![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Briefly describe two methods by which subjective values such as Quality Adjusted Life Years can be converted into a reasonably objective scale that can be used in decision tree analysis.
|
Sample surveys from groups or populations, also known as validated instruments, can be used to determine culturally sensitive values that can then be applied to an individual patient. This provides a starting point from which decisions appropriate for the patient’s particular values can made.
b. Computer Adaptive Testing uses Item Response Theory to tailor an exam and subsequent result to the abilities and values of the individual. This allows for a higher degree of precision with fewer questions than classical tests such as multiple choice questions. |
|
|
Briefly describe Bayes Theorem and demonstrate how it can be used by clinicians at the bedside.
|
The likelihood of an event such as pulmonary embolism depends not only the outcome of a specific test for pulmonary embolism, but also on the pre-test likelihood of the patient having the disease. This depends not only on the prevalence of the disease in the population, but also on the individual characteristics and risk factors of the patient. Taking a careful history and physical exam, therefore, helps establish the pre-test probability of a disease such as pulmonary embolism. Validated models such as the Modified Wells Criteria can then be used to determine which test is most helpful in either ruling in, or ruling out the disease.
|
|
|
Give a definition of the term ‘model’ in the context of clinical decision making.
|
A model is a simplified representation of what can occur in real life, that is comprehensive enough to capture important behaviors of the simulated scenario and simple enough to study.
|
|
|
Compare and contrast the terms “subjective probability” and “objective probability”
|
Both subjective and objective probability assign a degree of likelihood to a specific outcome.
Subjective probability is based on the strength of one’s judgment, while objective probability is based on unassailable theory or extensive empirical evidence of exactly the same combination of circumstances. |
|
|
What is a “spectrum effect” in the context of diagnostic certainty?
|
Variance in the calculated sensitivity and specificity of a medical test as the case mix of the studied population shifts.
|
|
|
How does Markov Decision Process modeling differ from traditional decision tree modeling?
|
Markov decision Process modeling looks at the ramifications of decisions over time-along a continuum-as opposed to a single point in time.
|
|
|
In looking at scientific studies, how can meta-analysis help reduce the degree of uncertainty?
|
Meta-analysis increases the validity and statistical power-while reducing the degree of uncertainty-by combining smaller studies of similar design.
|
|
|
Future demand for CDSS will come from
|
A. Providers
B. CMS C. Joint Commission D. NQF E. Leapfrog |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: The improved outcomes seen in homegrown systems such as IHC and Vanderbilt have been duplicated in broader use.
|
False
|
|
|
1.) Please describe the curley braces problem.
|
The curley braces problem is related to the differences in various data models among different systems. The same basic logic can work for all MLMs but at the point that the MLM logic depends on data from an individual database, modifications must be made to the query logic in the MLM (the part between the curley braces.) This creates technical challenges for MLM developers and generally requires a level of technical sophistication not possessed by the typical end-user.
Arden was developed so that end users might develop rules and logic, but the curley braces problem generally requires additional resources. |
|
|
2.) Please describe the purpose of an event monitor.
|
The event monitor is an application or service running inside an EHR system to wait for and observe ‘events’ that qualify for triggering MLMs. If the triggering event for an MLM is a penicillin order, the event monitor is responsible for monitoring orders until it detects one for penicillin and then performs a task, in this case firing a penicillin allergy MLM.
|
|
|
3.) Please describe 5 uses for MLMs.
|
a. Popups (reminders, warning, etc.)
b. Filling out forms based on some value i. Smart charting ii. Order attribution for protocols at NIH c. Notifications (sending emails/pages/faxes) i. Surgical pathology results returned ii. Patient admissions d. Ordering x based on y (suggestion or actual order) i. Vent modification per returned blood gasses e. Links to other knowledge sources |
|
|
4.) How is an MLM triggered? Please identify 3 triggers.
|
a. Interface transactions
b. User actions c. Other alerts |
|
|
5.) What is the purpose of 'slots' in an MLM?
|
Slots are the logical segments of the MLM and tell the MLM what to do (e.g. Action), how to do it (e.g. Data), and when (e.g. Evoke.)
|
|
|
What factors were utilized in calculating scoring values associated with various disease states?
|
Evoking Strength
Frequency Importance |
|
|
QMR is a CDSS designed to help the clinician______
|
Define Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine
|
|
|
QMR is a successor CDSS to what system developed at the University of Pittsburgh
|
INTERNIST – 1
|
|
|
QMR was unique as compared to other CDSS diagnostic systems in that it_________
|
Attempted to define casual reasoning through a scoring matrix
|
|
|
Dxplain has the characteristics of
|
Electronic Medical Textbook
Medical Reference System Decision Support Tool |
|
|
True / False
The most obvious way in which Dxplain can help a physician is in suggesting obscure or rare diseases that may be rarely seen by most physicians. |
True
|
|
|
True /False. One of Dxplain's objectives is determining the correct diagnosis
|
False. The reason this is false is the physician will always have a more complete picture of the patient than will be entered into a computer program, and that a more realistic goal for a decision support systems like Dxplain is to bring to the user’s attention the plausible explanations
|
|
|
Which one of these statements about Dxplain is false?
A. Emphasis on sensivity over specificity B. Provides links to relevant articles through automatic PubMed links C. Provides extra weight in the selection of diseases where immediate diagnosis and management is particularly important D. A cardiologist dealing with a patient with a complex murmur is likely to find Dxplain very helpful |
Answer is D . Dxplain is not intended to aid the specialist working in his/her specialty.
|
|
|
When was Iliad introduced?
|
1996
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Iliad is still in wide use in hospitals today |
False
|
|
|
What does Iliad offer?
|
a. consultation section to aid in developing diagnosis and differentials
b. treatment guidelines c. simulation training |
|
|
Iliad was developed by
|
Applied Medical Informatics
|
|
|
Characteristics of Centralized database
|
Data is pushed to a central repository.
Requires additional staff to maintain and support. RHIO controls the response time. RHIO determines data retention policies. |
|
|
Characteristics of a distributed approach
|
Institution (Hospital) maintains control of the data.
Data is pulled from multiple disparate systems. Institution (hospital) determines data retention policies. Has an advantage from an acceptability standpoint. |
|
|
True or False - Many RHIOs fail due to their dependence on grant funding and lack of a recurring revenue funding model.
|
True
|
|
|
Why is there such a high level of uncertainty in medical decisions?
|
Much of the evidence which the physician interprets is highly individual to the patient: people vary greatly in their manifestation of disease, response to treatment and their needs and preferences. In addition, availability of resources or lack thereof, enters into the equation thereby exacerbating uncertainty.
|
|
|
True or False: Evidence Based Medicine if made up of clinical data/studies, senior staff experience, and data standards?
|
False: Not data standards, but guidelines, policies and regulations.
|
|
|
Which of the following are the primary components required for a robust CDSS?
|
Evidence Based Medicine knowledge base
Electronic Health Record Incorporated Workflow |
|
|
How can CDSS improve healthcare outcomes?
|
Lower Adverse Drug Effects (ADE)
Limit unnecessary test and procedures Reduce Costs Increase preventative care |
|
|
How pay for performance can improve CDSS implementation?
|
Pay for performance can improve clinical outcomes in many ways. The following are some of the examples.
Rewarding groups that build systems capacity in order to deliver high quality care (e.g., clinical decision-support systems, disease and case management) will help development of such systems. Pay-for-performance programs should reward physicians for providing effective disease management services like CDSS and coordinating treatment efforts among primary care physicians and hospitalists or specialists. Programs should recognize and reward groups that successfully get patients to adhere to agreed-upon treatment plans. Using decision support tools, transparency of provider performance for price/quality sensitive consumers can be increased. By rewarding improvements in the care process, these coalitions believe they can save money by keeping patients healthier and by reducing avoidable hospital admissions. |
|
|
What are factors that could influence the clinicians to adapt CDSS?
|
a. Physician perception of the usefulness of computers in the clinical setting.
b. Physician knowledge of and attitude toward computers in general. c. Physician knowledge of the software program. d. Ease of use, usefulness, and flexibility of the software program. e. Applicability and tailoring of the software program to the work setting. f. Training in the use of the program and completeness of the information provided. g. Clinician involvement and participation in development and implementation. h. Involvement and support of senior clinicians in implementation. i. Organization climate of the work setting. j. Technical issues and support. |
|
|
Does government regulation play an important role in CDSS? How?
|
Yes, government regulations play an important role in healthcare improvement. Addressing policy/legal/financial barriers and creating additional support, enabler the widespread CDS adoption and deployment.
|
|
|
Arguments against FDA regulation of CDSS as medical devices include
|
a. Difficulty for CDSS developers of conducting prospective clinical trials
b. Inability of FDA to adequately review user complaints c. User is already licensed d. Stifling of software development |
|
|
True or False - Successful RHIOs lack a governance structure.
|
False
|
|
|
True or False - Successful RHIOs require planning, patience, persistence, and adaptation.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False - Successful RHIOs have a narrow stakeholder base.
|
False
|
|
|
By definition what differentiates the RHIO and HIE?
|
RHIO's facilitate access and retrieval of information
|
|
|
True or False: All stakeholders participate equally in a RHIO.
|
False
|
|
|
Governance for a RHIO is established by
|
Incorporation
Legislation Executive Order |
|
|
True or False: CDSS is included in HIMISS EMR adoption model.
|
True
|
|
|
When developing a business case for a CDSS you may want to consider
|
a) cost justification
b) regulatory justification c) quality of care benefits |
|
|
True or False: When evaluating vendors for implementing a CDSS cost is always the most important factor to consider?
|
False, while pricing is important and may be weighted heavily in the decision, you also want to make sure you consider all aspects of the system including functionality, implantation services and rapport with the vendor
|
|
|
True or False: “Expected Requirements” are those requirements that are commonly identified by the customer.
|
False
|
|
|
True or False: “Software Prototyping” is performed during CDSS installation to assist in training.
|
False
|
|
|
What are the pillars for CDSS adoption?
|
Best Knowledge Available When Needed
Continuous Improvement of Knowledge and CDS Methods High Adoption and Effective Use |
|
|
The 6 most important facets of operating a CDSS system
|
training,
support, change management, tailoring the system for your organization, communication and feedback, and monitoring system performance. |
|
|
Training should occur
|
as a part of implementation and post-implementation and ongoing
|
|
|
True of False: CDS systems always lead to better outcomes
|
False
|
|
|
What is anchoring bias?
|
The subjective adjusting of prevalence of a disease based on a physician’s opinion that published data do not fit her patient population or community.
|
|
|
On a ROC curve, the point at which all patients have the disease is
|
1,1
|
|
|
In making the choice to order a test to prior to a treatment decision, what applies?
|
The results of the test must change the treatment decision
The benefits must outweigh the risks to the patient For high probability of disease, treat has the lowest disutility |
|
|
The Bayesian Theorem is based on the rules of
|
conditional probability.
|
|
|
Is the complement of the Positive Predictive Value (1-PPV) and Negative Predictive Value (1- NPV) useful during disease diagnosis?
|
Yes, true
|
|
|
SnNout
|
When a test has a high sensitivity a Negative result RULES OUT the diagnosis
|
|
|
SpPin
|
When a test has a high specificity a Positive result RULES IN the diagnosis.
|
|
|
What are some of the functions of the Bayesian Network?
|
a) Diagnose
b) Simulate (the system’s behavior) c) Analyze data d) Make Decisions |
|
|
What are some of the Real world applications of the Bayesian Network?
|
a) Decision Support Systems
b)Diagnosis of illness c)Gene regulatory networks |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: The Expected Value Decision Making has three methods; decision tree, threshold probability method and Image processing.
|
FALSE.
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE:
When using the Expected Utility Method patient values for outcomes are derived through Risk Attitude where you are indifferent between two alternatives. |
TRUE
|
|
|
False positives
|
Healthy people incorrectly identified as sick
|
|
|
Posttest probability of the disease OR Posterior probability of the disease
|
The probability of the presence of the target disease conditional on the pretest information and the test result
|
|
|
RECONSIDER Program
|
used heuristic lexical matching techniques to identify diseases in Current Medical Information and Terminology (CMIT), a manual of diseases compiled and previously maintained by the American Medical Association?
|
|
|
Probability revision
|
is the process of converting the pretest probability to the posttest probability taking the test result into account.
|
|
|
Disease prevalence
|
is the frequency of existing disease in the population of interest at a given point in time.
|
|
|
The proportion of patients with target disease who have a positive test result is called
|
true-positive ratio
sensitivity |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE:
Test sensitivity applies to patients without the disease |
FALSE
|
|
|
Four classes of CDSS
|
Patient Care
Clinical Research Public Health Health Administration |
|
|
Patient Care class of CDSS
|
Diagnostic Assistance
Medication Management Therapy Critiquing Patient Monitoring |
|
|
Clinical Research class of CDSS
|
Drug & Device Development
Disease Management |
|
|
Public Health Class of CDSS
|
Disease Prevention
Social Networking |
|
|
Health Administration class of CDSS
|
Cost Effectiveness & Control
Billing Guidance |
|
|
CDS
|
providing clinicians/patients with clinical and patient info,
intelligently filtered, and presented at appropriate times, to enhance patient care, clinical research, public health, & health administration |
|
|
CDSS
|
process and/or technology which involves people that is used to implement CDS
|
|
|
Tools for CDSS
|
People
Processes Technologies (NLP, Machine Learning, Inductive Tree Methods, Case Based Reasoning, Artificial Neural Networks) Clinical Rules/Experts Systems |
|
|
Clinically useful information definition
|
Usefulness = (Relevance x Validity)/Work
|
|
|
Design Cycle for CDSS
|
Planning Phase
Design Phase Construction phase Further Development phase Maintenance, documentation and adaptation Evaluation |
|
|
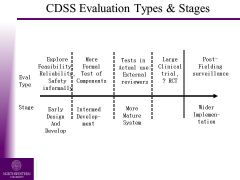
CDSS Evaluation Types & Stages
|
|
|
|
Landscape of CDSS
|
70 known proprietary CDSS
Proprietary attempts to help physicians have failed. *Cost to generate useful database outside reach of one company. |
|
|
Types of Decision Analysis
|
Expected Value Theory
Expected Utility Decision Tree Modeling Sensitivity Analysis |
|
|
Decisions
|
Selecting from alternatives
Components involved: Multiple choices Each with consequences Uncertain outcomes Different preferences Outcomes leading to have different values |
|
|
Expected Value Theory
|
A number signifying the relative worth of a given option on an underlying objective scale
EV Theory: Choose option with highest EV Value’- if the decision has no element of uncertainty EVT - correct choice is same for everyone - very specific advice |
|
|
Expected Utility
|
Both are gambles
EU Theory: Choose option with highest EU ‘Utility’- if the decision involves risk or uncertainty EUT - what is right for one, may not be for other - advice depends on utilities assigned |
|
|
Components of Decision Trees
|
Decision
Square node Multiple arcs, options Events Circle node Multiple arcs, probabilities Consequences End points Utilities, Values |
|
|
Analysis of Decision Trees: Folding back
|
Right-to-left
Replace each node with its expected value/utility |
|
|
Analysis of Decision Trees: Sensitivity analysis
|
Change input variables till conclusion is affected
Helps build confidence in the model Robust: if conclusion remains unchanged for wide input variation Identifies factors that contribute most to the output variability |
|
|
Importance of Sensitivity Analysis
|
It depends on:
How influential it is in the analysis Its range of uncertainty How close is the decision is to a particular threshold If a small δ in input variable -> large δ in output, it means that variable needs to measured very accurately, or model needs to be redesigned for low sensitivity |
|
|
Classification of DSS is based on
|
Type of Decision
Diagnosis, Therapy, Management Medical Domain Surgery, Medicine, Cancer Pain Interaction Mode Solicited / Unsolicited Advice Underlying Process Clinical Algorithms, Drug-Drug interactions Bayesian, Neural Networks, Supervised learning Answering Questions Informational Retrieval Systems Just provide knowledge & decision left to clinician Focusing Attention Lab systems for abnormal values Making Decisions Diagnosis, Test Selection, Treatment choice Workflow Optimization Guidelines, scheduling, protocols Monitoring Actions Event Monitors |
|
|
Simple Decision Support is
|
-highly specific
-widely implemented with a considerable impact |
|
|
DSS: Planning Phase consists of
|
Role of Culture
Control & Autonomy Local VS Commercial |
|
|
DSS: Operational Phase consists of
|
Lack of Use
Example: Quicksets Process Improvement |
|
|
DSS: Implementation Phase consists of
|
Organizational Considerations
Change Management Phases |
|
|
Planning Issues in Organization and Cultures
|
-Learning Stage of Clinicians
-Alert Fatigue -Rate of Implementation -Clinical content and pathways |
|
|
Planning Control and Autonomy
|
-CDSS Stakeholder Analysis
-Personal Order Sets -Organizational Structure (hierarchy and power) |
|
|
Planning Commercial vs Locally Produced CDSS
|
-Commercial
Extensive modifications needed Logic may be less sophisticated More possibility of rule sharing Software Configuration Local Harder to develop & maintain More easily accepted More tailored to local interests Often more fragmented Reactive development |
|
|
Implementation Organizational Considerations
|
Depending on Impact (workflow / number of users), consider:
Phased approach Big-Bang approach Kick-Off: Introduce DSS and get buy-in Build: User Profiles, Interfaces, Template Design, Licensing Training Go-Live support Support |
|
|
CDSS Implementation Challenges
|
Not all data available in electronic format
Not sufficiently structured to be directly used by DSS Considerable manual data entry required |
|
|
CDSS Evaluation: Impact Assessment
|
Quantitative
-Number of Alerts -Override/Acceptance rates -System response time Qualitative -Organizational Behaviors -Focus groups -Process Improvement Record a baseline....solicit feedback |
|
|
10 Commandments of Effective CDS
|
1. Speed is everything
2. Anticipate needs and deliver in real time 3. Fit into user’s workflow 4. Little things can make a big difference 5. Physicians resist stopping 6. Changing direction is fine 7. Simple interventions work best 8. Asking info is okay- but be sure you need it 9. Monitor impact, get feedback and respond 10. Manage and maintain the system knowledge |
|
|
What were the 3 (out of 14 categories) opportunities to leverage EHR data in support of Pharma and BioTechnology discussed
|
Clinical Trial Recruitment
Epidemiology, Understand Disease management |
|
|
how is quantitative analysis used within Clinical Recruitment
|
1. Clinical Trial recruitment via EHR
2. Clinical trial recruitment via patient-reported data 3. Identify investigators 4. Recruitment feasibility analysis |
|
|
how is quantitative analysis used within epidemiology
|
1. Study disease prevalence in population
2. Understand disease progression |
|
|
how is quantitative analysis used within Understand Disease Mechanism
|
1. Biomarker identification and validation
2. Genetic associate and linkage analysis 3. Target identification and validation |
|
|
Epidemiology case from presenter:
Understand Patient Populations By Disease compared what |
Myocardial Infarction and Cerebrovascular Accident in Patients with Retinal Vein Occlusion
|
|
|
Why is Quantitative Decision Making used in Clinical Trial Design
|
Used to target the right patient population for the medication,
Define the best fit for the medicine, find who would benefit from taking the medicine. |
|
|
From the vendor’s perspective, addressing Healthcare associated infection surveillance provides
|
1. Direct interactions with front line clinicians
2. Competition drives innovation 3. Collaboration with federal agencies 4. ARRA 2009 |
|
|
How big is the HAI problem (healthcare associated infection)
|
In American hospitals alone, healthcare-associated infections account for an estimated 1.7 million infections and 99,000 associated deaths each year.”
|
|
|
Who are the Stakeholders in the HAI problem?
|
Patient Groups (Consumers Union)
Payers (CMS) Providers Government (State and Federal) Quality Improvement Organizations (IHI, NQF, NCQA) Accreditation Organizations (JC) Professional Associations (APIC, IDSA |
|
|
Where does the funding (money) come from for HAI surveillance
|
American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, Public Law 111-51
HHS Action Plan To Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections2 CMS “meaningful use” criteria for quality measures3 |
|
|
What are the customer activities (concerning HAI) from the vendor’s perspective
|
Hospital patient safety programs
Infection prevention (IP) efforts Routine Surveillance Outbreak detection Process Measurement Outcome Measurement Reporting! Internal External |
|
|
What is the HAI Surveillance Workflow
|
1. Event Detection
2. Clinical Confirmation 3. Case Documentation 4. Clinical Intervention 5. Reporting and Analysis |
|
|
What are the barriers to making progress in HAI surveillance
|
Slow Adoption of Standards
Leadership Buy-in Staffing Clinical Resistance (to change practices) Emerging, Competing QI Efforts Fear of Litigation |
|
|
What are the HAI Surveillance Standards
|
Vocabulary (SNOMED CT®, LOINC)
Messaging (HL7) Document Content (HL7 CDA) Event Definitions (CDC Case Definitions) Detection and Reporting Protocols (CDC) Practices and Processes (APIC, IDSA) |
|
|
Effective Decision Support has these characteristics
|
• Integrated with the daily work process
• Evidence based • Easy to use • Affordable - maintenance • Reasonable to implement |
|
|
What are the functions of clinical decision support systems
|
* Tools for information management
* Tools for focusing attention * Tools for patient-specific consultation |
|
|
What are the key features of HIS for Decision Support
|
• Integrated data base (coded, timestamp)
• Knowledge base (medical logic) • Ability to data- and time-drive knowledge base • Computer data exchange (interfaces) • Long term storage of data base |
|
|
According to Scott Evans, what two technological advances in the 1800’s have had the largest impact on patient care?
|
Automobile and Telephone
|
|
|
What technological advance in the 1900s has the potential to provide the largest impact on patient care?
|
A. The computer
|
|
|
Time Driver
|
A program on the system that checks a table each minute to see if there are MLMs or other applications that should be run.
Example – after 4 hrs an alert is generated to notify that medication administration is required. |
|
|
What are the 5 main system-level requirements in a CDSS?
|
a. Integrated Clinical Database – clinical data stored, longitudinal data from patient
b. Interfaces (i.e. input of patient vital signs ) c. Knowledge Database – KB – needs integrated, interdisciplinary approach to incorporate rules. d. Decision Making Processor - ability to take rules stored in KB and apply to pt data stored in clinical db and generate alerts i. Data ii. Time e. Data Review Alerts, Computations, Interpretations, and Protocols – Does not need to be electronic. Paper always has a role in the healthcare delivery process. |
|
|
3 methods to get feedback to physicians - in order of effectiveness
|
1. c. Summary sheets generated in conjunction with a patient visit, that show the patient’s current management parameters and status relative to an evidence-based practice guideline, for a particular chronic disease.
2. b. Action lists that identify patients with a particular chronic disease who are “off protocol” based on an evidence-based best practice guideline. 3. a. Monthly outcomes comparison reports that show key process and outcomes measures for the physician being assessed as compared to other physicians or national norms. |
|
|
In which of examples of Consumer Health Informatics could decision support techniques/technologies be applied?
|
a. On-line Pharmacies
b. Smart Cards c. Health related websites d. PHRs |
|
|
What is the significance of the WWW for Consumer Health Decision Support?
|
Consumer based Health Decision Support Systems are web based systems therefore WWW would indicate the World Wide Web.
Primary features include: 1)Patient video interviews. 2)Online community network. 3)User-specific outcomes data. 4)Free, public access. |
|
|
Mycin was a rule-based system that demonstrated
|
Accurate use of probabilities through certain factors attached to rules
|
|
|
Fuzzy logic is based on
|
modification of set theory to allow degrees of membership in a set.
|
|
|
Simple Bayesian Networks require
|
assumptions concerning the number of diseases that a patient may have
|
|
|
What kind of networks can be derived (trained) from clinical data?
|
Neural Networks
|
|
|
What is the difference between bayesian and neural networks?
|
Neural networks can be trained from clinical data and bayesian cannot
|
|
|
What do rule-based systems often require to function properly?
|
rules about rule (meta-rules)
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: The order of rule firing does not effect the results in large rule-based systems
|
false
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: Detailed and explicit computerized protocols developed in one clinical site have never been exported and successfully used to standardize clinician decisions in other clinical sites.
|
False
|
|
|
Benefit of computerized protocols when they are properly implemented
|
reduce unnecessary clinical variation
|
|
|
Data Driver
|
Data Driver – when the correlation of 1 or multiple data points causes a trigger within the CDSS decision making process.
Example – HR and ST segment deviation identifies an ischemia event. |
|
|
List 5 different types of ways the computer can be used to improve human decision-making.
|
a. Answering Questions - Informational Retrieval Systems, Just provide knowledge & decision left to clinician
b. Focusing Attention - Lab systems for abnormal values c. Making Decisions - Diagnosis, Test Selection, Treatment choice d. Workflow Optimization - Guidelines, scheduling, protocols e. Monitoring Actions - Event Monitors |
|
|
In the hospital setting, the physician will do a good job of spotting relevant information if given all the clinical data
|
False?
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: Decision support applications will continue to benefit primarily the physician
|
False - they benefit the physician, patient, HCO
|
|
|
Fuzzy logic is most commonly used for
|
control of devices
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: Clinical judgments that are uniform among experts, and appear obvious to all observers, are reflections of the truth.
|
False?
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: Explicit, detailed computerized protocols that produce specific instructions and eliminate inter-clinician variability, are not achievable.
|
False?
|
|
|
What are the unintended consequences of using CDSS?
|
1. De-skilling effect. Too much reliance on CDSS will have a de-skilling affect
2. vocabulary mismatch |
|
|
Central challenge in access to information
|
Information security vs ease of access
|
|
|
Why are there ethical issues in CDSS
|
CDSS generates information that can be powerful
|
|
|
Where does CDSS stand today at the Intersection of
|
Medicine, IT and Law
|
|
|
T/F Medicine has a different legal tradition than IT
|
True
|
|
|
What are the legal traditions of Medicine?
|
a. Highly regulated
b. Closely followed in media c. Expect perfection d. No next release |
|
|
What are the legal traditions of IT?
|
a. Not highly regulated
b. Lack of standards c. Software piracy d. Next release |
|
|
T/F CDSS Vendors have a legal duty of care to both patients and healthcare providers
|
true
|
|
|
T/F Informaticists have a duty of care when developing CDSS
|
true
|
|
|
Proteus workflows are constructed with entities called
|
KC (Knowledge Components)
|
|
|
Characteristics of Proteus KC’s include
|
Modular
Intelligent Executable Editable Reusable Shareable |
|
|
From the technological perspective. What can Proteus be used for
|
1. Creating executable clinical practice guidelines to provide decision support to clinicians about patient care
2. Creating process-oriented EMR systems with integrated cds support 3. Creating kernel of integrated healthcare information systems |
|
|
What are the characteristics of Proteus KC (knowledge compents)
|
A modular building block for Clinical Processes, to represent Clinical Actions, Events and Processes, and a software component with a discrete bit of knowledge
|
|
|
A Proteus KC contains knowledge about which clinical activity?
|
A. Actions to be performed
B. Events to look for C. Data to be collected from the actions and events E. Interpretation and implications of that data F. Supplementary information about the activities (eg. Links to websites) |
|
|
Why would a Physician use Proteus
|
A. Reduced Errors
B. Increased compliance with best practices C. to collaborate with team members and establish standards within a clinical team D. Stay current with medical advances E. To acquire expertise of other will little or no effort F. Freedom from developers G. Unambiguous Communication F. Because its fun |
|
|
Why would a Physician share a Proteus KC
|
A. To show to the world their impressive work
B. To make a difference to others work C. Build name recognition in certain areas of expertise D. To create collaborations E. Because they expect others will improve what they share |
|
|
What are the sub-groups of the Missouri Health Exchange
|
1 governance
2.technical infrastrature 3. finance 4.business and technical operations 5. consumer engagement –goal is public outreach 6. Legal and ethical (focus) |
|
|
What is the most important sub-group according to the presenter of the Missouri Health Exchange
|
Technical Infrastructure
|
|
|
Two major issues within the Legal and Ethical Sub Groups of the Missouri Health Exchange
|
a. Privacy laws. (How to ammend HIPPA and further protect individuals)
b. Trust agreements between exchange members. Resistance comes from doctor groups and large medical institutions |

