![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
121 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

|
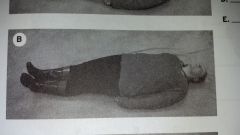
Prone
|
|
|

|
medial
lateral midline posterior superior anterior proximal distal inferor |
|
|
|
Supine
|
|
|

|
shock position
|
|
|

|
fowlers position
|
|
|
|
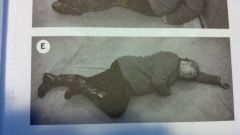
recovery position
|
|
|
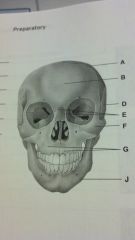
Skull
|
parietal bone
frontal bone maxilla temporal bone nasal bone zygomatic bone maxillae |
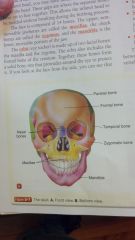
|
|
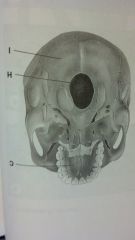
skull
|
foramen magnum
occipital bone mandible |
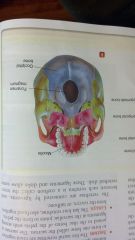
|
|
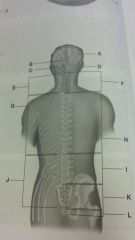
spinal column
|
cerebrum
foramen magnum brain stem cerebellum cervical nerve cervical certebrae thoratcic nerves thoracic vertebrae lumbar vertebrae lumbosacral nerves sacral vertebrae coccygeal vertebrae |
|
|
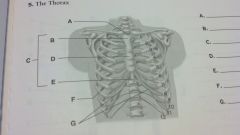
the thorax
|
jugular notch
manubrium sternum body xiphoid process anterior ribs costal arch |
|
|
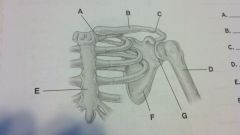
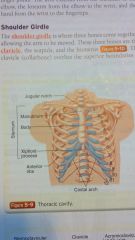
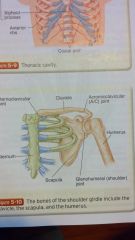
shoulder girdle
|
sternoclavicular joint
clavicle acromioclavicular joint AC joint humerus sternum scapula glenohumeral joint |
|
|
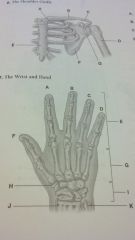
hand and wrist
|
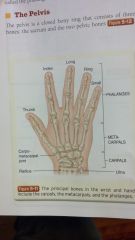
index
long ring small phalanges thumb metacarpals carpometacarpal joint carpals radius ulna |
|
|
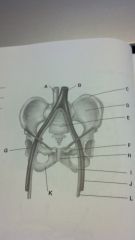
the pelvis
|
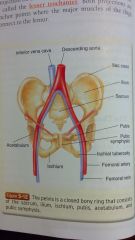
inferior vena cava
descending aorta iliac crest sacrum pubis acetabulum oubic symphysis ischial tuberosity femoral artery ischium femoral vein |
|
|
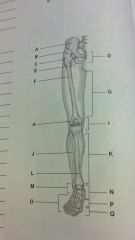
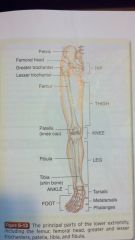
lower extremity
|
pelvis
femoral head greater trocanter femur thigh patella knee fibula leg tibia ankle tarsals foot metatarsals phalanges |
|
|
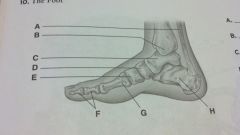
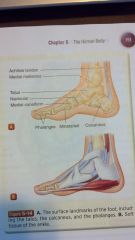
the foot
|
achilles tendon
medial malleolus talus navicular medial cuneiform phalanges metatarsals calcaneus |
|
|
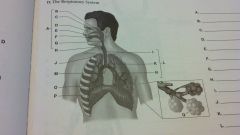
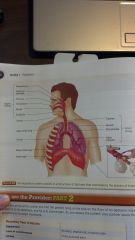
the respitory system
|
upper airway
nasopharynx nasal air passage pharynx mouth epiglottis larynx trachea apex of lung bronchioles lower airway carina main bronchi base of lung diaphram alveoli |
|
|
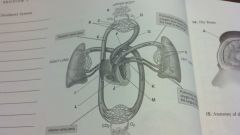
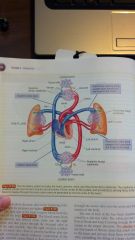
the circulatory system
|
tissue cells
systemic capillaries venule arteriole vein aorta artery pulmonary capillaries right atrium heart left atrium right ventricle left ventricle |
|
|
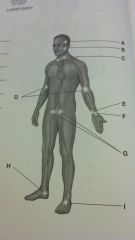
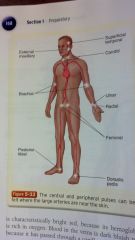
central and peripheral pulses
|
superficial temporal
external maxillary carotid brachial ulnar radial femoral posterior tibial dorsalis pedis |
|
|
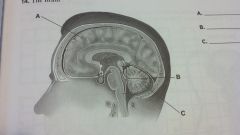
the brain
|
cerebrum
brain stem cerebellum |
|
|
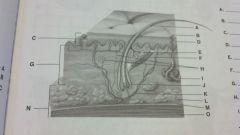
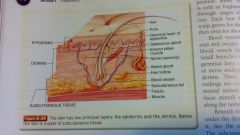
anatomy of the skin
|
hair
pore epidermis germinal layer of epidermis sabaceous gland erector pillae muscle dermis nerve sweat gland hair follicle blood vessel subcutaneous fat fascia subcutanious tissue muscle |
|
|
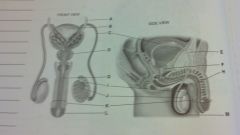
male reporductive
|
ureter
urinary ybladder vasa deferentia prostate gland pubic bone prostate gland urethra urethra epididymis testis penis glans penis scrotum |

|
|
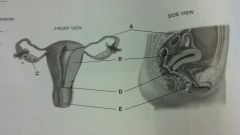
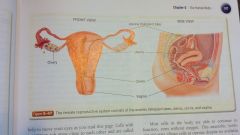
female reproductive
|
uterine fallopian tube
uterus ovary cervix vagina |
|
|
|
closer to the midline
|
medial
|
|
|
|
anterior
|
front surface of the body
|
|
|
|
farther from the midline
|
distal
|
|
|
|
capillary
|
connects arterioles to venules
|
|
|
|
anatomic position
|
standing, facing forward, palms facing forward
|
|
|
|
superior
|
closer to the head
|
|
|
|
midline
|
imaginary vertical line descending from the middle of the forehead to the floor
|
|
|
|
carotid
|
major artery that supplies blood to the head and brain
|
|
|
|
medial
|
closer to the midline
|
|
|
|
inferior
|
farther from the head; lower
|
|
|
|
femoral
|
major artery that supplies blood to the lower extremities
|
|
|
|
proximal
|
closer to the midline
|
|
|
|
brachial
|
major artery in the upper arm
|
|
|
|
distal
|
farther from the midline
|
|
|
|
flexion
|
bending of a joint
|
|
|
|
radial
|
major artery of the lower arm
|
|
|
|
posterior
|
back or dorsal surface of the body
|
|
|
|
farther from the head; lower
|
inferior
|
|
|
|
standing facing forward, palms facing forward
|
anatomic position
|
|
|
|
imaginary line descending from the middle of the forehead to the floor
|
midline
|
|
|
|
front surface of the body
|
anterior
|
|
|
|
closer to the head
|
superior
|
|
|
|
bending of a joint
|
flexion
|
|
|
|
back or dorsal side of body
|
posterior
|
|
|
|
closer to the midline
|
medial
|
|
|
|
connects arterioles to venules
|
capillary
|
|
|
|
major artery that supplies blood to the head and brain
|
carotid
|
|
|
|
major artery that supplies blood to the lower extremities
|
femoral
|
|
|
|
major artery of the lower arm
|
radial
|
|
|
|
major artery of the upper arm
|
brachial
|
|
|
|
upper extremity bones
|
clavicle
ulna humerus |
|
|
|
lower extremity bone
|
talus
patella fibula calcaneus |
|
|
|
exits the brain through an opening at the base of the skull
|
spinal cord
|
|
|
|
transmit electrical impulses to the muscles causing them to contract
|
motor nerves
|
|
|
|
brain and spinal cord make up
|
central nervous system
|
|
|
|
links the central nervous system to various organs in the body
|
peripheral nervous system
|
|
|
|
carry sensations of taste and touch to the brain
|
sensory nerves
|
|
|
|
controlling organ of the body
|
brain
|
|
|
|
TF the aorta is the major artery that supplies blood to the lower extremities
|
false
|
|
|
|
TF the knee is a ball and socket joint
|
false
|
|
|
|
TF the phalanges are the bones of the fingers and toes
|
true
|
|
|
|
TF the right atrium receives blood from the pulmonay veins
|
False
|
|
|
|
TF there are 12 ribs that attach to the sternum
|
False
|
|
|
|
TF exhaled air contains 21% oxygen
|
False
|
|
|
|
TF the spleen is a muscle that is commonly injured in abdominal blunt trauma injuries
|
false
|
|
|
|
muscle type: attached to the bone
|
skeletal
|
|
|
|
muscle type: found in the walls of the GI tract
|
smooth
|
|
|
|
muscle type: carries out much of the automatic work of the body
|
smooth
|
|
|
|
muscle type: forms the major mass of the body
|
skeletal
|
|
|
|
muscle type: under direct control of the brain
|
skeletal
|
|
|
|
muscle type: found only in the heart
|
cardiac
|
|
|
|
muscle type: responds only to primitive stimuli
|
smooth
|
|
|
|
muscle type: can tolerate blood supply interruption for only a very short period
|
cardiac
|
|
|
|
Muscle Type: responsible for all bodily movement
|
skeletal
|
|
|
|
muscle type: has its own blood supply and electrical system
|
cardiac
|
|
|
|
three bones that form the pelvic ring
|
ishium, illium, pubic
|
|
|
|
a collapsible tube that extends from the pharynx to the stomach
|
esophagus
|
|
|
|
seminal fluid ejacualted from the penis containing sperm
|
semen
|
|
|
|
the __________ magnum is a large opening at the base of the skull through which the brain connects to the spinal cord
|
foramen
|
|
|
|
the bending of a joint
|
flexion
|
|
|
|
the nuclotide involved in energy metabolism
|
ATP
|
|
|
|
a portion of the medulla oblongata where the primary respiratory pacemaker is found
|
DRG
|
|
|
|
the part of the pharynx that lies above the level of the roof of the mouth
|
nasopharynx
|
|
|
|
the ________ position is the position of reference in which the patient stands facing you arms at the side, with the palms facing forward
|
anatomic
|
|
|
|
the last three or four vertebrae of the spine
|
coccyx
|
|
|
|
the breast bone
|
sternum
|
|
|
|
an organ that lies below the midbrain and above the medulla and contains numerous important nerve fibers
|
pons
|
|
|
|
the connection point between the pelvis and the vertebral column is known as the _____ joint
|
sacroiliac
|
|
|
|
the ________ artery leads from the right ventrical of the heart to the lungs; it carries oxygen poor blood
|
pulmonary
|
|
|
|
a _______ muscle is a muscle over which a person has no conscious control
|
involuntary
|
|
|
|
movement of gas from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
|
diffusion
|
|
|
|
to bend
|
flex
|
|
|
|
any portion of the airway that contains air and cannot participate in gas exchange
|
deadspace
|
|
|
|
the part of the skeleton comprising the skull, spinal column, and rib cage is known as the ______ skeleton
|
axial
|
|
|
|
the longest and one of the strongest bone in the body
|
femur
|
|
|
|
the brain and the spinal cord
|
central nervous system
|
|
|
|
fluid produced in the ventricles of the brain that floes in the subarachnoid space and bathes the meninges
|
CSF
|
|
|
|
portion of the medulla oblongata that is responsible for modulating breathing during speech
|
VRG
|
|
|
|
the pointed extremity of a conical structure
|
apex
|
|
|
|
four parts of the blood
|
plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
|
|
|
|
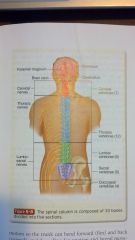
cervical spine has how many vertebrae
|
7
|
|
|
|
thoracic spine has how many vertebrae
|
12
|
|
|
|
lumbar spine has how many vertebrae
|
5
|
|
|
|
sacrum has how many vertebrae
|
5
|
|
|
|
coccyx has how many vertebrae
|
4
|
|
|
|
what organs are in the abdominal right upper quadrant
|
liver, gallbladder, large and small intestines
|
|
|
|
what organs are in the abdominal left upper quadrant
|
stomach, spleen, large and small intestines
|
|
|
|
what organs are in the abdominal right lower quadrant
|
large and small intestines, appendix, ascending colon
|
|
|
|
what organs are in the abdominal left lower quadrant
|
small and large intestines
|
|
|
|
list in the proper order the parts of the heart that blood flows through
|
superior and inferior vena cava
right atrium right ventrical pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary vein left atrium left ventricle arota |
|
|
|
number of bones in the adult body
|
206
|
|
|
|
connects bones to bones
|
ligament
|
|
|
|
connect bones to muscles
|
tendon
|
|
|
|
soft semi flexible material found within joints
|
cartilage
|
|
|
|
axial sketeton
|
form the foundation that the arms and legs are hung from. the skull, thoratic cage, and vertebral column
|
|
|
|
appendicular skeleton
|
the upper and lower extremities
|
|
|
|
thoracic cavity contains what organs
|
heart, lungs, esophagus, and great vessels
|
|
|
|
three bones making up the shoulder girdle
|
clavicle, scapula, and humerus
|
|
|
|
three parts of the sternum
|
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
|
|

