Foreign disks only occur for disks that are already dynamic disks. Initializing a disk specifies the partition format (either MBR or GPT); disks that are already formatted are already initialized. Reactivate a disk to try to fix Missing, Offline, or Online (Errors) statuses. Use the 'Convert' command to change the file system on a volume to NTFS. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a laptop running windows 7 Professional.
You have been having trouble with the laptop crashing. The support technician wants you to send him a memory dump that occurred when the computer crashed. You find that the computer did not create the memory dump file. You need to configure the system to create a memory dump file when it crashes. What should you do? - Place the paging file on the system drive. - Increase the paging file size from the default to at least 2 times the amount of physical RAM. - Place the paging file on a drive other than where the operating system files are stored. - Place the paging file on a USB flash device. |
- Place the paging file on the system drive.
Explanation You must place the paging file on the system drive if you want the system to be able to create a memory dump file when it crashes. The system cannot create a memory dump if the paging file is not on the system volume. The paging file must be at least the same size as the amount of physical memory. Section 7.6 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs windows 7.
You want to see memory statistics for a specific process. You need to view the working set, shareable, and private memory for the process. What should you do? - Filter on the process in Resource Monitor. - In Performance Monitor, create a data collector set using the process as the object and add the required memory counters. - View the Performance tab in Task Manager. - View the Processes tab in Task Manager. |
- Filter on the process in Resource Monitor.
Explanation Resource Monitor displays additional information not found in Task Manager. By filtering on an application or process, you can view the CPU, memory, disk, and network activity generated by the application or process. You can view detailed statistics for each category, such as working set, shareable, and private memory for a process. Using Task Manager, you can view the amount of memory used by a process on the Processes tab, but you cannot view additional memory statistics for that process. You can view some additional memory statistics for the entire system on the Performance tab, but this information does not separate memory use by process. With Performance Monitor you can view individual statistics (counters), but you cannot separate those counters by application or process. Section 7.4 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs windows 7.
Windows Update is continually notifying you to install an update that you have determined that you should not install on your machine due to incompatibility reasons. You want Windows Update to stop notifying you of this update. What should you do? - Hide the update. - Disable the messenger service. - Disable recommended updates. - Install the update, then uninstall it. |
- Hide the update.
Explanation Hide the update in Windows Update. Hidden updates do not provide notifications. Use the 'Restore hidden updates' option to view all hidden updates that are available. Once restored, you must still choose to install the update separately. Recommended updates are non-critical updates that address functionality issues. By default, Recommended updates are still downloaded and installed; the notification balloon will continue to prompt to install these updates as well as critical updates. Installing the update and then uninstalling it will not get rid of the notification balloon. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs windows 7.
The computer has a single hard drive with a single disk partition. The 500 GB system (C:) volume currently has 200 GB free. You decide to implement BitLocker, but find you need a 100 MB partition in addition to the system partition. You need to add a second partition for use with BitLocker with as little effort and cost as possible. What should you do? - Create a volume on a removable storage device. - Add a second hard disk. Create the 100 MB partition on the new hard disk. - Shrink the C: volume. Create a new partition using free space on the disk. - Boot to the Windows installation disc. Reparation and reformat the disk. Restore your computer from a system image. |
- Shrink the C: volume. Create a new partition using free space on the disk.
Explanation The easiest way to create a new partition on the same disk is to shrink the existing volume. When you shrink a volume, the partition boundaries are changed to remove disk space from the existing partition. You can then create a new partition using the unallocated disk space. Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have a windows 7 computer that you manage at work.
Because of the security requirements of your company, you need to prevent all users from being able to use USB flash devices on this computer. What should you do? - Configure removable storage policies in the local security policy. - Configure driver installation policies in the local security policy. - Run 'pnputil -d' to delete the device drivers from the driver store. - Configure user rights in the local security policy. |
- Configure removable storage policies in the local security policy.
Explanation use the Removable Storage Access policies in Group Policy to control read, write, and/or execute actions from removable storage devices. You can restrict on an existing device type, such as CD/DVD or floppy, or you can use the unique identifier (GUID) to restrict devices based on a custom class. Drivers for USB devices exist by default in the driver store, so USB devices are installed automatically without having to have rights to add drivers to the system. You cannot remove the driver from the driver store to prevent installing USB devices. Use driver installation policies to allow non-administrative users to add drivers on the system, not to prevent users from installing specific devices. You can prevent users from loading new drivers using user rights, but because the driver is already in the driver store, user rights cannot control USB device use. Section 3.4 |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7 Enterprise.
You use an external USB hard drive to store data files. You often find yourself waiting as Windows writes data to the external drive. Although it is portable, you rarely remove the external drive from the computer. You need to increase the access speed of the hard drive. What should you do? - Configure the write caching drive policies for quick removal. - Configure the process affinity for the drive. - Configure the write caching drive policies for better performance. - Configure the paging file location to be on the USB drive. |
- Configure the write caching drive policies for better performance.
Explanation Change the drive policies for better performance to enable write caching. Write caching uses RAM to collect write commands sent to data storage devices and caches them until the slower storage media (including hard drives or USB flash devices) can process those requests. The better performance option is best for devices that you intend to remove from the system infrequently. Optimized for performance: * Data may be lost if the device is disconnected from the system before all the data is written. * Use the Safely Remove hardware feature before removing the device to avoid data loss or corruption caused by write caching. The quick removal drive policy option disables write caching and sends the write commands to the device as if there were no cache. This could result in slower disk access, but allows you to remove the storage device from the sytem quickly without risking data loss. This option is the default for removable devices. Configuring the paging file to the external drive would decrease write performance because the computer would use the external drive as if it were RAM. The processor affinity identifies which processors or processor cores that the process can use. For example, you can configure a process to run only on one of the cores in a quad-core CPU. Section 7.6 |
|
|
You manage a computer that runs Windows 7.
While working with a new application, the application stops responding. You would like to analyze the application and its associated processes to identify which processes the application is waiting on. What should you do? - In Task Manager, go to the service associated with the process. open the Services console and view the dependencies for that service. - In Task Manager, end the process tree for the process. - In resource Monitor, analyze the wait chain for the process. - In Event Viewer, create a filtered view for events related to the process. Examine the details of each event. |
- In resource Monitor, analyze the wait chain for the process.
Explanation You can use Resource Monitor to identify processes that a process is waiting for. a process wait chain includes all of the applications which are waiting for other processes to finish. To view the process wait chain, right-click the name of the process, then click 'Analyze Wait Chain'. A process tree is the list of all processes and dependent processes used by an application. Ending the process tree terminates the selected process and all dependent processes, but does not show you processes that cause the process to wait. Dependencies in the Service console show services that rely on the selected service. The selected service must be started before dependent services can start. Section 7.4 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7. You started using the computer three months ago.
Since that time, you have found that, from time to time, the system has had slowdowns and crashes. You want to look at a report that shows important events for the server since it was installed. you'd like to see when software was installed, along with any hardware or application failures. You want to view this information with as little effort as possible. What should you do? - Add objects and counters to performance Monitor for events you want to view. - Create a custom view in Event Viewer that filters on the events you are looking for. - Open the System Stability Chart in Reliability Monitor. - Configure a data collector set with performance counter data collectors and configuration data collectors. |
- Open the System Stability Chart in Reliability Monitor.
Explanation The System Stability Chart in Reliability Monitor keeps track of overall server health on a daily basis. it shows you a historical record of system changes and events, and assigns an overall server health value to each day (with 1 being the least stable and 10 being the most stable). You might be able to create filters or a custom view in Event viewer to see the same kind of information. However, if the event logs were full or cleared, data might be missing. In addition, you would have to configure the custom view, and then possibly interpret the events that you see. With Performance Monitor, you can configure objects and counters to see current information, but you cannot go back and review past information. You can use a data collector set to capture information, but the collector must have already been configured and running in order to view historical data. Section 7.5 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Ultimate.
You recently upgrade the computer from windows XP Professional. The client who uses the computer has called to complain that the windows 7 interface is very slow. For example, after clicking on the Windows start button, the Start Menu slowly appears on the screen. You want to improve performance without upgrading any hardware. What should you do? - Increase the color depth of the display. - Increase the resolution of the display. - Set the visual effects for best performance. - Enable DEP. |
- Set the visual effects for best performance.
Explanation Adjust the visual effects for best performance. This will disable animation, shading, and fading effects used by Windows 7. Doing so reduces the load on the older hardware used in the client's system and should increase the performance of the user interface. Changing the resolution setting changes the size of text and windows in relation to the screen. Changing the color depth affects the number of colors that can be displayed at one time. Data Execution Protection (DEP) helps prevent damage to your computer from viruses and other security threats. Section 7.6 |
|
You have a computer that runs windows 7.
You would like to configure windows update to download updates that Microsoft suggests, but does not mark as important. You would also like to ensure that updates are installed on the computer without the intervention of an Administrative user. Select the settings that you should enable on the computer. |
- Give me recommended updates the same way I receive important updates.
- Allow all users to install updates on this computer. Explanation To automatically download non-important updates, select 'Give me recommended updates the same way I receive important updates. To ensure that an Administrator is not required before updates can installed, select 'Allow all users to install updates on this computer'. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs windows 7.
The computer is a member of a domain. windows Update settings are controlled through Group Policy. You need to determine if a specific security update from Windows Update is installed on the computer. What should you do? - Check the local security policy. - Run 'wuauclt.exe /listupdates' - Run 'wsusutil.exe /approvals' - Go to Programs and Features in the Control Panel |
- Go to Programs and Features in the Control Panel
Explanation To check a computer for specific update, you click the 'View update history' link in windows UPdate, or click 'View installed updates' in Programs and Features (both available through the Control Panel). Wuauclt.exe is the client component for Windows Update. One of the few functions of this program is to check for updates using settings configured locally or through Group Policy. You can run 'wuauclt /detectnow' to force the computer to check for updates immediately, but there is no option for seeing which updates have been installed. 'Wsusutil.exe' is a command-line utility for managing updates on a WSUS server. Use this command to see which updates have been approved for clients. Seeing approved updates does not tell you if those updates have been installed. The local security policy shows you the update settings that would be controlled locally. In this scenario, because Group Policy is being used, these settings would tell you noting about the configuration of the computer. Section 7.7 |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7 Ultimate.
You have an application that compresses videos used in your online business. You want to make sure that the application continues to run in the background, even if you open other applications. You need to adjust the amount of attention given to that application. What should you do? - Use Task Manager to modify the process priority. - Use Task Manager to modify the processor affinity. - Use the services console to change the startup type to Automatic. - Use Task Manager to switch to the running application. |
- Use Task Manager to modify the process priority.
Explanation Use Task Manager to configure the process priority. The priority controls how the system can delay or switch between processes. * By default, the system typically gives higher priority to a process that has active user input or interaction. * (Processes can continue to run in the background (i.e. when the user is not actively interacting with the application). Virus scanners, video compression, and backups are examples of processes that run in the background while you can continue working in a different application. * If a background process has a priority that is too high, the system might seem slow and unresponsive when running other programs. The affinity identifies which processors or processor cores that the process can use. For example, you can configure a process to run only on one of the cores in a quad-core CPU. Switching to an application simply brings that application to the front where you can work with it. The service startup type identifies whether a service starts automatically when the system boots. Section 7.4 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Ultimate.
When running multiple applications, the computer is slow to respond. To improve performance, you enable ReadyBoost on a USB flash drive. You need to edit the ReadyBoost settings. What should you do? - Use the 'Customize' tab in the properties of the USb flash drive. - Right-click USB flash drive in Windows Explorer, and select 'ReadyBoost'. - Use the 'ReadyBoost' tab in properties of the USB flash drive. - Use the 'Policies' tab in the properties of the USB flash drive. |
- Use the 'ReadyBoost' tab in properties of the USB flash drive.
Explanation Use the 'ReadyBoost' tab in the properties of the USB flash drive to edit the 'ReadyBoost' settings. ReadyBoost treats the USB drive as extra RAM. It has slower access speeds than physical RAM, but is still much faster than accessing the page file (virtual memory) on the hard drive. Use the 'Customize' tab in the properties of the USB flash drive to optimize the drive for specific types of files, such as documents, pictures, or videos. Use the 'Policies' tab in the properties of the USB flash drive to set the removal policy. You cannot right-click the USB drive in Windows Explorer and receive a ReadyBoost option. Section 7.6 |
|
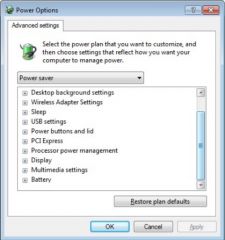
You have a laptop running Windows 7 Enterprise.
You would like the laptop to Sleep when the battery level becomes critically low. Select the area you would use to configure this setting. |
- Battery
Explanation Select the 'Battery' branch to configure the low and critical battery levels as well as the actions to take when those levels are reached. The 'Sleep' branch allows you to configure a time limit for when the computer will go into Sleep mode and to configure the hybrid Sleep option. The 'Power buttons and lid' branch allows you to configure the actions that are taken when the lid is closed or the Power button is pressed. The 'Processor power management' branch allows you to configure the processor state and the cooling policy. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7 Enterprise. The computer is a member of a workgroup.
For several months, the computer acted like a sever in the workgroup. It was optimized to share files and folders to the other computers. You no longer need the computer to act like a server. You want the computer to focus on applications which are found on typical workstations. After installing the applications, you believe the computer is not reacting quickly enough while using the applications. You know the machine has enough video memory and physical memory to handle the applications. What should you do? - Use ReadyBoost on a USB flash drive. - Edit the Processor Scheduling settings. - Configure System Protection settings. - Configure visual effects settings. |
- Edit the Processor Scheduling settings.
Explanation Configure Processor Scheduling to adjust the response times of interactive applications or background applications running as services. in this scenario, you should adjust the Processor Scheduling for programs. This option gives the active application the best response time and the greatest share of available resources. Use the Visual Effects settings to affect the appearance of window borders, window contents, mouse printers, and text. If the system has a slower processor, low memory, or not enough video memory, using visual effects can make the system respond slowly. System Protection settings enable backups of system files and user data files. ReadyBoost is a feature that treats a USB drive as extra RAM in the machine. It has slower access speeds than physical RAM, but is still much faster than accessing the page file on the hard drive. Section 7.6 |
|
|
You have a shared computer that runs Windows 7.
You are concerned about the disk space use on the computer. You would like to be notified by e-mail when the used disk space exceeds 85%. What should you do? - Configure a performance counter alert. - Configure an event trace data collector. - Configure event subscriptions. - Attach a task to the System log |
- Configure a performance counter alert.
Explanation Use a performance counter alert to configure triggers that take an action when a counter reaches a threshold value. Alerts monitor a system performance statistic, such as processor time or disk space. Use an event trace data collector in Performance Monitor to capture events logged by software processes. Attach a task to an event or a log to receive notification or take other actions when an event is logged. Use Event subscriptions to view a set of events stored in multiple logs on multiple computers. Events that occur on one computer are sent to another computer where they are saved and can be viewed. Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7.
The second hard disk in the computer has been assigned D: as the drive letter. The volume is formatted with NTFS. You decide that you would like to modify the D: volume to make it a RAID-0 volume. You want to convert the volume to a RAID-0 volume using the least amount of effort and expense as possible. What should you do? - Add a mirror to the existing volume using the new disk. - Delete the existing volume. Create a new mirrored volume. Restore data to the volume from a backup. - Delete the existing volume. create a new striped volume. Restore data to the volume from a backup. - Extend the existing volume to the new disk. |
- Delete the existing volume. create a new striped volume. Restore data to the volume from a backup.
Explanation A RAID-0 volume is a striped volume. you cannot stripe an existing volume. instead, you must delete the existing volume, then create a new striped volume that uses two disks. After the volume is created, restore data to the disk. A RAID-1 volume is a mirrored volume. With an existing volume, you can add fault tolerance by adding a mirror to the existing volume in Disk Management. The mirroring process duplicates the data from one disk to the new disk without destroying the existing volume. Extending a volume adds space to the volume, but does not result in a striped or mirrored volume (just a volume with more disk space). Section 3.2 |
|
|
You have two computers that run window 7: Computer 1 and Computer2.
You have configured event subscriptions with the default settings to forward events from these two computers to a third Windows 7 computer, Computer3. You want to view the events from these two computers on Computer3. What should you do? - In Event Viewer, create an event filter that includes all logs, with a source of Computer 1 or Computer2. - In Performance Monitor, create a data collector set to gather data from Computer 1 and Computer2. - In Event Viewer, open the ForwardedEvents log. - In resource Manager, apply a filter for Comptuer1 and Computer2 |
- In Event Viewer, open the ForwardedEvents log.
Explanation By default, events received from source computers are saved in the ForwardedEvents log in Event Viewer. You could create a filter, but the filter would not show any information that is different from what is in the ForwardedEvents log. use a filter if you want to add additional filters to the events in that log. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7 and a custom application.
The application generates Event Viewer events and logs those events to the default Application and Security logs in the Event Viewer. As you monitor the application, you'd like to be able to do the following: * View all events related to the application from a single log. * View only the events related to the application and no others. * View the necessary events with minimal future configuration. * Save the Event Viewer configuration so that you can easily export and import the solution to other servers that will be running the application. What should you do? - Configure event subscriptions. - Create a custom view. - Create a filter on the Application and Security logs. - Attach a task to the event ID's generated by the application. |
- Create a custom view.
Explanation A 'custom view' is a saved filter. Custom views apply filter criteria to one or more event logs. The filter criteria for a custom view is similar to that for a filter, but also includes the log(s) you want to include int he view. Custom views are saved between Event Viewer sessions, and are available each time you use Event Viewer. You can export a custom view and import it on another system. This exports and imports the custom view criteria, not the events showing in the view. Adding a filter in Event Viewer has the following limitations: * You cannot save a filter. each time you start Event Viewer, you will need to redefine the filter criteria. * Filters apply only to a single log; you cannot filter multiple logs into a single view. * You cannot export and import filter criteria to other computers. Use Event Subscriptions to view a set of events stored in multiple logs on multiple computers. Events that occur on one computer are sent to another computer where they are saved and can be viewed. Attach a task to an event or a log to receive notification or take other actions when an event is logged. Section 7.2 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Ultimate.
The computer is performing poorly. You want to check the memory component subscore of your computer. What should you do? - Run Windows memory Diagnostic Tool (WMDT) - Run System Configuration - Run Windows Experience Index - Run Device Manager |
- Run Windows Experience Index
Explanation The Windows Experience Index assesses the performance of a PC and assigns a score to it. The higher the score, the better the PC will perform. The overall PC performance is represented by the base score. The base score is derived from five subscores for each of the following attributes; processor, memory, graphics, gaming graphics, and primary hard disk. While the other tools may be useful for troubleshooting, none provide a component rating. Use Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool (WMDT) to look for symptoms of defective memory. Use Device Manager to verify that all devices have been recognized and configured. Use system Configuration to configure startup preferences and disable/enable services. Section 7.3 |
|
|
You have a windows 7 Professional computer that is sued by three users. Each user has a folder for storing personal data.
Chad copies a file from a CD-RW to his folder and receives the message 'Insufficient disk space'. he finds that he cannot even add data to an existing file and save it. other users of the computer do not have the same problems. you see that the volume has over 20 GB of free disk space. You need to let Chad create and edit files. What should you do? - Increase the quota limit. - Add chad to the Power users group. - Configure that Backup is not running. - Confirm that NTFS compression has been enabled. - Defragment the hard drive. |
- Increase the quota limit.
Explanation The 'Insufficient disk space' means that either the server's hard disk is full or that a user has reached the limit of his or her disk quota. Because nobody else is having problems, Chad must have reached his quota limit. When the select the 'Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit' option, users who exceed their limit receive an insufficient disk space error and cannot write additional data to the volume without deleting or moving files. To an application, it appears that the volume is full. Therefore, you should increase Chad's quota limit. Section 3.3 |
|
|
You have several computers running windows 7 Ultimate. The computers are members of a domain.
For all the computers, you want to remove access to administrative tools for the Start menu and hide notifications from the System tray. What should you do? - Use account policies - Use account restrictions - Use Group Policy - Use file screens |
- Use Group Policy
Explanation Use Group Policy to control the desktop for groups of users or computers. For example, you can prevent access to specific desktop or Start menu features. Account policies are specific Group Policy settings that control user passwords. Account restrictions are settings applied in the user account that restrict logon hours or computers. Use file screens to control the types of files that can be saved withing a folder. Section 1.5 |

