![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the features of an ideal radiopharmaceutical?
|
1. Localize to a high degree in the target organ
2. high target to background ratio 3. very little radiation dose to the patient. 4. affordable, safe and ready to use. |
|
|
Radioisotopes emit energy in one of two forms what are they and examples?
|
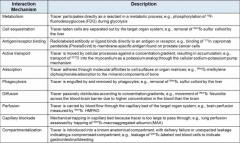
1. particle radiation (beta, positor, alpha)
2. Photon radiation (xray and gamma) |
|
|
What are the 2 key components of a radiopharmaceutical?
|
The physiologic moiety and the radioisotope.
Some radioisotopes (18F, 125I) can serve as both at the same time. |
|
|
What are the two main categories of radioisotopes used in nuclear medicine?
|
Single photon emitters (scintigraphy and SPECT imaging)
positron emitters (PET imaging) |
|
|
how does a cyclotron work?
|
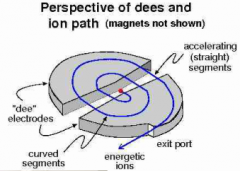
1) a positively charged ion (ie. 1He, 3He, 4He) is placed between 2 D shaped magnets separated by a gap.
2) the gap has a voltage applied which accelerates the particle to the lower voltage electrode. 3) the particle enters the 1st D shaped magnet and feels only the magnetic effect causing it to torque in an arch relative to it's kinetic energy which bends it back towards the gap. 4) the polarity in the gap is reversed and the positive ion is acclerated in the other direction. This occurs over and over until the positive ion acquires the desired kinetic energy. 5. The positive ion is then ejected out an exit port directed towards the target |
|
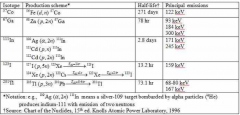
Are the radioisotopes produced in cyclotrons tend to be rich in (protons/electrons)
How do they decay? |
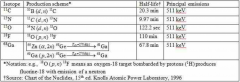
protons
positron emission electron capture |
|
|
How do reactors work?
What nuclear medicine isotopes are generated this way? What's the downside of this method |
Nuclear fission: A fuel rod (such as 235U) is bombarded by neutrons which results in fission with release of more neutrons (chain reaction). Multiple split products are generated with 2 characteristic peaks generated with masses around 90 and 140.
99Mo, 131I and 133Xe radionuclidic purity may be an issue |
|
|
What is neutron absorption?
|
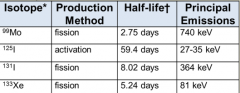
An atom in a reactor absorbs a low energy (thermal) neutron and emits a gamma ray (n, gamma) this produces isotopes of the target atom which are difficult to separate. Because this is neutron rich, they decay by beta emission
|
|
|
How does a moly generator work?
|
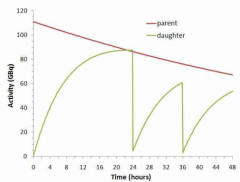
The generator contains 99Mo from fission reaction. In the "generator" 99Mo decays to daughter 99Tcm. This will occur until an equilibrium is reached between the 2. Once the equilibrium is reached, this effectively "freezes" further decay of 99Mo to 99Tc. Once the generator is eluted, the equilibrium occurs again. This will "extend" the half life of Tc to about a week even though its half life is 6hrs
|
|
|
How is a moly generator elluted?
|
The core of the generator contains alumina. The 99Mo tightly adheres to the alumina. The 99Tc however does not and when saline is run through the system, the 99Tc is washed away leaving the 99Mo bound to the alumina.
|
|
|
What is 99Mo breakthrough?
|
When the 99Tcm ellution contains 99Mo. This can be detected by placing an ellution in a lead sheild and measuring for activity. The 140 keV photon emitted form the 99Tc will be absorbed but the 740 keV photon emitted by the 99Mo will not and will be measurable.
|
|
|
Define radiochemical purity. How is this assessed?
|
proportion of desired radiopharmaceutical to the total amount of radioisotope in a solution.
Chromatography |

