![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Upper Motor Neuron Injury:
Injury of corticospinal system (pyramidal tract) anywhere above the pyramidal decussation causes ___ paralysis. Injury below the pyramidal decussation will cause ___ paralysis below the lesion. |
-contralateral
-ipsilateral |
|
|
Sensory loss:
Injury to the spinal cord will cause loss of pain and temperature sense on the ___ side below the lesion. Such an injury will cause ___ loss of fine (discriminative) touch, proprioception and vibration below the lesion. |
-contralateral
-ipsilateral |
|
|
Uncal Herniation:
Uncal herniation is heralded by the clinical triad of: Blown pupil – ___ Hemiplegia – compression of the ___ Coma – due to ___ |
-ipsilateral, dilated unresponsive pupil
-cerebral peduncles -distortion of the midbrain reticular system (involved in altertness/consciousness) for illustration: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uncal_herniation#Uncal_herniation |
|
|
Epidural Bleed:
Epidural, AKA extradural hemorrhage Usually caused by tearing of the ___ artery, particularly ___ branch from trauma to the pterion Blood collects between the ___ Slowly separates the ___ from the bone |
-middle meningeal a.
-anterior -calvaria and the periosteal later of dura -periosteal dura s. 63 |
|
|
Epidural hemorrhage:
Accumulation of blood appears ___ shaped |
*Lens-shaped accumulation of blood
|
|
|
Subdural Bleed:
Blood from torn veins fills the potential space between the ___ Typically occurs in ___ individuals Brain is atrophied [in older individuals] and therefore ___ Puts strain on veins from brain to ___ Slow, insidious History may be a trivial injury with or without loss of consciousness. [Mvt of brain tears emissary vv.] |
-dura and the arachnoid mater
-older -more space between the brain and arachnoid -dural venous sinuses |
|
|
Subdural Bleed:
___-shaped hemorrhage |
*Cresent
s. 69 |
|
|
Subarachnoid Bleed:
May be the result of ___ More frequently caused by ___ Arterial blood flows between ___, into ___. |
-SIGNIFICANT head trauma.
-the bursting of a cerebral aneurysm. -the gyri of the brain -the sulci s. 70 |
|
|
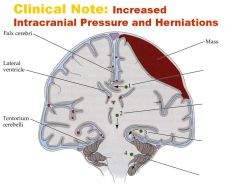
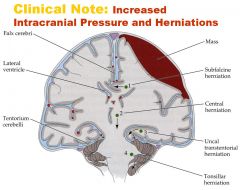
Increased Intracranial Pressure and Herniations:
The cranium is an enclosed space, so increased pressure from blood or a mass can cause regions of the brain to ___. Four typical sites of herniation. 1. ___ 2. ___ 3. ___ 4. ___ |
-herniate
1. Subfalcine – under the falx cerebri 2. Central – downward herniation of the brainstem 3. Uncal – herniation of the medial temporal lobe and the uncus through the tentorial notch 4. Tonsilar herniation – herniation of the cerebellar tonsil through the foramen magnum [compresses respiratory centers in brainstem] |
|
|
|
|
|
Cavernous Sinus Syndrome:
Cavernous sinus can be the site of ___ cancer Can be the site of a ___ aneurysm Cavernous sinus syndrome can cause ___ May be ___ sensory loss |
-metastatic breast, prostate and lung
-carotid artery -diplopia, painful ophthalmoplegia [paralysis of the eye muscles.] -trigeminal |
|
|
Hydrocephalus:
Can be due to congenital obstruction of ___ ___ can block the aqueduct In young children, before the skull sutures are fused, the head ___ Hydrocephalus can severely damage ___ |
-aqueduct of Sylvius
-Tumors -swells -brain tissue |

