![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_____ are the fundamental units of all living things.
|
cells
|
|
|
Using metric units, give the range of sizes most plant and animal cells fall in.
|
10 - 100 µm
|
|
|
The _____ _____ (outer membrane) marks the boundary between the outside and inside and regulates what enters and exits cells.
|
plasma membrane
|
|
|
What carries on chemical reactions inside the cell.
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
The concepts that all organisms are composed of cells, and that cells come only from preexisting cells, are the two central tenets (principles) of the _____ _____.
|
cell theory
|
|
|
_____ cells lack a membrane-bounded nucleus.
|
prokaryotic
|
|
|
_____ cells have a membrane-bounded nucleus.
|
eukaryotic
|
|
|
What does the nucleoid hold?
|
DNA
|
|
|
Where is the DNA located in a eukaryotic cell?
|
nucleus
|
|
|
Scientists believe that Bacteria and Archaea, which are prokaryotic cells, were the first . . .
|
cells on Earth.
|
|
|
Why are prokaryotic cells smaller than eukaryotic cells?
|
absence of a nucleus
|
|
|
The _____ _____ maintains the shape of the cell.
|
cell wall
|
|
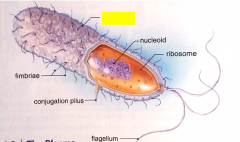
Label the structure.
|
capsule
|
|
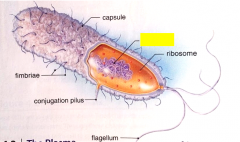
Label the structure.
|
nucleoid
|
|
|
What do ribosomes synthesize?
|
proteins
|
|
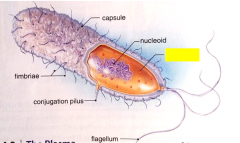
Label the structure.
|
ribosome
|
|
|
What structure allows bacteria to propel themselves?
|
flagella
|
|
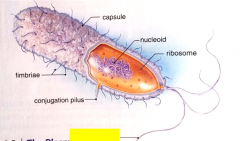
Label the structure.
|
flagellum
|
|
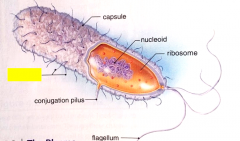
Label the structure.
|
fimbriae
|
|
|
Fimbriae don't have anything to do with motility, but they do help bacteria . . .
|
attach to a surface.
|
|
|
What do bacteria use conjugation pili for?
|
passing DNA from cell to cell
|
|
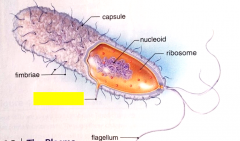
Label the structure.
|
conjugation pilus
|
|
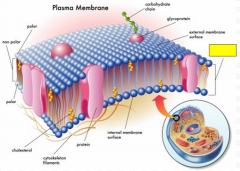
Label the yellow box. (Hint: this is a general structural reference.)
|
phospholipid bilayer
|
|
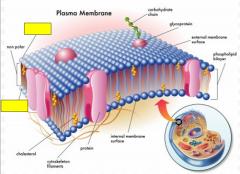
Label the yellow boxes as polar or non-polar.
|
polar
|
|
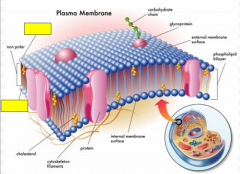
Label the yellow boxes as hydrophilic or hydrophobic
|
hydrophilic
|
|
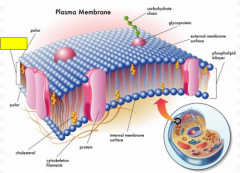
Label the yellow box as polar or non-polar.
|
non-polar
|
|
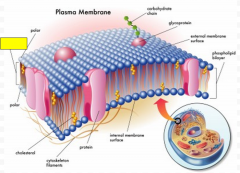
Label the yellow box as hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
|
hydrophobic
|
|
|
In animal cells (versus plant cells), waxy cholesterol molecules give _____ to the plasma membrane.
|
support
|
|
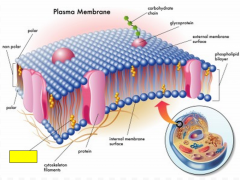
Label the yellow box.
|
cholesterol
|
|
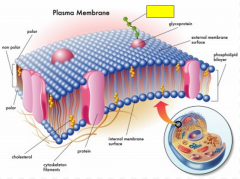
Label the yellow box.
|
carbohydrate chain
|
|
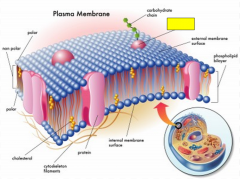
Label the yellow box.
|
glycoprotein
|
|
|
_____ proteins from a tunnel across the entire membrane that allows only one or a few types of specific molecules to simply move across the membrane.
|
channel
|
|
|
_____ are specific types of channel proteins that allow water to enter or exit a cell.
|
aquaporins
|
|
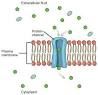
What specific type of plasma membrane protein does this diagram represent?
|
channel protein
|
|
|
Transport proteins often _____ with a substance in order to help it move across the plasma membrane.
|
combine
|
|
|
The combination of the transport protein and the substance it is helping move across the membrane requires an expenditure of _____.
|
energy
|
|
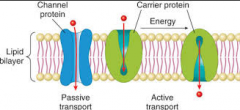
The membrane proteins represented in green in this diagram are _____ proteins.
|
transport
|
|
|
What is the key difference in how channel proteins and transport proteins allow movement of substances across the membrane?
|
transport requires energy; channel requires no energy
|
|
|
Cell recognition proteins allow our cells to identify _____ (microorganisms).
|
pathogens
|
|
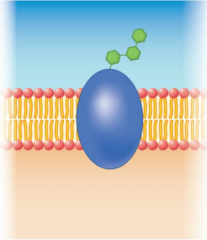
This diagram represents what specific type of membrane protein?
|
cell recognition protein
|
|
|
A _____ protein has a shape that allows a signal molecule to bind to it.
|
receptor
|
|
|
The binding of a signal molecule causes the receptor protein to _____ its shape.
|
change
|
|
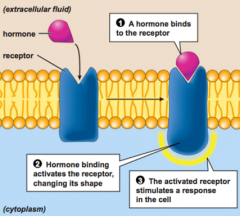
What type of membrane protein is this? (Hint: the "notch" at the top is where the signal molecule attaches.)
|
receptor protein
|
|
|
Some plasma membrane proteins are _____ proteins that directly participate in metabolic reactions.
|
enzymatic
|
|
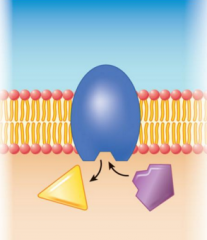
This diagram represents what specific type of membrane protein?
|
enzymatic proteins
|
|
|
Junction proteins are involved in forming various types of _____ between cells.
|
linkages
|
|
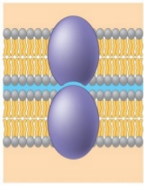
The purple protein represents a _____ protein. (Note: there are two cells in this image.)
|
junction protein
|

