![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
You have a laptop running windows 7 Professional.
You configure the computer to enter sleep mode after 10 minutes of inactivity. After 15 minutes with no activity, the computer doe snot enter sleep mode. You need to identify what is preventing the computer from entering sleep mode. What should you do? - At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /devicequery wake_from_any'. - At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /energy'. - At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /list'. - At a command prompt, run 'msconfig'. |
- At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /energy'.
Explanation Run 'powercfg /energy' at the command prompt. This command provides a report of the power management settings, including diagnostics that can indicate which applications or devices might be causing power management issues. 'Powercfg /list' displays all available Power Plans, including the active plan. 'Powercfg /devicequery wake_from_any' displays all of the connected devices that can wake up a client from sleep mode (e.g. keyboard or mouse). 'Msconfig' starts the System Configuration Utility which is used to troubleshoot technical issues, such as startup preferences and services. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a laptop that runs Windows 7 Professional.
You want to protect the hard drive using BitLocker and a startup key saved to a USB device. What should you do first? - Run the 'cipher -r' command. - Open the BitLocker Drive Encryption tool from the Control Panel. - Upgrade the computer to Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. - Copy a DRA certificate to the computer. - Use the TPM Management console to enable the TPM. |
- Upgrade the computer to Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise.
Explanation BitLocker is only supported on Windows 7 Ultimate or enterprise editions. You must first upgrade the computer to configure BitLocker. With the correct Windows edition, you can configure BitLocker using the BitLocker Drive Encryption tool in the Control Panel. A TPM is not required when using a startup key saved to a USB device. A data recovery agent (DRA) is used to recover files when the encryption key is lost. Run the 'cipher -r' command to add a DRA certificate or to change the encryption certificate for files encrypted with EFS. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You have purchased a new laptop that runs Windows 7 Ultimate.
You want to use DirectAccess to connect the computer to your corporate intranet from home. Your home network is connected to the Internet with a single public IP address and NAT. Firewalls between your network and the intranet allow only HTTP and HTTPS traffic. What should you do to configure the laptop for the DirectAccess connection.? - Disable IPv6 on your computer. - Run Windows firewall with Advanced Security and enable the Directaccess firewall rules. - Create a VPN connection that uses SSTP for the tunneling protocol. - Obtain a computer certificate for the laptop. |
- Obtain a computer certificate for the laptop.
To configure DirectAccess on a client computer: * The computer must be running Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. * Join the computer to a domain. * Issue a computer certificate to the computer. This certificate is used for authentication. * Make the computer account a member of the security group that was created when DirectAccess was configured on the server. With this configuration, additional configuration information comes automatically through Group Policy. DirectAccess does not establish a traditional VPN connection. When necessary, DirectAccess automatically uses IP over HTTPS. You do not create a VPN connection or configure the computer to use SSTP. DirectAccess requires IPv6 on clients and servers. Communication over IPv4 networks is done automatically through tunneling. GPO settings automatically configure any firewall settings that are required by DirectAccess on the client computers. Section 6.3 |
|
|
You are working on a computer running windows 7 Enterprise.
You need to manually synchronize the offline files on your computer with the versions on the network. What should you do? (Select two. Each answer is an independent solution.) - Open the Sync Center - Run Synchronize - Edit the mapped drive properties - Edit the Folder Options. |
- Open the Sync Center
- Edit the mapped drive properties Explanation Although files are automatically synchronized when the system comes back online, files might not be continuously synchronized. To force a synchronization in Windows 7, use the Synch Center or edit the mapped drive, folder, or file properties and use the Offline Files tab. You can also right-click the folder or file in windows Explorer and choose Synch. The Synchronize or Folder Options applets are only used for computers running Windows XP. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer named comp1 that runs Windows 7. The computer is located in a branch office.
A server running windows Server 2008 R2 named Srv1 is located in the main office. You share a folder named 'Data' using the default caching settings. You use Offline Files in the branch office to make the files in the 'Data' share available when the WAN link is down. On Comp1, you want to see your synchronization partners, see the results of the latest synchronization, and view and resolve any conflicts. What should you do? - Use the Shared Folders node in computer Management. - Open the Network and Sharing Center. - Edit the properties for cached file or folder. - Open the Sync Center in the Control Panel. |
Open the Sync Center in the Control Panel.
Explanation Use the Synch Center to see synchronization partners, the results of the latest synchronization, view and resolve any conflicts, and configure Offline Files settings. You can edit the file or folder to view its status (either online or offline) or to configure whether to make the file or folder available offline. use the Shared Folders node in computer Management to manage folders that you have shared on the local computer with other network computers. You can modify sharing settings through the Network and Sharing Center, but you cannot manage Offline Files. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You manage a computer running Windows 7.
You would like to configure your system so that an event is recorded any time a user successfully or unsuccessfully logs on. You do not want to record events related to logoff. What should you do? - Configure standard audit policies in the local security policy. - Configure advanced audit policies in the local security policy. - Configure user rights int he local security policy. - Attach a task to an event in Event Viewer. - Configure a custom view in event Viewer. |
- Configure advanced audit policies in the local security policy.
Explanation Use advanced audit policies for more granular control over audit policies and the types of events that are logged. The standard Audit logon 'events' and 'Audit account logon events' policies track both log on and log off events. With advanced auditing, you can audit only logon or only logoff events. Configure user rights policies to enable or disable actions that users can perform, such as logging on over the network, shutting down the system, or installing device drivers. A custom view in Event Viewer filters events but does not prevent the events from being recorded. attach a task to an event to send an e-mail, run a program, or take another action when a specific event takes place. Section 5.5 |
|
|
You have a laptop that runs Windows 7. The computer is a member of a domain.
You would like to protect the data on your laptop to meet the following requirements. * All operating system and user data should be encrypted. * All user data should be inaccessible (unreadable) if the hard disk is removed and connected to a different computer. * The computer should not boot unless a special key is found on a USB drive. * The computer should not boot if a change ids detected in the boot files. You need to implement a solution to meet the stated requirements. What should you do? - Implement BitLocker without a TPM. - Encrypt the volume using the Encrypting File System (EFS) - Implement BitLocker with a TPM - Encrypt the user profile folder using the encrypting File System (EFS) |
- Implement BitLocker with a TPM
Explanation Use BitLocker to encrypt the entire system volume and protect both operating system and user data. use BitLocker with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to protect the boot environment components such as the BIOS, Master Boot Record, Boot Sector, Boot Manager, and Windows Loader. The system is shut down if a boot environment change is detected. Using BitLocker, drives are locked if they are moved to another computer, and you can require a startup key on a USB drive or a PIN before the system will boot. If you use BitLocker without a TPM, system integrity checks are not performed. The TPM is required for saving the startup file information that is used to verify system integrity. When using BitLocker without a TPM, you must use a startup key on a USB device; when using a TPM, this is an optional configuration. EFS encrypts individual files. With EFS, only the user who encrypted the file and any additionally-designated users can access the file. EFS does not provide integrity checks for boot files. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You use a laptop named M400 which runs Windows 7 Ultimate. M400 is a member of a domain and is located in the main office.
you want the files in the 'Data' share to be cached automatically when the M400 computer opens them. You also need the files in the 'Data' share to synchronize between Server1 and M400. What should you do? - On Server 1, enable transparent caching. - On M400, edit the 'Data' folder properties. - On Server1, edit the 'Data' folder properties. - On M400, enable transparent caching. |
- On Server1, edit the 'Data' folder properties.
Explanation To control caching on a network share to meet the scenario requirements, edit the 'Data' folder properties on Server1 and enable the 'All files and programs that users open from the share are automatically available offline' option. This option caches files open on the local machine automatically. Transparent caching keeps a cached copy of all files that a user opens from a shared folder on the local client. Transparent caching does not attempt to keep the local copy synched with the copy of the file in the shared folder. The transparent caching features is enabled on the client, not on the server. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have several laptops running Windows 7 Enterprise. The laptops are members of a domain with a server running Windows Server 2008 R2.
You have been put in charge of providing a VPN solution for your company. you want the VPN connection to automatically reconnect if the VPN connection is lost or disconnected. You decide to use VPN Reconnect, but you need to ensure each laptop will make the correct VPN connection to the server. What should you do? - use Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) as the VPN protocol. - Use Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) as the VPN protocol. - Use Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) as the VPN protocol. - Use Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) as the VPN protocol. |
- Use Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) as the VPN protocol.
Explanation Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) is required to use the VPN Reconnect feature. IKEv2: * Supports IPv6, smart card authentication, and certificate authentications. * Supports data origin authentication, data integrity, replay protection, and data confidentiality. * Uses UDP ports 500 and 4500 for IKE traffic and protocol 50 for ESP traffic. * Enables the VPN connection to reamin intact as a mobile client moves from one IP network to another. * Is the default protocol for a new VPN connection for Windows 7. All the other VPN security protocols do not support the VPN Reconnect feature. Section 6.2 |
|
|
You have previously installed Windows 7 on two new computers and configured both computers with BitLocker. Both computers have a TPM installed.
Because of a hardware failure , one of the computers will not boot. You replace the failed hardware, but now BitLocker is preventing the system from starting because it has failed the startup system integrity checks. Which of the following would you use to reconfigure BitLocker so the system will start? - Startup key - Recovery key - TPM owner password - PIN |
- Recovery key
Explanation use the recovery key to gain access to encrypted volumes for recovery purposes. For example, you would need the recovery key to unencrypt the drive if you move it to a new computer, or to access the drive if the system integrity checks fail. Use the PIN or the startup key to boot the system normally if these items were required for system startup. use the TPM owner password to make future modifications tot he TPM, such as enabling or disabling the TPM. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You manage several laptops running Windows 7 Enterprise. The computers are members of a domain.
You have ten regional sales people who travel extensively and use laptops to access company resources. The users have complained that although they can take copies of important files with them into the field, occasionally they have been caught with out-of-date documents because no one told them the files had been updated. Additionally, some files they modified need to be distributed to all the other sales staff. You need to address this problem and easily provide the appropriate access to these shared files. What should you do? - Use Microsoft Outlook to e-mail the important files between users. - Configure transparent caching on the folder that contains these files. - Use NTFS permission to control access. create logon scripts to keep them synchronized. - Configure Offline Files for the folder that contains these files. |
- Configure Offline Files for the folder that contains these files.
Explanation The Offline Files feature meets the scenario requirements. Offline Files creates locally cached copies of files stored on the server, and synchronizes changes made to the local copies. Transparent caching keeps a cached copy of all files that a user opens from a shared folder on the local client. With transparent caching, the client contacts the server before opening the cached file to make sure that the file has not changed. If the server is unavailable, the cached copy will not be used. Transparent caching does not allow locally editing a file and synchronizing that file with the copy on a server. Use NTFS permissions to control access and creating scripts is possible but is more work than configuring Offline Files. E-mailing the files creates the same potential delay and would require that a mail server be provided. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You manage a Windows 7 computer that is a member of a workgroup.
The computer is shared by three users. Each user has a standard user account. Mary is one of the three users of this computer. She wants to access the computer using a Remote Desktop connection. You need to allow Remote Desktop access for Mary while granting her the least amount of privileges possible. What should you do? - Make Mary's user account a member of the Remote Desktop users group. - Grant Mary's user account the 'Access this computer from the network' user right. - Grant Mary's user account the 'Impersonate a client after authentication' user right. - Make Mary's user account a member of the Administrators group. |
- Make Mary's user account a member of the Remote Desktop users group.
Explanation By default members of the Administrators group can connect to a computer remotely. To allow other users to access the remote client, make user accounts members of the Remote Desktop Users group. You can also grant the user the Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services user right. This right is configured for members of the Administrators and Remote Desktop Users group. If you make Mary a member of the Administrators group, this would allow Remote Desktop access but also give her too many privileges on the computer. By default, Everyone has the Access this computer from the network user right. While this right is required to use Remote Desktop, the right by itself does not allow Remote Desktop. Section 7.8 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7 Ultimate.
You want to configure the computer so that write access to removable storage devices is only allowed on drives protected with BitLocker To Go. What should you do? - Edit the System properties for the computer. - Configure the local security policy. - Configure the computer with a smart card reader. - Run 'manage-bde -lock'. |
- Configure the local security policy.
Explanation Enable the 'Deny write access to remove drives not protected by BitLocker' policy in Group Policy to allow write access only to removable drives that use BitLocker. Run 'manage-bde -lock' to prevent access to content protected with BitLocker. A smart card reader can be used to control access to BitLocker drives, but does not prevent write access to drives. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You have several laptops running Windows 7. The laptops are members of a domain.
You have been put in charge of providing a VPN solution for all members of the Sales team. Salesmen complain that with the previous VPN solution, there were many times that they were unable to establish the VPN solution because the hotel or airport firewalls blocked the necessary VPN ports. You need to come up with a solution that will work in most instances. What should you do? - Use Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) as the VPN protocol. - Use Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) as the VPN protocol. - Use layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) as the VPN protocol. - Use Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) in tunnel mode as the VPN protocol. |
- Use Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) as the VPN protocol.
Explanation use Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) for the VPN protocol. SSTP uses SSL which uses port 443. Because SSL is used by many web sites for secure transactions, this port is already opened in most firewalls. PPTP, L2TP, and IPsec require special firewall ports to be opened. While many organizations that provide Internet access have these ports opened, many do not. In situations where you cannot control the firewall ports that are opened, choose SSTP for the broadest support. Section 6.2 |
|
|
You have a laptop that runs Windows 7 Ultimate.
You want to protect all of the files on the hard drie to prevent unauthorized access. you want to prevent access to any file on the hard drive, even if the hard drive is moved to another computer. Which feature should you implement.? - DirectAccess - Smart card with PIV - InPrivate - EFS - BitLocker |
- BitLocker
Explanation BitLocker protects unauthorized data access on lost or stolen laptops or other compromised systems. BitLocker encrypts the entire contents of the operating system partition, including operating system files, swap files, hibernation files, and all user files. a special BitLocker key is required to access the contents of the encrypted volume. EFS is a windows file encryption option, but only encrypts individual files. Encryption and decryption is automatic and dependent upon the file's creator and whether other uses have read permission. DirectAccess is an automatic connectivity solution that allows clients running Windows 7 to connect seamlessly to the corporate intranet through an Internet connection. The moment the Windows 7 device connects to the Internet, DirectAccess allows authorized users to access corporate file servers and view intranet Web sites without establishing and going through a VPN connection. A smart card is a physical card that contains a memory chip. Authentication credentials are embedded in this memory chip. The Personal Identity Verification (PIV) standard allows the use of smart cards without requiring specific vendor software. By supporting PIV, Windows 7 obtains drivers for smart cards from Windows Update or built-in PIV-compliant min-drivers. InPrivate is a feature of Internet Explorer that protects a user's privacy while browsing the Internet. InPrivate Filtering restricts what information about a browsing session can be tracked by external 3rd party Web sites and applications. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You have several laptops running Windows 7. The laptops are members of a domain.
Several employees in your company use the laptop computers to connect to the company network. Because they often use these laptops while traveling or to help them do their jobs, you can't prevent them from connecting to the network. However, you are concerned that many of these laptops don't have the latest security patches installed. You want to implement a solution so that laptops are checked for the latest security updates as they connect to the network. If the required updates are missing, you want to prevent these computers from having full access to the private network. What should you do? - Configure Software Restriction Policies in Group Policy. - Configure a Software Installation policy in Group Policy. - Configure windows Server Update Services (WSUS) with Automatic Updates. - Implement Network Access Protection (NAP) with a quarantine network. |
- Implement Network Access Protection (NAP) with a quarantine network.
Explanation Use Network Access Protection (NAP) to regulate network access or communication based on a computer's compliance with health requirements policies. When you configure NAP, you define health requirements, such as the presence of security updates or antivirus software, that must be met before a full connection to the network is allowed. For computers that are not compliant with the health requirements, you can create a limited access quarantine network. This network can contain servers and other resources that the computer can use to become compliant. Use Windows server Update Services (WSUS) to approve product updates for client computers. While you can use WSUS to make sure that all computers have the latest patches installed, you cannot use WSUS to deny access to the network. Use a Software Installation policy to make software automatically available to computers or users. use a Software Restriction policy to prevent running a specific software. Section 6.1 |
|
|
You have a laptop computer that runs windows 7. The computer is a member of a domain.
You want to use DirectAccess to access application servers on your corporate intranet. Application servers run Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008. You want to configure a single access method for all servers and clients. Which connection method should you use? - Full enterprise network access (end-to-edge) - End-to-end access - Selected server access (modified end-to-edge) |
- Full enterprise network access (end-to-edge)
Explanation Because the intranet includes severs running windows server 2003, the only access method that is possible is the full enterprise (end-to-edge) access method. Using this method, the client computer authenticates to the Directaccess server, and communications are only encrypted between the client and the DirectAccess server. Communications on the private network are not encrypted. Both end-to-end and modified end-to-edge methods require application servers that run Windows Server 2008. These servers must support IPv6 and IPsec. Section 6.3 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7.
The hard drive has been protected using BitLocker. You need to update the BIOS on the computer. What should you do first? - Run 'cipher /d /s' - Run 'BdeHdCfg.exe' - Run 'manage-bde -pause' - Run 'manage-bde -off' - Run 'cipher /r' |
- Run 'manage-bde -pause'
Explanation Disable (pause) BitLocker for temporary maintenance of BIOS or boot files. Disabling BitLocker creates a plaintext key on the hard drive. The plaintext key is removed when BitLocker is re-enabled. Use 'manage-bde -pause' to temporarily disable encryption. Decrypt the drive (turn off BitLocker) when you want to permanently remove BitLocker. You must re-encrypt the drive to restore protection. Use the '-off' parameter with the 'manage-bde' command to decrypt the drive. Use the 'BdeHdCfg.exe' command-line tool to repartition the disk drive. Use the 'cipher' command to manage the Encrypting File System (EFS). Section 6.4 |
|
|
You have a laptop named Comp1 that runs Windows 7. The laptop connects to the company network in a branch office.
A server running windows Server 2008 R2 named Srv1 is located in the main office. You share a folder named 'Data' using the default caching settings. You use Offline Files to automatically access files when the WAN link connecting the two offices is slow. You want to encrypt the Offline Files cache on Comp1. What should you do? (Select two. Each choice is a possible answer.) - On Srv1, edit the properties for the 'Data' folder. - On Srv1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. - On Srv1, edit the local security policy. - On Comp1, edit the local security policy. - On Comp1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. |
- On Comp1, edit the local security policy.
- On Comp1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. Explanation To encrypt the Offline Files cache, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center and use the Encryption tab. You can also use the local security policy or Group Policy to enforce encrypting the Offline Files cache. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7. The computer is a member of a domain.
Your domain contains a VPN server that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. You will use a smart card for authentication to the VPN server. What should you do? - Use CHAP as the authentication to the VPN server. - Use PAP as the authentication protocol. - Use MS-CHAP v2 as the authentication protocol. - Use EAP as the authentication protocol. |
- Use EAP as the authentication protocol.
Explanation EAP is used for smart cards, biometric authentication, and certificate-based security environments. EAP allows the client and server to negotiate the characteristics of authentication. This means that the authenticator requests authentication information (name, PIN, card token value in the case of security token cards) from the client. MS-CHAP v2 uses a challenge/response mechanism, and is the highest level of authentication possible without using EAP. CHAP is a three-way handshake (challenge/response) authentication protocol. CHAP uses Message Digest 5 (MD5) hashing of the shared secret for authentication. PAP sends the username and password in plain text. You should use PAP only when no other form of authentication is supported. Section 6.2 |
|
|
You have a new laptop that you want to configure with Windows 7.
You would like to use BitLocker on the laptop to protect the volume used for the operating system and all user data. Your laptop does not have a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). You need to configure the computer to use BitLocker. What should you do? (Select two. each choice is a required part of the solution.) - Install windows 7 Ultimate on the laptop. - Configure BitLocker to use a startup key on a USB drive. - Install Windows 7 Professional on the laptop. - Configure BitLocker to start without requiring a PIN or USB drive. - Configure BitLocker to require a Pin for startup. |
- Install windows 7 Ultimate on the laptop.
- Configure BitLocker to use a startup key on a USB drive. Explanation BitLocker requires windows 7 enterprise or Ultimate edition. When implementing BitLocker without a TPM, you must use a startup key on a USB device. Windows 7 Professional does not support BitLocker. When using a TPM with BitLocker, you can configure the computer to start with a PIN, a startup key on a USB drive, or without any additional intervention. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You manage several laptops running Windows 7 Ultimate. The computers are members of a domain.
Laptop computers are located at a branch office and access files across a WAN link stored on a serer in the main office. all files are in a network shared named 'Data' on the server. You want to reduce the amount of traffic across the WAN link for file reads from the 'Data' share. you want the laptops to save copies of the files locally, and use their local copies if the files on the server have not been modified. Files should not be available ont he client computers when the WAN link is down. What should you do? - Change the synchronization conflict settings. - Clear the 'Always Available Offline' options in the 'Data' folder properties. - Configure the Offline Files. - Enable transparent caching. |
- Enable transparent caching.
Explanation Transparent caching keeps a cached copy of all files that a user opens from a shared folder on the local client. Transparent caching does not attempt to keep the local copy synched with the copy of the file in the shared folder. |
|
|
You have a laptop that runs Windows 7.
The hard drive has been encrypted using BitLocker. BitLocker uses a TPM with a PIN and startup key. You have lost the USB device containing the startup key. You also find that you are unable to locate the recovery key. You need to be able to boot the computer. What should you do? - Disable the TPM, then re-enable it. - Reformat the hard drive and rei9nstall Windows. - Move the drive to another computer. boot the computer and run 'manage-bde -off' for the volume. - Boot the computer using the installation disc to the Recovery console. Open a command prompt and run 'manage-bde -off'. |
- Boot the computer using the installation disc to the Recovery console. Open a command prompt and run 'manage-bde -off'.
Explanation if you lose both the startup key and the recovery key, you will be unable to unlock the drive and gain access to the drive. The only option will be to reformat the hard drive and reinstall windows. If you lose the startup key but still have the recovery key, you can start the computer using the recovery key and then remove the encryption. Disabling the TPM does not remove encryption from the drive. Moving the hard drive to another computer retains the encryption, and the drive cannot be accessed on the other computer without the recovery key. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You want to make a network file available when you are not connected to the network. You right click the file and receive the following context menu options
*Open *Edit *Always available offline *Restore previous versions *Send to *Cut *Copy *Create shortcut *Delete *Rename *Properties Select the option that you should choose to make a cached version of the directory available when you are disconnected from the office network. |
- Always available offline
Explanation Select Always available offline to identify the file/folder for offline caching when manual caching is configured on the server. also, make sure the client computer has offline files enabled in Sync Center. If automatic caching is being used, simply open the file to cache it. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You manage Windows 7 computers connected to the mydomain.com Active Directory domain.
You have decided to implement DirectAccess on your network. you run the setup for DirectAccess on the DA1 server with the following choices: * End-to-end authentication with a smart card required for authentication * Root certificate from 'ca1.mydomain.com' * Security group name of 'DirectAccessGroup' * The network Location service runs on the DirectAccess server You need to configure the client computers for the DirectAccess connection. What should you do? - Configure a static IPv6 address for each client computer. - Copy the private certificate for ca1.mydomain.com to each client computer. - Run the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on each client computer to open the DirectAccess firewall ports. - Add the computer account for each client computer to the 'DirectAccessGroup' security group. |
- Add the computer account for each client computer to the 'DirectAccessGroup' security group.
Explanation To configure DirectAccess on a client computer: * The computer must be running windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. * Join the computer to a domain. * Issue a computer certificate to the computer. This certificate is used for authentication. * Make the computer account a member of the security group that was created when DirectAccess was configured on the server. With this configuration, additional configuration information comes automatically through Group Policy. For example, GPO settings automatically configure any firewall settings that are required by DirectAccess on the client computers. While DirectAccess requires IPv6 on each client, the IPv6 address can be automatically generated. The client computer must have received a computer certificate from a certification authority that is trusted by the root CA (ca1.mydomain.com), but you do not copy the private certificate of the root CA to any other computer (the private certificate must remain private). Section 6.3 |
|
|
You would like to implement Directaccess on your corporate network.
Which of the following is not an infrastructure requirement for using Directaccess? - Active Directory Certificate Services - Active Directory Domain Services - Network access for files server role - IPv6 |
- Network access for files server role
Explanation DirectAccess requires: * Active Directory Domain Services * Active Directory Certificate Services or another method of issuing certificates to servers and clients * IPv6 * Server running Windows Server 2008 R2 or higher for the DirectAccess server The Network access for files server role is required for allowing file sharing that uses BranchCache. Section 6.3 |
|
|
You have several computers running Windows 7 Enterprise. The computers are members of a domain.
You manage a custom application that is currently installed on the computers in the domain. You receive a new version of the software. Installing the software on a client computer overwrites the existing installation such that both versions cannot be used at the same time on the same computer. You decide to use Remote Desktop Services on a server in the domain to allow clients to run both the new and the old version of the software. Clients should be able to run each version using an icon on their desktops. What should you do? (Select two. Each choice is a required part of the solution.) - Configure Remote Desktop Gateway on the server. - Install both the old and the new versions of the application on a server. - Install the new version of the application on the server. - Configure RemoteApp on the server. |
- Install the new version of the application on the server.
- Configure RemoteApp on the server. Explanation To allow both versions of the application to run, you must install the old and the new versions on different computers. The easiest solution would be to install the new version on a server in the domain, and clients would continue to use the old version that is installed locally. You could also install the new version on one server in the domain, and clients would continue to use the old version that is installed locally. You could also install the new version on one server and the old version on a different server. You cannot install both versions on the same server because the two versions cannot run at the same time. On the server, configure RemoteApp to configure how the application will be launched by clients. Remote Desktop Gateway 9RD Gateway) is a role service that allows users with the Remote Desktop client and an Internet connection to connect to computers on an internal network. Section 7.8 |
|
|
You have a laptop that runs Windows 7. The computer is a member of a domain.
You want to use BitLocker on the laptop. Your implementation should meet the following requirements: *The computer should start up automatically without user intervention. * To meet security requirements, USB support must be disabled on the laptop. * You want to automatically generate recovery keys and store those keys in a central location. You need to implement a solution to meet the stated requirements. What should you do? (Select two. Each choice is a required part of the solution.) - Save the recovery key as a password. Store all passwords on a network share. - Configure Group Policy to store recovery keys in Active Directory. - Implement BitLocker without a TPM. - Save the recovery key as a file. Store all recovery keys on a network share. - Implement BitLocker with a TPM |
- Configure Group Policy to store recovery keys in Active Directory.
- Implement BitLocker with a TPM Explanation To allow the computer to boot without a PIN or a startup key on a USB drive, you must use a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). If the system does not have a TPM, you must use a startup key on a USB drive. Use Group Policy to configure each server to automatically generate the recovery key and save the key in Active Directory. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7. The computer is a member of a domain.
Your domain contains a DHCP server that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. The server is configured as a Network Access Protection (NAP) enforcement point. You need to configure the computer as a NAP client. What should you do? (Select two. Each answer is a required part of the solution.) - On the client, enable the System Health Validator (SHV). - On the client, start the Network Access Protection Agent service. Configure the service to auto-start. - On the client, start the VSS service. Configure the service to auto-start. - On the client, enable the enforcement client for DHCP. |
- On the client, start the Network Access Protection Agent service. Configure the service to auto-start.
- On the client, enable the enforcement client for DHCP. Explanation Configuring NAP requires configuration of the NAP server, the client, and the enforcement server. Complete the following steps to configure NAP on the client computer: 1. Start the Network Access Protection Agent service. Configure the service to auto-start. 2. Enable the enforcement client that corresponds to the type of enforcement point you are using on the enforcement server: * DHCP Quarantine Enforcement Client * IPsec Relying Party * RD Gateway Quarantine Enforcement Client * EAP Quarantine Enforcement Client (for 802.1x and VPN enforcement) The Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) manages and implements shadow copies for previous versions. The System health Validator (SHV) runs on the NAP server and identifies the client health requirements. The SHV compares the statement of health submitted by the client to the health requirements. Section 6.1 |
|
|
You manage a computer running windows 7 Enterprise.
You are configuring security settings that will identify when people attempt to log on with an incorrect password. You need the computer to note the failed attempts in its own audit log. You want to use Local Security Policy that create the settings. What should you do? - Enable the 'Audit account logon events' setting. - Enable the 'Audit account management' setting. - Enable the 'Audit system events' setting. - Enable the 'Audit Privilege use' setting. |
- Enable the 'Audit account logon events' setting.
Explanation Enable the 'Audit account logon events' setting to track when a user account is used to authenticate to a computer, and to view the event on the local system. If the computer was a member of a domain, you would view the event on the domain controller instead. Account management tracks changes to user accounts, such as creating, renaming, or deleting an account. System events occur when a computer restarts, shuts down, or when an event that affects system security or the security log occurs. Privilege use events occur when a user exercises a user right defined in the computer's user rights assignments. A few user rights do not generate auditing events, such as backing up or restoring files. Section 5.5 |
|
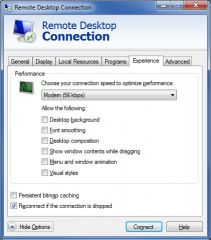
You have a computer running windows 7 Professional.
You have just enabled Remote Desktop on the computer so you can connect to it using a dial-up modem from home and run a few reports. You need to optimize the performance of your Remote Desktop session for your slow connection. Select the Experience setting(s) that will optimize performance. |
- Persistent bitmap caching
Explanation Enabling 'Persistent bitmap caching' will cache graphics locally, improving load time of commonly-used graphics. Leave the remaining settings on the Experience' tab unchecked to improve performance by not displaying graphic-intensive operations that the host system may be using. Section 7.8 |
|
|
You are managing two computers: Comp1 is running Windows 7 Ultimate; Comp2 is running Windows XP Professional.
You want to use Remote Desktop to manage Comp1 from Comp2. What should you do? - On Comp2, enable the 'Don't allow connections to this computer' option in the system properties. - On Comp2, enable the 'Allow connections from computers running any version or Remote Desktop' option in the system properties. - On Comp1, enable the 'Allow connections from computers running any versions of Remote Desktop' option in the system properties. - On Comp1, enable the 'Allow connections from computers running Remote Desktop with Network level Authentication' option in the system properties. |
- On Comp1, enable the 'Allow connections from computers running any versions of Remote Desktop' option in the system properties.
Explanation When using a computer running windows XP to manage a computer running Windows 7, you must enable the 'Allow connections from computers running any versions of Remote Desktop' option in the system properties of the remote computer. This is also a good option if you don't know the version or Remote Desktop Connection that another computer will use to connect to the computer. Enable the 'Allow connections from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentications' option if all the computers using Remote Desktop to connect to this computer run Windows 7. This is the most secure method for Remote Desktop connections. You do not need to enable or disable Remote Desktop on the local computer to connect to a remote computer. Section 7.8 |
|
|
You are getting ready to install windows 7 Ultimate on a new laptop.
You would like to configure the laptop to use BitLocker. The laptop should start up without requiring a PIN or a USB device during startup. What should you do? (Select two. Each choice is a required part of the solution.) - Install two hard disks. Put boot and operating system files on the first disk, and user data on the second disk. - Create two partitions on the hard disk. Put boot files on the first partition, and operating system files and data on the second partition. - Enable the TPM. - Disable the TPM. |
- Create two partitions on the hard disk. Put boot files on the first partition, and operating system files and data on the second partition.
- Enable the TPM. Explanation To allow the computer to boot without a PIN or a startup key on a USB drive, you must use a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). If the system does not have a TPM, you must use a startup key on a USB drive. Implementing BitLocker requires two NTFS partitions: * The system partition is a 100MB volume that contains the boot files. This partition is set to active, and is not encrypted by the BitLocker process. * The operating system partition must be large enough for the operating system files. This partition is encrypted by BitLocker. While you can use two hard disks instead of separate partitions on the same disk, the boot files are stored separate from the operating system files. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You have a computer that runs Windows 7. The computer is shared by three other users.
You notice that some of your documents have been modified. You want to use auditing to track any changes to your documents. In the audit policy in the local security policy, you enable auditing of successful object access events. To test auditing, you make some changes to some files. However, when you examine the computer's Security log, no auditing events are listed. You want to make sure an event is listed in the Security log whenever one of your documents is modified. What should you do? - Configure the local security policy to audit successful system events. - Edit the advanced security properties of the folder containing your documents. - Configure the local security policy to audit failed object access events. - In the local security policy, enable the Audit File System policy in Advanced Audit Policy Configuration. |
- Edit the advanced security properties of the folder containing your documents.
Explanation Object access events occur when a user accesses any object with its own access control list (such as a file, folder, registry key, or printer). In addition to enabling auditing of these types of events, you must also edit the properties of the specific objects you want to audit and define what type of access to the object you will audit. The object access policy in the Audit Policy section enables auditing for all object types. Use the Audit File System policy in Advanced Audit Policy Configuration to enable auditing only for the file system. When you enable this policy, you still need to configure audit settings on the folder or the file. Section 5.5 |
|
|
You have a computer named comp1 that runs Windows 7. The computer is located in a branch office.
A server running Windows Server 2008 R2 named Srv1 is located in the main office. The server has multiple shared folders. You use Offline Files in the branch office to make the files on the server available when the WAN link is down. You want to prevent all files in the 'Data' share from being cached. Files in other shared folders should still be available. What should you do? - On Srv1, edit the local security policy. - On Srv1, edit the properties for the 'Data' folder. - On Comp1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. - On Srv1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. |
- On Srv1, edit the properties for the 'Data' folder.
Explanation To prevent files in one share from being cached, edit the properties for the folder. On the share properties, caching settings, select 'Files or programs from the share will not be available offline'. Edit the local security policy or Group Policy or the Offline Files settings in the Sync center on the client to encrypt the offline files cache, enable or disable offline files, or configure the disk space used by offline files. With policy settings you can also exclude certain file types from being cached as well as enable transparent caching. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer named comp1 that runs windows 7. The computer is located in a branch office.
A server running windows Server 2008 R2 named Srv1 is located in the main office. You share a folder named 'Data' using the default caching settings. You use Offline Files in the branch office to make the files int he 'Data' share available when the WAN link is down. You want to prevent all files with the .iso and .mp3 extensions from being cached. What should you do? - On Srv1, edit the local security policy. - On Comp1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. - On Srv1, edit the properties for the 'Data' folder. - On Srv1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. |
- On Srv1, edit the local security policy.
Explanation On Srv1, edit the local security policy. You can exclude certain files from being cached with Offline Files. Files are excluded based on file extension. Edit the local security policy or Group Policy and configure the 'Exclude files from being cached' policy to identify the file extensions. Be aware that these exclusions apply to all shared folders (you cannot selectively restrict files in different shares). Edit the folder properties on the server to control how files are cached, such as to prevent all files in a shared folder from being cached. Edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync center on the client to enable or disable Offline Files, encrypt the Offline Files cache, or to configure how much disk space is used for the cache. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer named comp1 that runs windows 7. The computer is located in a branch office.
A server running Windows Server 2008 R2 named Srv1 is located in the main office. You share a folder named 'Data' using the default caching settings. On Comp1, you access files on the 'Data' share across a WAN link. You want to use transparent caching to reduce WAN traffic. What should you do? - On Srv1, edit the local security policy. - On Comp1, edit the local security policy. - On Comp1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. - On Srv1, edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync Center. - On Srv1, edit the properties for the 'Data' folder. |
- On Comp1, edit the local security policy.
Explanation Transparent caching is not enabled by default. To enable transparent caching, edit the local security policy or use Group Policy to enable the 'Enable Transparent Caching' policy on each client computer (not on the server). Transparent caching relies on the Offline Files feature and requires that Offline Files caching is enabled on the share. By default, when you share a folder, caching is enabled for documents that are opened. Edit the folder properties on the server to configure Offline Files caching for the shared folder. Edit the Offline Files settings in the Sync center on the client to enable or disable Offline Files, encrypt the Offline Files cache, or to configure how much disk space is used for the cache. By default, Offline Files is enabled, but you cannot change the transparent caching feature from this location. Section 6.5 |
|
|
you use a laptop named M400 which runs windows 7 Ultimate. m400 is a member of a domain and id located in a branch office.
A Windows 2008 R2 server named Server1 contains a shared folder named Data. The server is located in the main office. You need to configure M400 to cache the files from the 'Data' share so they can be used when M400 is not connected to the network. You want the files in the 'Data' share to automatically synchronize each time M400 connects to the network. The files must be protected by encryption; other files on M400 do not need encryption. What should you do? - On Server1, encrypt the files in the 'Data' share. On M400, make the 'Data' share available offline. - On M400, copy the files from the 'Data' share to the Documents library and configure BitLocker Drive Encryption. - On server1, configure BitLocker Drive Encryption. On M400, make the 'Data' share available offline. - On M400, make the 'Data' share available offline and enable encryption of offline files. |
- On M400, make the 'Data' share available offline and enable encryption of offline files.
Explanation You should: * Make the 'Data' share available offline. When network files are made available offline, the network versions of files and folders are copied to the local hard disk. * Protect offline files by encrypting the offline file cache. when the cache is encrypted, a user key is used. Only the user who encrypted the files has access to the files. BitLocker Drive Encryption encrypts the entire contents of the operating system partition and is unnecessary on M400. You should not enable BitLocker Drive Encryption on Server1. Encrypting the files on NTSERV prevents other users from accessing the files. Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a laptop running windows 7 Enterprise. The laptop is a member of a domain with a server running Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to use a VPN connection to access company resources from your home. You configure a new VPN connection using the IKEv2 security protocol, and then test the connection while at work. The connection is successful. When you test the VPN connection from your home, you find that the connection cannot be made. What should you do? - Open TCP port 1723 on your home router. - Open TCP port 1701 and UDP port 500 on your home router. - Open UDP ports 500 and 4500 and protocol 50 on your home router. - Open TCP port 443 on your home router. |
- Open UDP ports 500 and 4500 and protocol 50 on your home router.
Explanation Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) uses UDP ports 500 and 4500 for IKE traffic and protocol 50 for ESP traffic. The ports must be open on the local firewall for successful VPN connection using IKEv2. IKEv2: * Is the default protocol for a new VPN connection for Windows 7. * Supports IPv6, smart card authentication, and certificate authentication. * Supports data origin authentication, data integrity, replay protection, and data confidentiality. * Enables the VPN connection to remain intact as a mobile client moves from one IP network to another. Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) uses TCp port 1701 and UDP port 500. Secure socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) uses port 443. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) uses TCP 1723. Section 6.2 |
|
|
You have a laptop that runs Windows 7.
You want to use the laptop to connect to your corporate intranet while you are at home or traveling. Your solution should meet the following requirements: * The computer should connect automatically to the intranet without user initiation. * All communications between your laptop and the intranet should be encrypted. * The connection should allow for remote management of the computer from corporate intranet. * Internet traffic should be directed to Internet servers without going through servers at the corporate network. * The solution should work through firewalls where only HTTP and HTTPS are permitted. Which feature should you implement? - BranchCache - DirectAccess - BitLocker To Go - IKE v2 VPN |
- DirectAccess
Explanation DirectAccess is an automatic connectivity solution that allows clients running Windows 7 to connect seamlessly to the corporate intranet through an Internet connection. The moment the Windows 7 device connects to the Internet, DirectAccess allows authorized users to access corporate file servers and view intranet Web sites without establishing and going through a VPN connection. DirectAccess has the following benefits: * The client computer (not the user) connects and authenticates automatically. * Because computers connect automatically, they can be remotely managed by remote administrators or automated processes. For example, Group Policy or system updates can be applied automatically as long as the computer has been turned on. * DirectAccess works through all firewalls that allow HTTPS (virtually all firewalls). * End-to-end authentication and encryption is provided. communications with hosts on the intranet are automatically encrypted and protected. * Client computers connect directly to Internet hosts without going through the encrypted tunnel connection. Use IKEv2 to establish a VPN connection to an intranet. IKEv2 requires special firewall ports to be opened. Use BitLocker To Go to encrypt data on removable drives. Use BranchCache to save copies (cache) data on computers in a branch office. Section 6.3 |
|
|
You have a laptop computer that runs Windows 7 Ultimate. The computer is a member of a domain.
You want to use DirectAccess to access application servers on your corporate intranet. Application servers run Windows Server 2003. You need to implement a solution that does the following: * All communications sent to the private network over the Internet are encrypted. * Client computers authenticate with application servers on the intranet. * Following authentication, traffic on the intranet is not encrypted. What should you do? (Select two. Each choice is a required part of the solution.) - Upgrade application servers to Windows Server 2008 R2 - Upgrade your laptop to Windows 7 Enterprise. - Configure selected server access (modified end-to-edge). - Configure full enterprise network access (end-to-edge). - Configure end-to-end access |
- Upgrade application servers to Windows Server 2008 R2
- Configure selected server access (modified end-to-edge). Explanation Configure DirectAccess using selected server access (modified end-to-edge). IPsec encrypts communications between the client and the IPsec Gateway, but authenticates all the way to the application server. Once authenticated, traffic on the private intranet is not encrypted (encryption is removed at the DirectAccess server). Using modified end-to-edge access requires that application servers run Windows Server 2008 R2 or higher. End-to-end access both authenticates and encrypts all traffic between the client and the application server. End-to-edge access authenticates and encrypts traffic with the DirectAccess server, but does not authenticate or encrypt traffic between the DirectAccess server and application servers. Section 6.3 |
|
|
You have two computers that run Windows 7: Computer 1 and Computer 2. Both computers are configured with BitLocker. Both computers have TPM installed.
Because of a hardware failure, Computer 1 will not boot. You need to access the data on the drive where BitLocker was enabled as quickly as possible. What should you do? - Move the hard disk from Computer 1 to Computer 2. use the recovery key from the Computer 1 to gain access to the encrypted volume. - Move the hard disk from Computer 1 to Computer2. Insert the USB drive containing the startup key from computer 2 and reboot computer2. - Move the hard disk from Computer 1 to Computer 2. insert the USB drive containing the startup key from Computer 1 and reboot Computer 2. - Move the hard disk from Computer 1 to Computer 2. Use the recovery key from Computer 2 to gain access to the encrypted volume. |
- Move the hard disk from Computer 1 to Computer 2. Use the recovery key from the Computer 1 to gain access to the encrypted volume.
Explanation To access an encrypted volume when the drive is moved to another computer, sue the recovery key that was created on the original computer (in this case Computer 1). The startup key is used to prevent system startup when the startup key is not present. To boot Computer 2, use the startup key for Computer 2. The startup key for Computer 1 can only be used to boot computer 1, and cannot be used for volume recovery. Section 6.4 |
|
|
You have purchased a new laptop that runs Windows 7 Professional.
You want to use DirectAccess to connect the computer to your corporate intranet. You will use Group Policy to enforce DirectAccess settings on the client. What should you do to configure the laptop for the DirectAccess connection? (Select two.) - Run Windows firewall with Advanced Security and enable the DirectAccess firewall rules. - Create a VPN connection that uses the IKE v2 protocol. - Join the computer to a domain. - Upgrade the computer to Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. - Run the 'netsh' command and set the service mode to distributed. |
- Join the computer to a domain.
- Upgrade the computer to Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. Explanation To configure DirectAccess on a client computer: * The computer must be running windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. * Join the computer to a domain. * Issue a computer certificate to the computer. This certificate is used for authentication. * Make the computer account a member of the security group that was created when DirectAccess was configured on the server. With this configuration, additional configuration information comes automatically through Group Policy. IKE v2 is a VPN protocol new with Windows 7. DirectAccess does not establish a traditional VPN connection and does not use IKE v2, but uses SSL instead. GPO settings automatically configure any firewall settings that are required by DirectAccess on the client computers. Using 'netsh' to configure the computer for Distributed mode is used with BranchCache configuration. Section 6.3 |
|
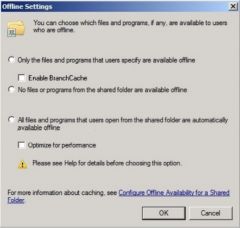
You have ten reginal sales people who travel extensively and use laptops to access company resources.
a Windows 2008 R2 server named Server1 contains a shared folder named 'Data'. The server is located in the main office. You want the files in the 'Data' share to be cached automatically when opened by one of the laptops. You also want the laptop to cache any executable files that it uses from the 'Data' share. Select the setting(s) you would choose to meet these requirements. |
- All files and programs that users open from the shared folder are automatically available offline.
- Optimize performance Explanation Select 'All files and programs that users open from the share are automatically available offline' to cache files opened on the laptops. Select 'Optimized for performance' to cache executable files from the network share to the laptops. Use 'Only the files and programs that users specify are available offline' to cache only files which are manually selected by the user. This is the default setting. Use 'No files or programs from the share are available offline' to prevent caching of offline files Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7.
You have configured a USB thumb drive with BitLocker To Go that has been formatted with FAT32. You use a password to protect the drive. You want to be able to read and write files to the drive from a computer that is running windows XP Professional. You need to implement a solution with the least amount of effort as possible. What should you do? - Configure BitLocker To Go to use a smart card for authentication. - Include the BitLockerToGo.exe file on the USB drive. - Reformat the drive using NTFS. - Upgrade the Windows XP computer to Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. - Copy the private key used to encrypt the drive to the Windows XP computer. |
- Upgrade the Windows XP computer to Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise.
Explanation Read/write access to a BitLocker To Go drive is only possible from a computer running Windows 7. Your only option in this scenario is to upgrade the Windows XP computer. You can open and modify files from any version of Windows 7; you can only save new files using Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. You can have read access to a BitLocker To Go drive from a computer running Windows XP or Vista if the drive was formatted with FAT32 and uses a password for access. Run the BitLockerToGo.exe program to view files on the drive. By default, the BitLockerToGo.exe is included on drives formatted with FAT32. Section 6.4 |
|
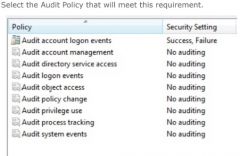
You have several computers running windows 7 Enterprise. The computers are members of a domain.
You are configuring security settings that will be distributed to all computers on your network. You want to identify denied attempts to manipulate files on computers that have been secured through NTFS permissions. Select the Audit Policy that will meet this requirement. |
- Audit object access
Explanation In this scenario, you should enable the 'Audit object access' setting in Group Policy. The object access events occur when a user accesses any object with its own access control list (such as a file, folder, registry key, or printer). In addition to enabling auditing of these types of events, you must also edit the properties of the specific objects you want to audit and define what type of access to the object you will audit. Use 'Audit account management' for events that occur when user or group objects are created, deleted, or edited in a computer's database. System events occur when a computer restarts or shuts down a computer, or when an event that affects system security or the security log occurs. Use 'Audit privilege use' for events that occur when a user exercises a user right defined in the computer's user rights assignments. A few user rights do not generate auditing events, such as backing up or restoring files. Use 'Audit system events' for events that occur when a computer restarts or shuts down a computer, or when an event that affects system security or the security log occurs. Use 'Audit policy change' for events that occur when a computer's audit policies, user rights assignments, or trust policies changes. Section 5.5 |
|
|
You have a laptop running Windows 7 Professional.
You configured a power plan which is optimized for this laptop, and then you set it as the active plan. You need to migrate the settings to other laptops running windows 7. Before you migrate the plan, you need to validate the power plan. What should you do? (Select two. Each answer is a required part of the solution.) - At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /energy' - At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /setactive' - At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /export' - At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /devicequery wake_from_any' |
- At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /energy'
- At a command prompt, run 'powercfg /export' Explanation To validate the power plan and migrate the settings to other laptops running Windows 7, use the following 'powercfg' options: * /energy validates a power plan configuration prior to deployment. This command provides a report of the power management settings, including diagnostics that can indicate which applications or devices might be causing power management issues. * /export (along with /import) migrates the Power Plans between computers running Windows 7. 'Powercfg /setactive' sets the active Power Plan. 'Powercfg /devicequery wake_from_any' displays all of the connected devices that can wake up a client form sleep mode (e.g. keyboard or mouse) Section 6.5 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Ultimate.
You will connect to the computer using Remote Desktop. With the least amount of effort, you need to copy files from your local hard drive to the hard drive of the remote computer. What should you do? - In the Remote Desktop client properties, edit the local devices and resources options. - In System Properties, add yourself to the Remote Desktop Users group. - In the Remote Desktop client properties, change your connection speed to optimize performance. - Map a network drive to the remote machine. |
- In the Remote Desktop client properties, edit the local devices and resources options.
Explanation Use the local devices and resources options in Remote Desktop to access your local hard drives while using Windows Explorer on the remote machine. Mapping a network drive would solve the problem, but not the with the least administrative effort. You need to be a member of the Remote Desktop users group on the remote machine to connect in the first place, and changing your connection speed will only improve the graphical experience of your connection. Section 7.8 |
|
|
You have a computer running Windows 7 Ultimate.
While connecting to a computer using Remote Desktop, you need to prevent the desktop background on the remote computer from displaying on the local computer. What should you do? - Set the connection speed of the Remote Desktop connection to the 'LAN (10Mbps or higher)' option. - Remove the desktop background image from the remote computer. - On the 'Experience' tab of the Remote Desktop connection, clear the 'Desktop Background' option. - Use the Control Panel's display settings to remove the desktop background. |
- On the 'Experience' tab of the Remote Desktop connection, clear the 'Desktop Background' option.
Explanation Clear the 'Desktop Background' option in the Remote Desktop's 'Experience' tab to prevent the desktop background on the remote computer from displaying on the local computer. Use the display settings int he Control Panel to extend your display to an external monitor, or to change the screen resolution. Removing the image from the desktop background will still display the background from the remote computer. Using the LAN (10Mbps or higher) connection speed setting automatically checks the 'Desktop Background' option and will display the remote computer's background. Section 7.8 |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7 Professional.
You use a VPN connection to access resources on a corporate intranet. In addition to accessing the intranet resources, you need to access the Internet while the VPN connection is active; however, you do not want to send Internet traffic through the VPN connection. What should you do? - Configure the advanced TCP/IP settings of the VPN connection. - Configure a static IP address and default gateway. - Configure the security protocol as IKEv2. - Change the ICS properties of the VPN connection. |
- Configure the advanced TCP/IP settings of the VPN connection.
Explanation In advanced TCP/IP Settings, clear the 'Use default gateway on remote network' option to not route Internet traffic through the VPN connection. Edit the Internet connection Sharing (ICS) properties of the VPN connection if you want to allow others on the network to use the connection. Configure a static IP address and default gateway if your network does not have a DHCP server, or if you want to eliminate DHCP traffic from your network. Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) is a VPN tunneling protocol that is the default protocol for a new VPN connection for Windows 7. Use IKEv2 to use the fast reconnect option for a VPN connection. Section 6.2 |
|
|
You have a computer running windows 7.
You want to save some files on a USB thumb drive and protect the drive using BitLocker To Go. you want to be able to read these files on a computer that is running windows XP Professional. You need to implement a solution with the least amount of effort as possible. What should you do? ( Select two. Each choice is a required part of the solution.) - Include the BitLockerToGo.exe file on the USB drive. - Upgrade the computer to Windows 7 Ultimate or Enterprise. - Configure BitLocker To GO to use a smart card for authentication. - Format the drive using NTFS. - Format the drive using FAT32 |
- Include the BitLockerToGo.exe file on the USB drive.
- Format the drive using FAT32 Explanation Computers running Windows XP or Vista can access data stored on a drive protected with BitLocker To Go. * The drive must be formatted with FAT32. Only Windows 7 computers can read a BitLocker To Go volume formatted with NTFS. * Include the BitLockerToGo.exe program on the USB drive, or download the program to the computer. When stored on the USB drive, a special unencrypted portion of the drive contains this file. * Encrypt the drive using a password. using smart cards with BitLocker To Go is only supported on Windows 7 computer. You could upgrade the computer to windows 7 and then use NTFS or smart cards; however, this solution would require more effort and is not necessary to enable file access under Windows XP. Section 6.4 |
|
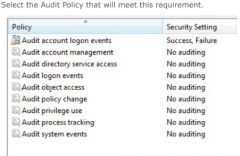
You have several computers running windows 7 Enterprise. The computers are members of a domain.
You are configuring security settings that will be distributed to all computers on your network. You want to identify denied attempts to change a user's group membership in a computer's local database. |
- Audit account management
Explanation You should enable the 'Audit account management' setting in Group Policy. Account management events occur when user or group objects are created, deleted, or edited in a computer's database. Use 'Audit system events' for events that occur when a computer restarts or shuts down a computer, or when an event that affects system security or the security log occurs. Use 'Audit object access' for events that occur when a user accesses any object with its own access control list (such as a file, folder, registry key, or printer). In addition to enabling auditing of these types of events, you must also edit the properties of the specific objects you want to audit and define what type of access to the object you will audit. Use 'Audit policy change' for events that occur when a computer's audit policies, user rights assignments, or trust policies change. Use 'Audit privilege use' for events that occur when a user exercises a user right defined int he computer's user rights assignments. A few user rights do not generate auditing events, such as backing up or restoring files. Section 5.5 |
|
|
You manage a computer running windows 7.
Previously, you configured the following auditing settings: * You enabled the 'Audit object access' policy to log failed events. * You configured auditing on several files, folders, and registry settings for a specific group for failed Read and Modify actions. Now you would like to audit only failed attempts to view or modify registry settings. You no longer want to log audit entries for file access. You need to make the change with the least amount of effort possible. What should you do? - In the local security policy, stop auditing for the 'Audit object access' policy. Enable the 'Audit Registry' advanced audit policy. - Attach a task to a failed audit entry in Event Viewer. - Edit the security settings for each file and folder. Remove the audit entries. - Configure a custom view in Event Viewer using the registry as a filter criteria. |
- In the local security policy, stop auditing for the 'Audit object access' policy. Enable the 'Audit Registry' advanced audit policy.
Explanation Use advanced audit policies for more granular control over audit policies and the types of events that are logged. The standard 'Audit object access' policy tracks access to both file system and registry settings. Use the 'Audit Registry' advanced policy to control auditing for only registry settings without logging file system access. When configuring any type of object access auditing, you must configure both the audit policy and configure auditing on the object itself. By disabling standard auditing and using advanced auditing, you can make the necessary change without having to reconfigure audit settings on each file system object. A custom view in Event Viewer filters events but does not prevent the events from being recorded. Attach a task to an event to send an e-mail, run a program, or take another action when a specific event takes place. Section 5.5 |

