![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
brownsted lowery acid |
a substance which can donate a proton |
|
|
bronsted lowry base |
a substance which can accept a proton |
|
|
what happens in a reaction when both reactants are acid? |
The acid with the bigger Ka will act as acid |
|
|
what is the diffrence between a weak acid and a strong acid? |
A week acid partially discociates in aqueous solutions wheras a weak acid completely dissociates |
|
|
why is the value of [H20 (L)] assumed constant? |
because the concentration of H20 is much bigger than the concentration of the ions |
|
|
how can Le chatelier's principle be used to predict the change of pH at different temperatures? |
The dissociation of water is endothermic so by increasing the temperature the reaction favour the forward endothermic reaction pushing equilibrium to the right and giving a bigger concentration of H+ ions. The bigger the concentration of H+ ion the lower the pH. |
|
|
what happens when Ka increases? |
The acid becomes stronger. |
|
|
when calculating the pH of a weak acid what two assumptions are made to simplify the Ka expression? |
1) [H+ (aq)]eqm = [A- (aq)]eqm because they have dissociated according to the 1:1 acid 2) as the amount of dissociation is small we assume that the initial concentration of the udissociated acid has remained constant. So [HA (aq)]eqm = [HA (aq)]initial |
|
|
what are the products when you react an acid with a metal? |
a salt and hydrogen |
|
|
what are the products when you react an acid with an alkali? |
salt and water |
|
|
what are the products when you react an acid with a carbonate? |
salt, water and carbon dioxide |
|
|
buffer solution |
A buffer solution is one where pH does not change significantly when small amounts of acid or alkali are added to it. |
|
|
how do you make a basic buffer solution? |
A basic buffer solution is made from a weak base and a salt of that weak base (made by reacting the weak base with a strong acid). |
|
|
how do you make a acidic buffer solution? |
A acidic buffer solution is made from a weak acid and a salt of that weak acid (made by reacting the weak acid with a strong base). |
|
|
how can the salt be added to make the buffer solution? |
A salt solution or solid salt can be added to the acid or a weak acid can be partially neutralized with an alkali to create a mixture of acid and salt. |
|
|
What substance has the highest concentration in a buffer solution? |
In a buffer solution the salt has a higher concetration that the the acid |
|
|
What happens to pH when small amount of acid is added to a buffer? |
In the equilibrium between the acid and the conjugate base (and H+ ion) the equilibrium will shift to the left removing nearly all the H+ added as the there is a large concentration of salt ion the buffer ratio stays almost constant so pH stays the same. |
|
|
what happens to pH when small amount of alkali is added to to a buffer? |
The OH- ions will react with the H+ ions to form water. Therefore in the equilibrium between the acid and the conjugate base (and H+ ion) the equilibrium will shift to the right to produce more H+ ion. Overall the concentration of H+ ions and the pH will remain constant but some o the acid is changed to the conjugate base. |
|
|
what assumption are made when working out the acid dissociation constant in buffer solutions? |
1) the [A-] is due to the added salt only 2) the initial concentration of the acid remains constant as the amount that has been dissociated or reacted remains small. |
|
|
what happens to the calculation of pH when small amount of alkali is added to the buffer solution? |
The moles of the acid would reduce by the number of moles of alkali added and moles of the salt would increase by the same amount so a new calculation would be done with new values. |
|
|
How does adding a carbonic acid control pH of blood? |
hydrogen carbonate acts as a buffer in blood plasma and maintains the pH between 7.34 - 7.45. An equilibrium is formed when the hydrogen carbonate dissociated into bicarbonate ion and H+. Adding alkali reacts with H+ so the equilibrium will shift right forming new H+ and more HCO3-. |
|
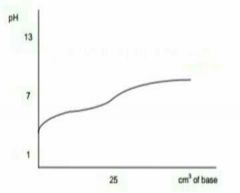
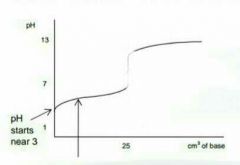
Describe this graph |
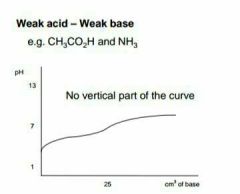
|
|

Describe this graph |
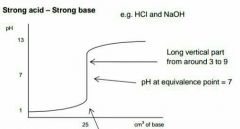
|
|
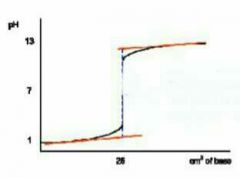
Describe this graph |
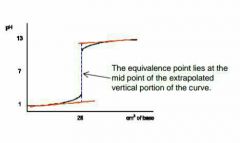
Strong acid - weak base |
|
Describe this graph |
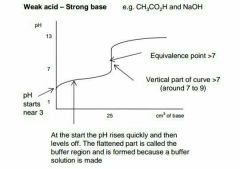
|
|
|
how do you choose an indicator? |
An indicatorwill work if thr yhr ph range ofthe indicator lies on the verticle part of titration curve. In this case the color will change rapidly aand respond to the neutralising point. |
|
|
when do you use phenolphthalein and what is the colour change and pH range? |
Use phenolphthalein for titration with strong and not weak bases. pH range: 8.2-10 colour change: colourless acid > pink alkali |
|
|
when do you use methyl orange and what is the colour change and pH range? |
Use methyl orange for titration with strong and not weak acids. pH range: 3.1-4.4 colour change: red acid > yellow alkali (orange endpoint) |
|
|
what are the three types of acid? |
Monobasic – each molecule may release 1 proton (HCl) Dibasic – Each molecule may release 2 protons (H2SO4) Tribasic – Each molecule may release 3 protons (H3PO4) |
|
|
how do you show the role of H+ ion a reaction with metals and bases using ionic equations? |
Write an ionic equation by splitting any aqueous compounds into ions, cancel out the ions to leave the final equation.
|
|
|
What is the equation for the acid dissociation? |
Ka = [H+(aq)][ A-(aq)] / [HA(aq)] |
|
|
what is the relationship between Ka and PKa and ph aand H+? |
pKa = -log10Ka Ka = 10-pKa pH = –log[H+] [H+] = 10–pH |
|
|
what is the expression for KW? |
Kw = [H+(aq)][ OH-(aq)] |

